CDM-625A Advanced Satellite Modem MN-CDM625A
Appendix F Revision 4
F–12
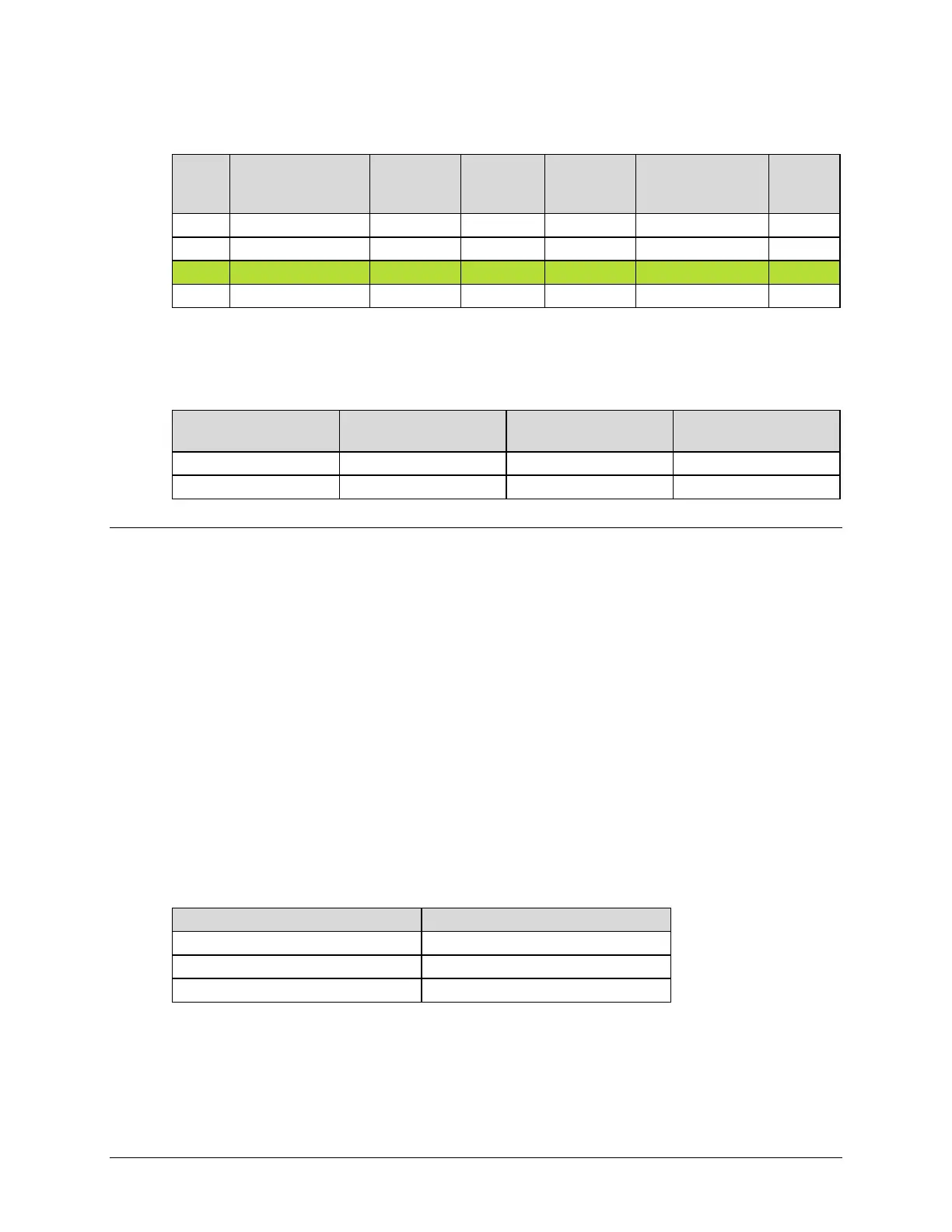
The link budget summary for the different ModCod combinations is as follows:
S. No. Modulation & FEC
Allocated
BW (MHz)
PEB (MHz)
Leased BW
(MHz)
Savings Compared
to Original
Ratio
Based on this analysis, QPSK, LDPC 2/3 with Carrier-in-Carrier provides the maximum savings of
40%. In addition to 40% reduction in Leased Bandwidth, using Carrier-in-Carrier also reduced the
required HPA Power by almost 40%:
HPA Power
Traditional Link
(QPSK, TPC 3/4)
CnC Link
(QPSK, LDPC 2/3)
HPA Power Reduction
F.2.5.2 Asymmetric Data Rate Link
As occupied (or allocated) bandwidth of a Carrier-in-Carrier circuit is dictated by the larger of the
two carriers, it is strongly recommended that the smaller carrier be spread as much as possible
using a lower order modulation and/or FEC, while meeting the PSD ratio spec. Spreading the
smaller carrier using a lower order modulation has multiple benefits:
• Lower order modulation is always more robust;
• Lower order modulation uses less transponder power – this reduces total transponder, and
increases available link margin;
• Lower order modulation uses less transmit power on the ground – this can significantly
reduce the BUC/SSPA size by not only reducing the transmit EIRP, but also reducing the
BUC/SSPA backoff
Consider the following example:
IS-901 @ 342º W, 22/22 (EH/EH)
While the traditional link was based on QPSK, TPC 3/4 and required 3.9 MHz of leased
bandwidth, the Carrier-in-Carrier link was based on QPSK, LDPC 3/4 and QPSK, LDPC 1/2 and
required 2.8 MHz of leased bandwidth.
 Loading...
Loading...