VXLAN achieves L2 over L3 overlay using the tunneling mechanism. VTEPs are the end points of a tunnel
located within the hypervisor on the server that hosts VMs. The VXLAN frame format is shown in the following
figure:
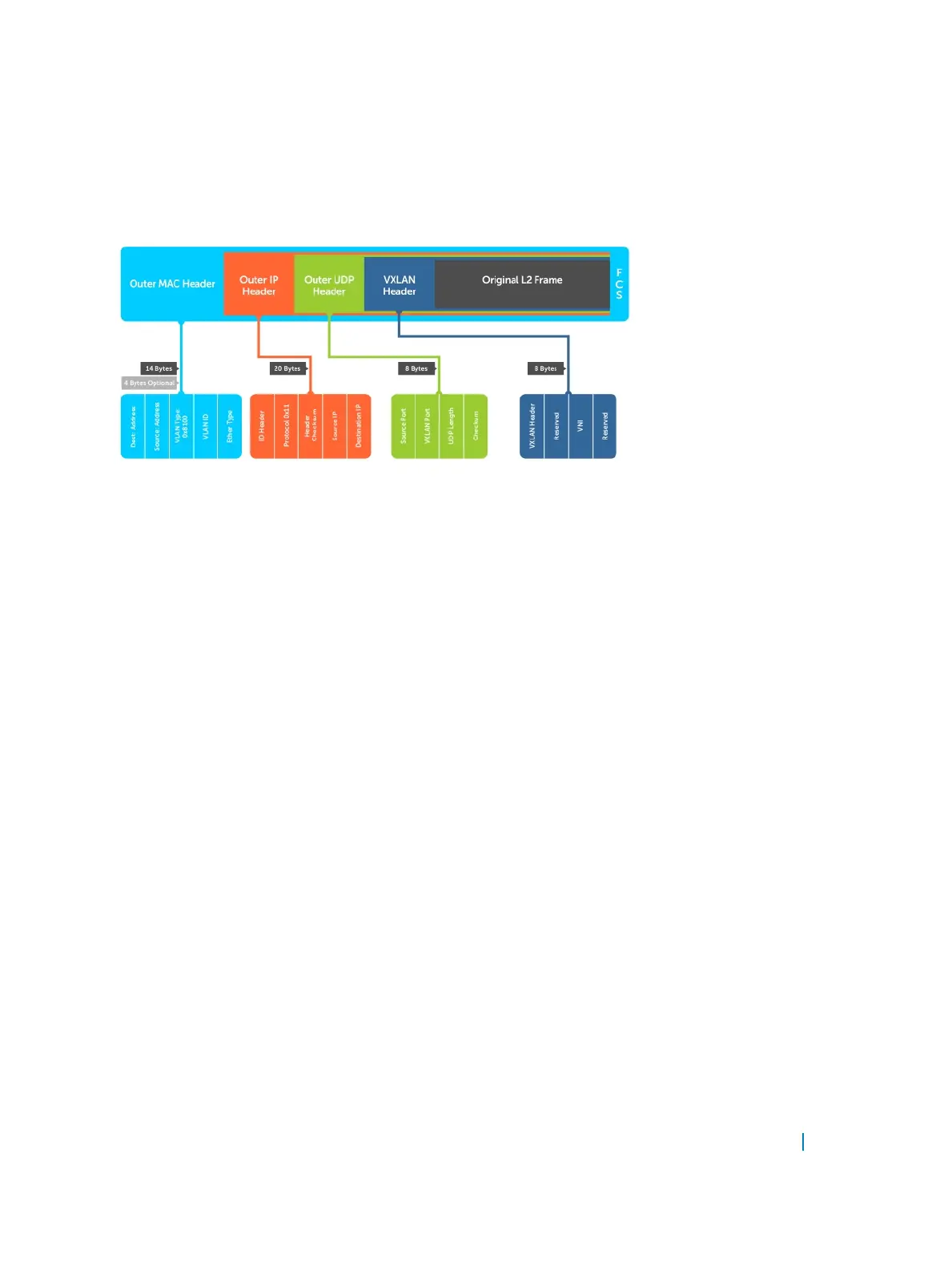
Figure 146. VXLAN Frame Format
Components of VXLAN Frame Format
Some of the important fields of the VXLAN frame format are described below:
Outer Ethernet
Header:
The Outer Ethernet Header consists of the following components:
• Destination Address: Generally, it is a first hop router's MAC address when the
VTEP is on a different address.
• Source Address : It is the source MAC address of the router that routes the
packet.
• VLAN: It is optional in a VXLAN implementation and will be designated by an
ethertype of 0×8100 and has an associated VLAN ID tag.
• Ethertype: It is set to 0×0800 because the payload packet is an IPv4 packet. The
initial VXLAN draft does not include an IPv6 implementation, but it is planned for
the next draft.
Outer IP Header: The Outer IP Header consists of the following components:
• Protocol: It is set to 0×11 to indicate that the frame contains a UDP packet .
• Source IP: It is the IP address of originating VTEP.
• Destination IP: : It is the IP address of target VTEP.
Outer UDP
Header:
The Outer UDP Header consists of the following components:
Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN) 1177

 Loading...
Loading...











