4.1 Introduction to PIM-SM
This section describes the basic information about PIM-SM.
PIM indicates that a static route or any unicast routing protocol such as RIP, OSPF, IS-IS, or
BGP can provide routing information for IP multicast. Although the multicast routing entry is
generated through the unicast routing table, the multicast routing is independent of unicast
routing protocols.
NOTE
The switch referred in the following contents is an S9300 supporting the Layer 3 multicast protocol and
multicast routing function.
PIM forwards multicast packets through the RPF mechanism. The RPF mechanism uses the
existing unicast routing information to create a multicast forwarding tree. When a multicast
packet reaches an S9300, the S9300 performs the RPF check. If the RPF check is passed, the
S9300 creates the mapping multicast routing entry and forwards the multicast packet. The the
multicast packet fails to pass the RPF check, the S9300 discards the packet.
PIM-SM belongs to a multicast routing protocol in sparse mode. PIM-SM performs the following
operations: neighbor discovering, asserting, DR election, rendezvous point (RP) discovering,
joining, pruning, registering, and SPT switchover.
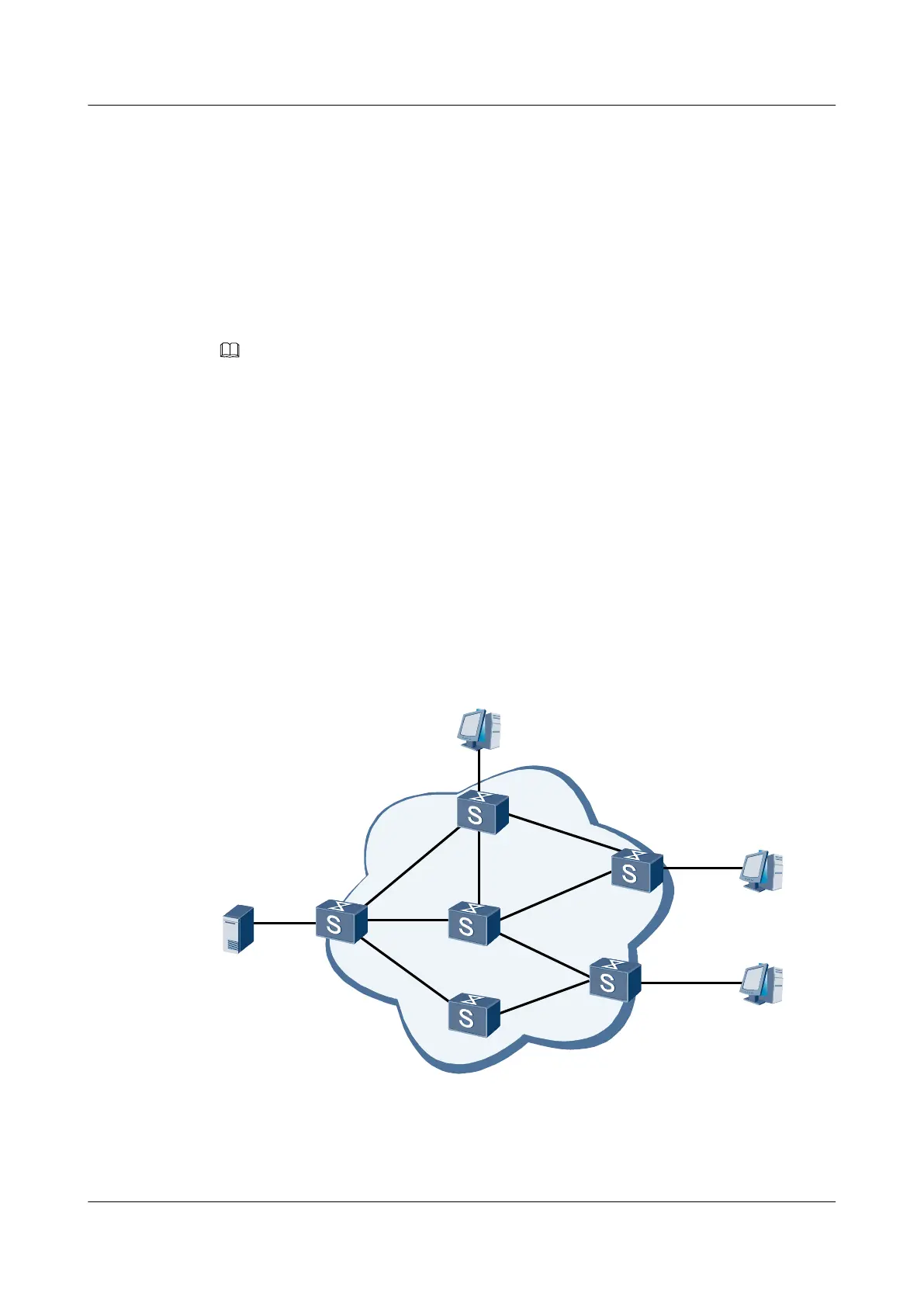
As shown in Figure 4-1, PIM-SM is applicable to a large-scale network with sparsely-distributed
members.
Figure 4-1 Application of PIM-SM in a multicast network
Source
Multicast
UserB
UserC
Receiver
Receiver
IGMP
IGMP
PIM-SM
PIM-SM
PIM-SM
PIM-SM
PIM-SM
PIM-SM
IGMP
Receiver
UserA
PIM-SM
PIM-SM
By using PIM-SM, you can construct two multicast models: ASM and SSM.
Quidway S9300 Terabit Routing Switch
Configuration Guide - Multicast 4 PIM-SM Configuration
Issue 01 (2009-07-28) Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4-3

 Loading...
Loading...















