How to ? Using math waveforms
Creating math waveforms
Youcreatemathwaveformswhenyoucreateamathexpression.Youdosobyapplyingnumerical
constants, math operators and functions to operands. You can display and manipulate t hese derived
math waveforms much like you can the channel and referenc e waveforms (see Using Math
Waveforms (s
ee page
606)).
Some examples of typical math waveforms follow:
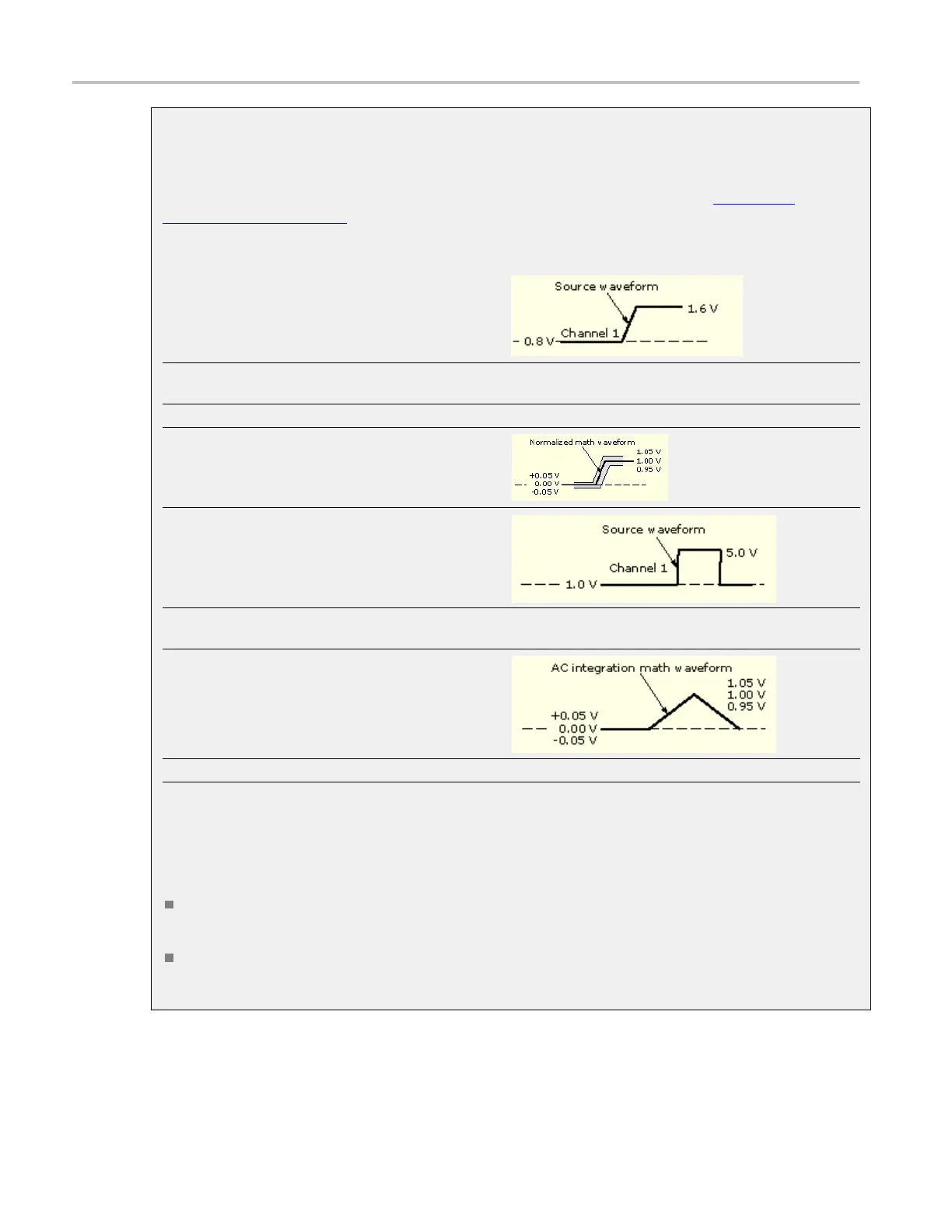
To normalize this waveform:
Enter this math expression:
(Ch1- Meas1)/ Meas2, where Ch1 is the waveform shown
at left Meas1 = Low of Ch1 Meas2 = amplitude of Ch1
And get this math waveform:
To simulate AC coupling on this w aveform:
Enter this expression:
Intg(Ch1-Avg(Ch1)), where C h1 is the waveform shown
at left Avg is the average function
And get this math waveform:
xxx
Offset, p osition, and scale
The settings that you make for offset, scale, and position affect the math waveform you obtain.
Here are some tips for obtaining a good display:
Scale and position the source waveform so that it is contained on the screen. (Off-screen
waveforms may be clipped, resulting in errors in the derivative waveform.)
Use vertical position and vertical offset to position your source waveform. The vertical position
and offset will not affect your derivative waveform unless you position the source waveform off
screen so that it is clipped.
608 DSA/DPO70000D, MSO/DPO/DSA70000C, DPO7000C, and MSO/DPO5000 Series

 Loading...
Loading...











