Cortex-M4 Peripherals
ARM DUI 0553A Copyright © 2010 ARM. All rights reserved. 4-14
ID121610 Non-Confidential
See the register summary in Table 4-12 on page 4-11, and the Type descriptions in Table 4-15,
for the ICSR attributes. The bit assignments are:
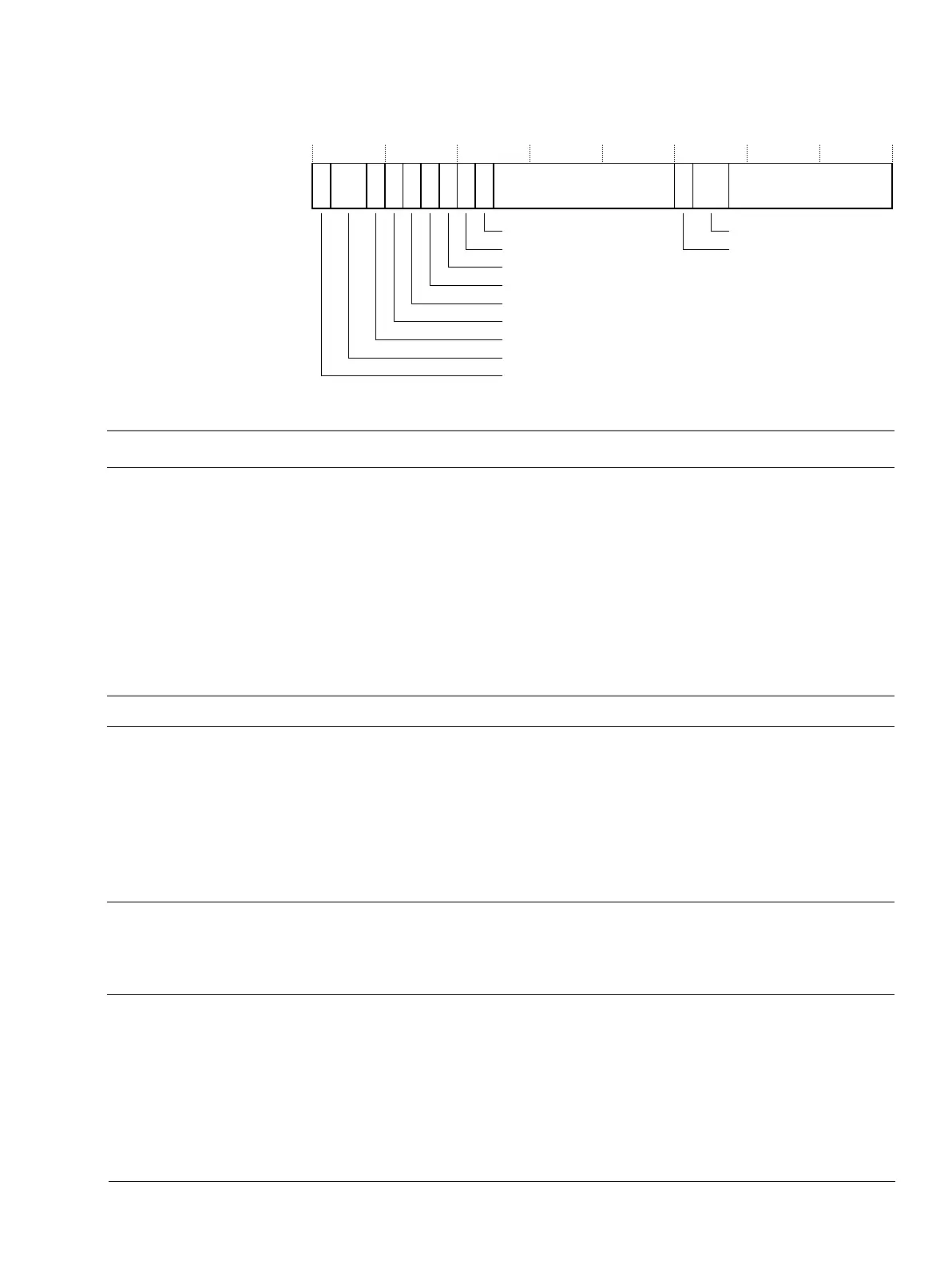
31 28 22 21 910 0
VECTACTIVE
30 29 27 26 2324 12 11
VECTPENDING
NMIPENDSET
PENDSVSET
PENDSVCLR
Reserved for Debug
ISRPENDING Reserved
RETTOBASE
25
PENDSTSET
PENDSTCLR
8
Reserved
Reserved
Table 4-15 ICSR bit assignments
Bits Name Type Function
[31] NMIPENDSET RW NMI set-pending bit.
Write:
0 = no effect
1 = changes NMI exception state to pending.
Read:
0 = NMI exception is not pending
1 = NMI exception is pending.
Because NMI is the highest-priority exception, normally the processor enter the NMI
exception handler as soon as it registers a write of 1 to this bit, and entering the handler clears
this bit to 0. A read of this bit by the NMI exception handler returns 1 only if the NMI signal
is reasserted while the processor is executing that handler.
[30:29] - - Reserved.
[28] PENDSVSET RW PendSV set-pending bit.
Write:
0 = no effect
1 = changes PendSV exception state to pending.
Read:
0 = PendSV exception is not pending
1 = PendSV exception is pending.
Writing 1 to this bit is the only way to set the PendSV exception state to pending.
[27] PENDSVCLR WO PendSV clear-pending bit.
Write:
0 = no effect
1 = removes the pending state from the PendSV exception.
[26] PENDSTSET RW SysTick exception set-pending bit.
Write:
0 = no effect
1 = changes SysTick exception state to pending.
Read:
0 = SysTick exception is not pending
1 = SysTick exception is pending.
 Loading...
Loading...