Appx.26
Terminology
IEC61000-4-30 A standard governing testing involving power quality measurement in AC power supply
systems and associated measurement technologies. Target parameters are restricted
to phenomena that are propagated in power systems. The target parameters consist
of frequency, supply voltage amplitude (RMS), icker, supply voltage dips, swells,
(momentary) interruptions, transient overvoltage, supply voltage unbalance, harmonics,
interharmonics, supply voltage carrier signals, and high-speed voltage variations.
The standard denes measurement methods for these parameters as well as the
necessary instrument performance. It does not dene specic threshold values.
Measurement classes:
The standard denes three classes (A, S, and B) for various instrument measuring
methods and measurement performance levels:
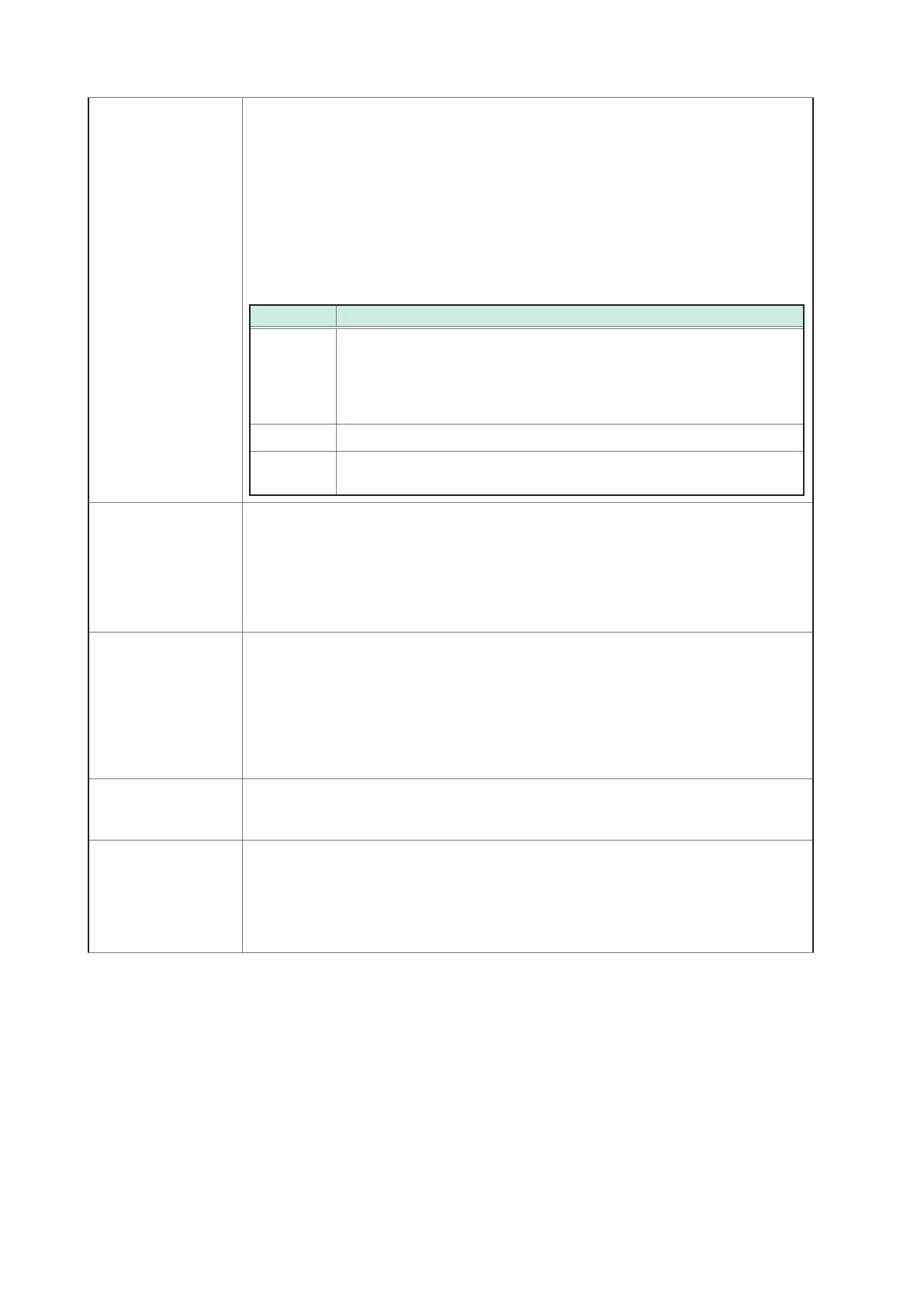
Class Applications
Class A Used in applications where accurate measurement is required, for
example verication of standard compliance and dispute settlement. In
order to ensure accurate measurement, the standard includes detailed
stipulations concerning instrument time clock accuracy, RMS value
calculation methods, and trend data grouping.
Class S Used in surveys and power quality evaluation.
Class B Used in applications where a high level of accuracy is not required, for
example troubleshooting.
Inrush current A large current that ows temporarily, for example when an electric device is turned on.
An inrush current can be equal to or greater than 10 times the current that ows when the
device is in the normal operating state.
Inrush current measurement can be a useful diagnostic when setting circuit breaker
capacity.
The inrush current measurements by the instrument use the RMS value refreshed each
half-cycle.
Interharmonics All frequencies that are not a whole-number multiple of the fundamental frequency.
The interharmonics include inter-order harmonics. The term refers to RMS values for
the spectral components of electrical signals with frequencies between two contiguous
harmonic frequencies.
(Interharmonics of the order 3.5 assume a drive of 90 Hz or similar rather than a
frequency synchronized to the fundamental wave of an inverter or other device. However,
interharmonics do not generally occur in high-voltage circuits under present-day
conditions. Most interharmonics are currently thought to be caused by the circuit load.)
Interruption A phenomenon in which the supply of power stops momentarily or for a short or long
period of time due to factors such as a circuit breaker tripping as a result of a power
company accident or power supply short-circuit.
ITIC curve This curve was created by the Information Technology Industry Council.
Voltage disturbance data for detected events is plotted on a graph using the event duration
and worst value (as a percentage of the declared input voltage). The graph format makes
it easy to clearly identify which event data distribution should be analyzed.
The supplied software PQ One can be used to create ITIC curves using the data of the
instrument (available after the rmware update).

 Loading...
Loading...