Appx.21
3-phase 3-wire Measurement
Appx. 7 3-phase 3-wire Measurement
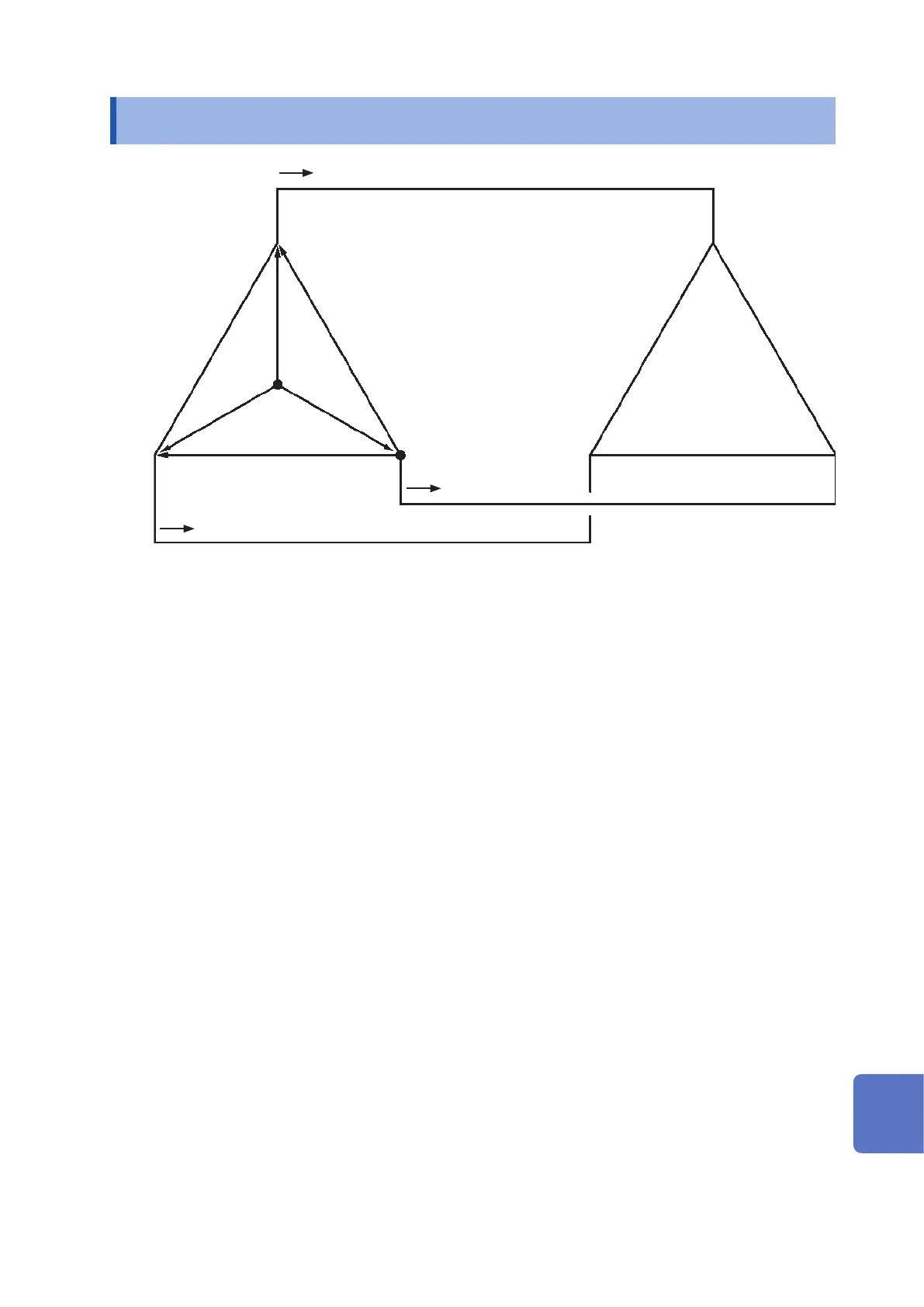
3-phase 3-wire
Source
3-phase 3-wire
Load
Neutral
point
I
.
1
I
.
2
I
.
3
U
.
3
U
.
1
u
.
1
u
.
3
u
.
2
U
.
2
1
2
3
Similar circuit of 3-phase 3-wire line
U
.
1
,
U
.
2
,
U
.
3
: The vectors of line-to-line voltage
u
1
,
u
2
,
u
3
: The vectors of phase to neutral voltage
I
.
1
,
I
.
2,
I
.
3
: The vectors of line (phase) current
3-phase/3-wire/3-wattmeter measurement (3P3W3M)
In 3-wattmeter measurement, 3 phase voltages
u
.
1
,
u
.
2
,
u
.
3
and three line (phase) currents
I
.
1
,
I
.
2
,
I
.
3
are
measured.
Measuring actual phase voltages are not possible because of the lack of a neutral point in the
3-phase, 3-wire line, therefore, phase voltages are measured from a virtual neutral point.
The 3-phase active power P is calculated as the sum of all the phase active power values.
P = u
.
1
I
.
1
+ u
.
2
I
.
2
+ u
.
3
I
.
3
(1)
3-phase/3-wire/2-wattmeter measurement (3P3W2M)
In 2-wattmeter measurement, two line-to-line voltages
U
.
1
,
U
.
2
and two line (phase) currents
I
.
1
,
I
.
3
are
measured.
The 3-phase active power P can be derived from two voltage and current values, as shown below:
P = U
.
1
I
.
1
+ U
.
2
I
.
3
(from U
.
1
= u
.
1
- u
.
2
, U
.
2
= u
.
3
- u
.
2
)
= (u
.
1
- u
.
2
)I
.
1
+ (u
.
3
- u
.
2
)I
.
3
= u
.
1
I
.
1
+ u
.
2
(-I
.
1
-I
.
3
) + u
.
3
I
.
3
(from
I
.
1
+I
.
2
+I
.
3
=0
as the precondition of a closed circuit)
= u
.
1
I
.
1
+ u
.
2
I
.
2
+ u
.
3
I
.
3
(2)
Since equations (1) and (2) agree, it is possible to prove that 2-wattmeter measurement can
be used to measure the power of a 3-phase, 3-wire line. The circuit allowing 3-phase power
measurements with this method is a only closed circuit without leakage current. Since there are no
special conditions other than the above, it is possible to calculate 3-phase power regardless of the
balanced or unbalanced state of the electric circuit.
Additionally, since the sum of the voltage and current vectors always equals 0 under these
conditions, the instrument internally calculates the third voltage
U
.
3
and current
I
.
2
values as follows:
U
.
3
=
U
.
1
-
U
.
2
I
.
2
= -
I
.
1
-
I
.
3
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Appx. Ind.

 Loading...
Loading...