- 110 -
temperature rise of the motor increase.
•
If the carrier frequency is high, power loss and temperature rise of the motor declines.
However, the system has an increase in power loss, temperature rise and interference.
Adjusting the carrier frequency will exert inuences on the aspects listed in the following
table.
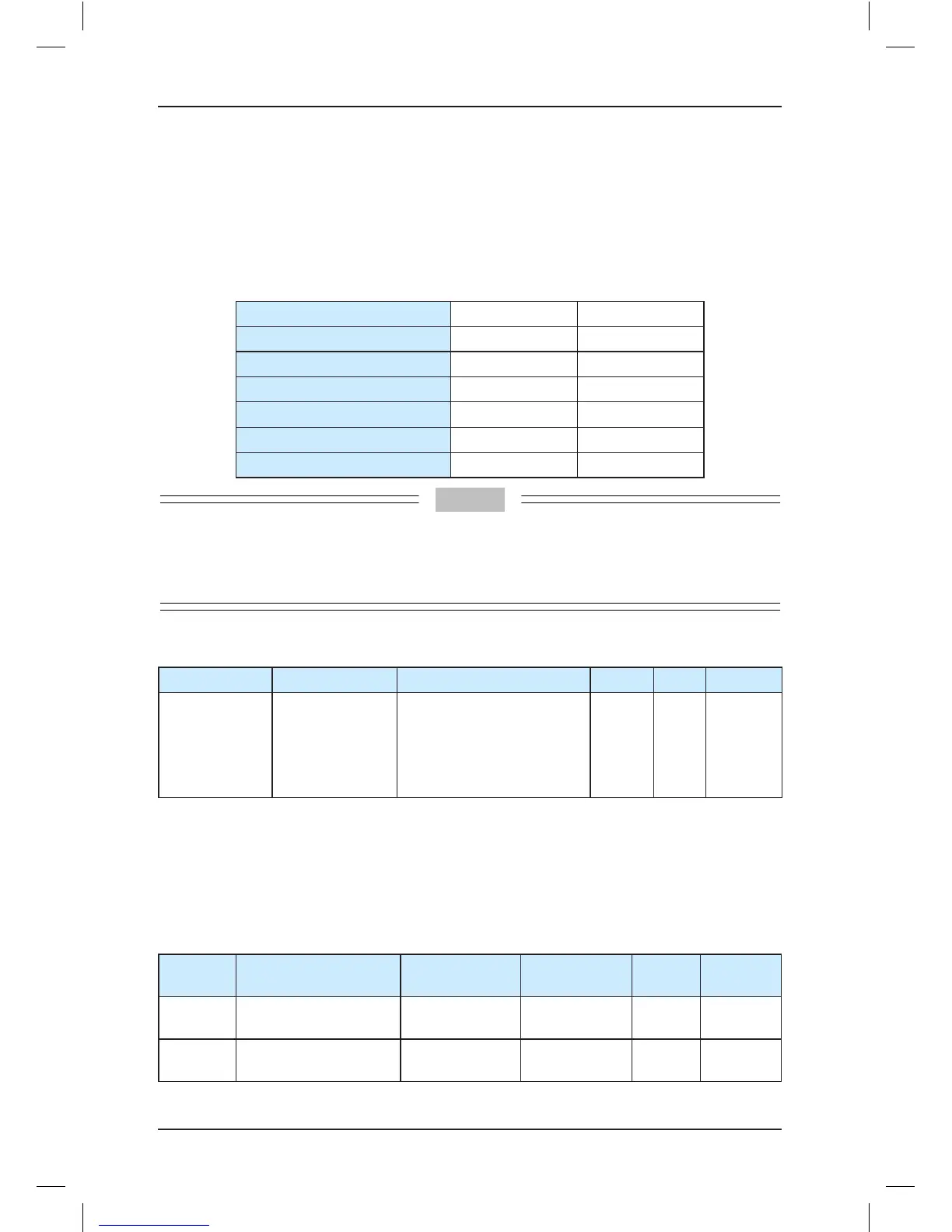
Table 7-1 Inuences of carrier frequency adjustment
Carrier frequency
Low High
Motor noise
Large Small
Output current waveform
Bad Good
Motor temperature rise
High Low
Controller temperature rise
Low High
Leakage current
Small Large
External radiation interference
Small Large
On certain environment conditions (the heatsink temperature is too high), the system will reduce
the carrier frequency to provide overheat protection for the controller, preventing the controller
from being damaged due to overheat. If the temperature cannot reduce in this case, the controller
reports the overheat fault.
Group F1: Motor Parameter
Function Code Parameter Name Setting Range Default Unit Property
F1-00 Encoder type
0: SIN/COS encoder,
absolute encoder
1: UVW encoder
2: AB incremental encoder
(for asynchronous motor)
0 - ★
It is used to set the encoder type matching the motor.
When F1-25 is set to 1 (Synchronous motor), this parameter is automatically changed to 0.
If the actually used is UVW encoder, manually set this parameter to 1 before auto-tuning.
Otherwise, the system fails to run.
When F1-25 is set to 0 (Asynchronous motor), this parameter is automatically changed to 2.
You need not modify it manually.
Function
Code
Parameter Name Setting Range Default Unit Property
F1-01 Rated motor power 0.7–75.0
Model
dependent
kW ★
F1-02 Rated motor voltage 0–440
Model
dependent
V
★
 Loading...
Loading...