Special Signal modules
5-2
Programmable Logic Controllers S7-300 Module Data
A5E00105505-03
5.1 Module Overview
Introduction
The following table summarizes the most important features of the signal modules
described in this chapter. This overview is intended to make it easy to choose the
suitable module for your task.
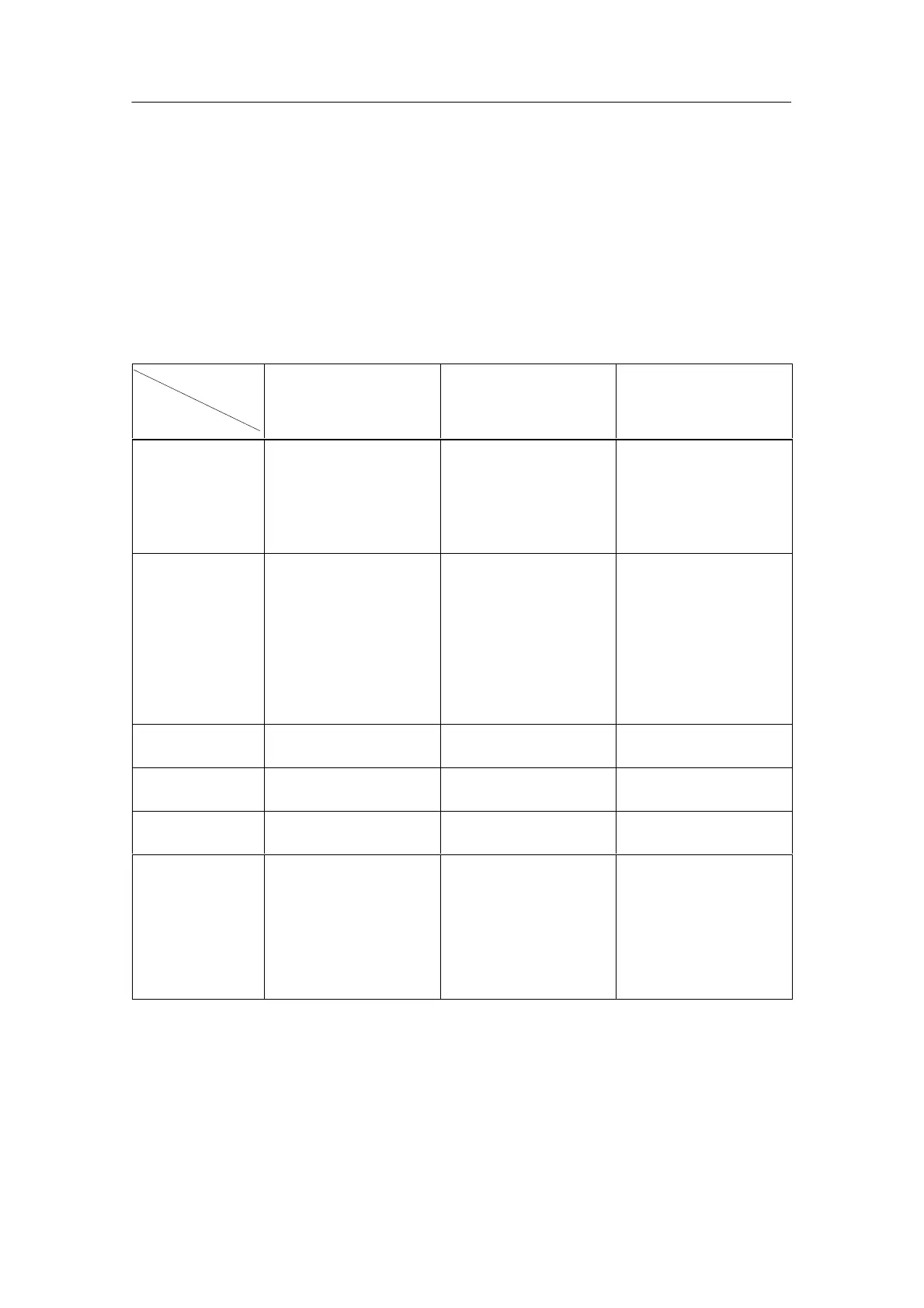
Table 5-1 Special signal modules: Characteristics at a Glance
Module
Char-
acter-
istics
Simulator module
SM 374; IN/OUT 16
Dummy module DM 370 Position decoder
module
SM 338; POS-INPUT
Number of
inputs/outputs
• max. 16 inputs or
outputs
1 slot reserved for 1
non-parameterized
module
• 3 inputs for connection
of absolute value
encoders (SSI)
• 2 digital inputs for
freezing the encoder
values
Suitable for... Simulation of:
• 16 inputs or
• 16 outputs or
• 8 in– and outputs
Placeholder for:
• Interface Modules
• Non-parameterized
signal modules
• Modules which occupy
2 slots
Position decoding with up
to 3 absolute value
encoders (SSI)
Encoder types: Absolute
value encoder (SSI)
with 13-bit, 21-bit or 25-bit
message lengths
Data format: Gray code or
binary code
Supports clocked
operation
No No Yes
Programmable
diagnostics
No No No
Diagnostic
interrupt
No No Adjustable
Special Features Function adjustable with
screwdriver
When replacing the
DM 370 with another
module, the mechanical
assembly and address
assignment/address
location of the entire
assembly remain
unchanged
Absolute value encoders
with a monoflop time
greater than 64s cannot
be used on the SM 338

 Loading...
Loading...











