1-55
IM MW100-01E
Explanation of Functions
1
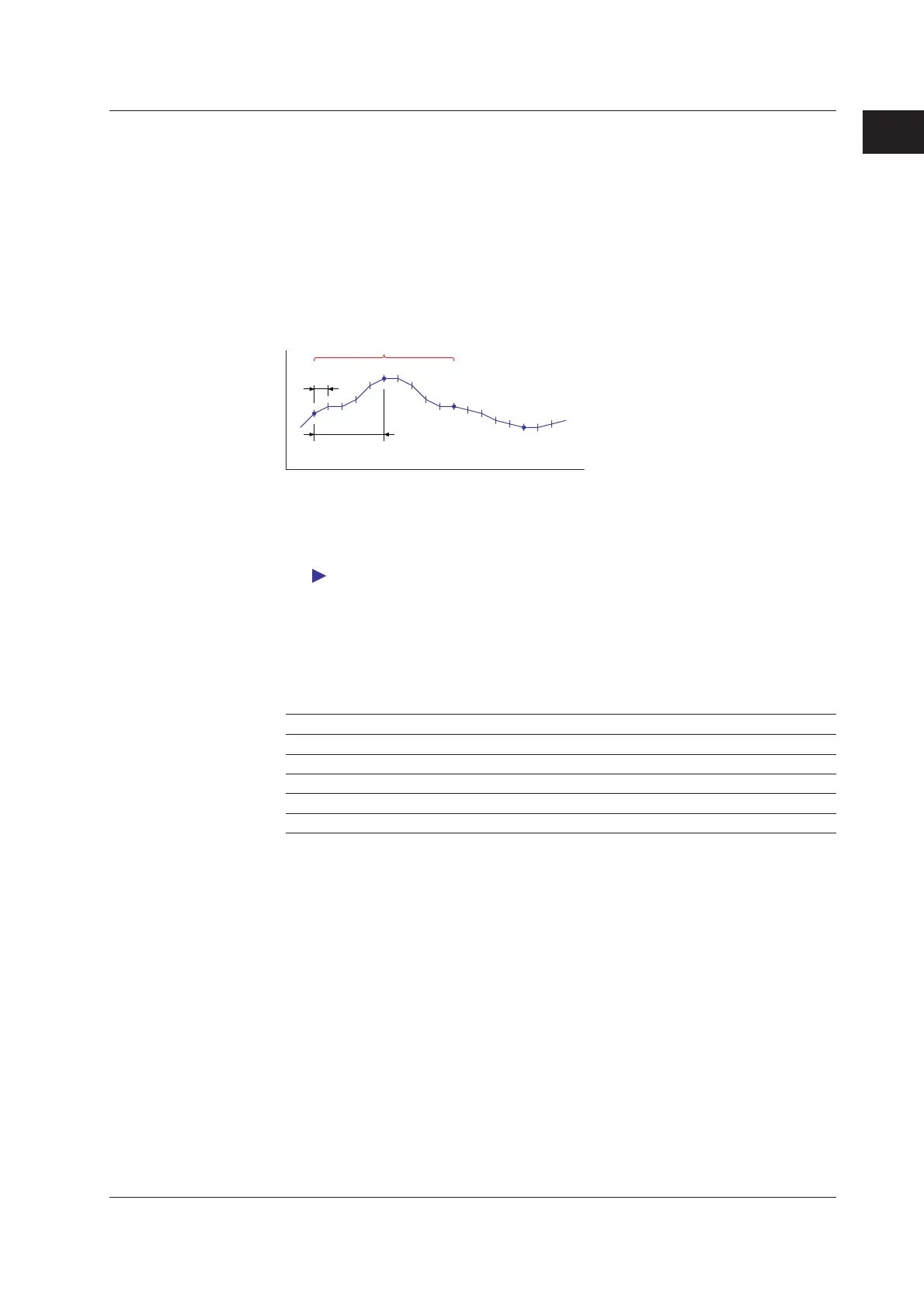
Rolling Average
Determines the rolling average of the computed results on the measurement channel and
uses it as the computed result of that channel. The number of samples and the sampling
interval can be specified for each computation channel.
The setting ranges are as follows:
Sampling interval: 1 s to 1 hour (23 levels)
Number of samples: 1 to 1500
• Example
If the MATH interval is 2 s, the sampling interval is 10 s, and the number of samples is
3, the computed data on which rolling average is calculated is as follows:
Time (s)
MATH interval
Moving average source
Sampling interval
Set the sampling interval to an integer multiple of the MATH interval. If the sampling
interval is shorter than the MATH interval, the sampling interval is matched to the MATH
interval.
For details on setting the sampling interval, see “MATH Function Specifications (/M1
Option)” in section 5.2.
Math Span
The upper and lower limits for the display of the monitor screen and other items.
The specifiable range of numbers is as follows according to the decimal place. If the
computed results fall outside of the allowable numerical value setting range, they are
displayed on screen as plus over or minus over data.
Decimal Place Computation span setting range
0 –9999999 to 99999999
1 –999999.9 to 9999999.9
2 –99999.99 to 999999.99
3 –9999.999 to 99999.999
4 –999.9999 to 9999.9999
Handling Units in Computations
In computations, computed values (measured and computed data) are handled as
numbers without units. Also, they are unrelated to the math channel units.
Example:
Expression = 001 + 002 + K01
001 (measurement ch 1) = 20 mV, 002 (measurement ch 2) = 30 V, K01 (math constant)
= 10
Given the above, the computed result is 60.
Pulse Integration (TLOG.PSUM) Settings
Computation is performed at 100-ms intervals or longer, but pulse integration can be
performed at the measurement interval of the module that can receive DI input. The
fastest measurement interval is 10 ms.
1.13 MATH Function (/M1 Option)

 Loading...
Loading...