Chapter 3
3.2 Active markers
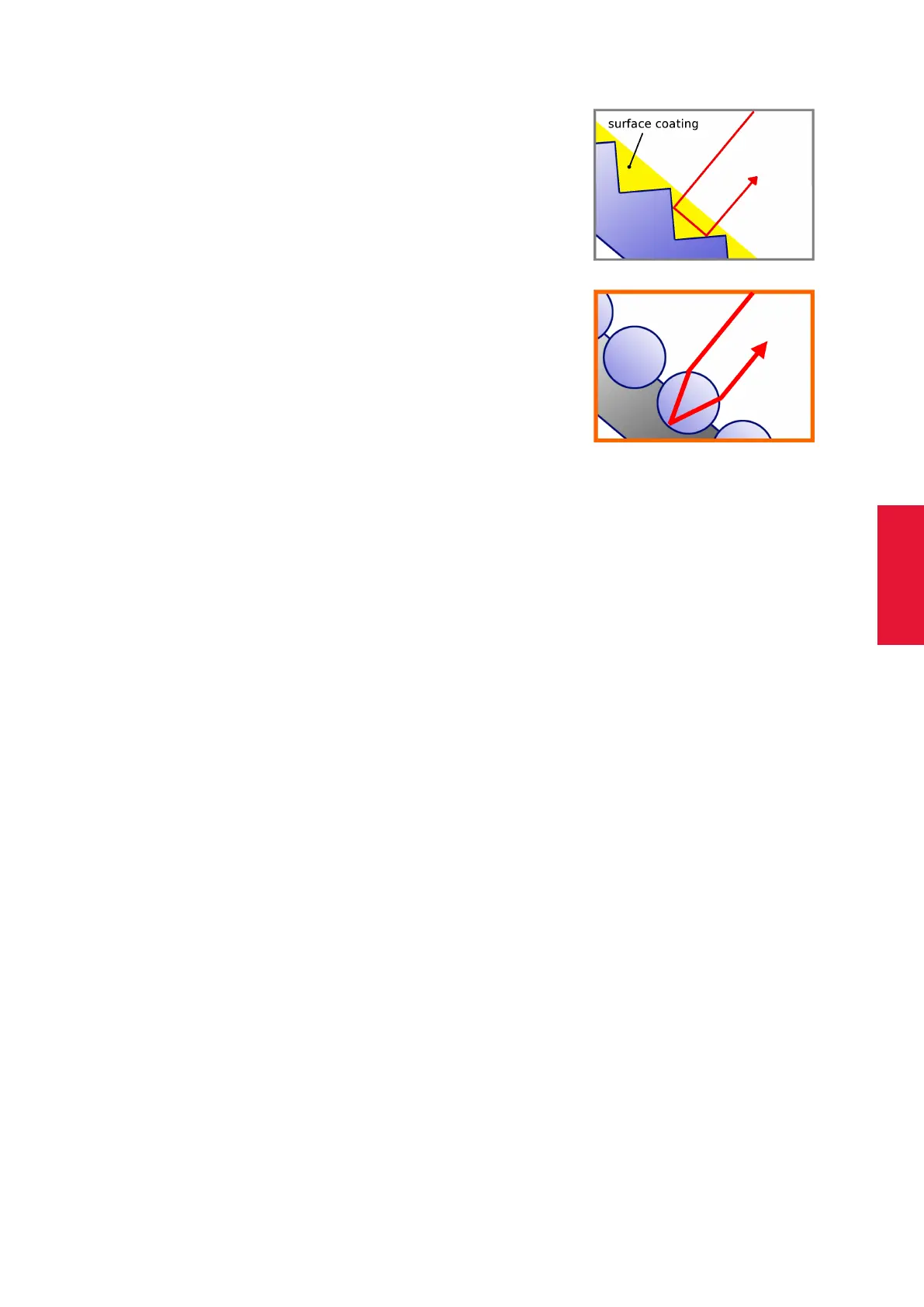
1. Triple mirrors, which are arranged such that their planes
form angles of 90
◦
by pairs, are reflecting light in the de-
scribed way. Mostly foils with arrangements of many very
small mirrors in a plane are used.
2. Glass spheres (with a proper refraction index) are fo-
cussing incoming light approximately to the opposite sur-
face of the ball. A layer of microscopic glass spheres, car-
ried by a reflecting material, acts as a retro reflector. These
foils can be fabricated on a flexible carrier material, thus
they are widely used for equipping spherical markers with
retro reflecting surfaces.
i
ART spherical markers are covered with retro reflecting foils, based on
the glass spheres principle.
Z
The quality of the markers decreases when they are in contact with
dust, dirt, fat, liquids, glue or comparable contaminants. Please make
sure that the markers are not touched or damaged.
3.2 Active markers
Basics Active markers are light (i.e. infrared light) emitting elements, usually LEDs.
In ART tracking systems four types of LED-based active markers may be used, depend-
ing on the application:
1. Single LEDs without diffusor sphere:
+ can be covered with acrylic protection film,
+ results in simple and robust markers providing visibility up
to high distances (up to 10m),
- the angular range of visibility is limited to approx. ±60
◦
.
21
 Loading...
Loading...