Chapter 11 Motion Control Instructions
11-77
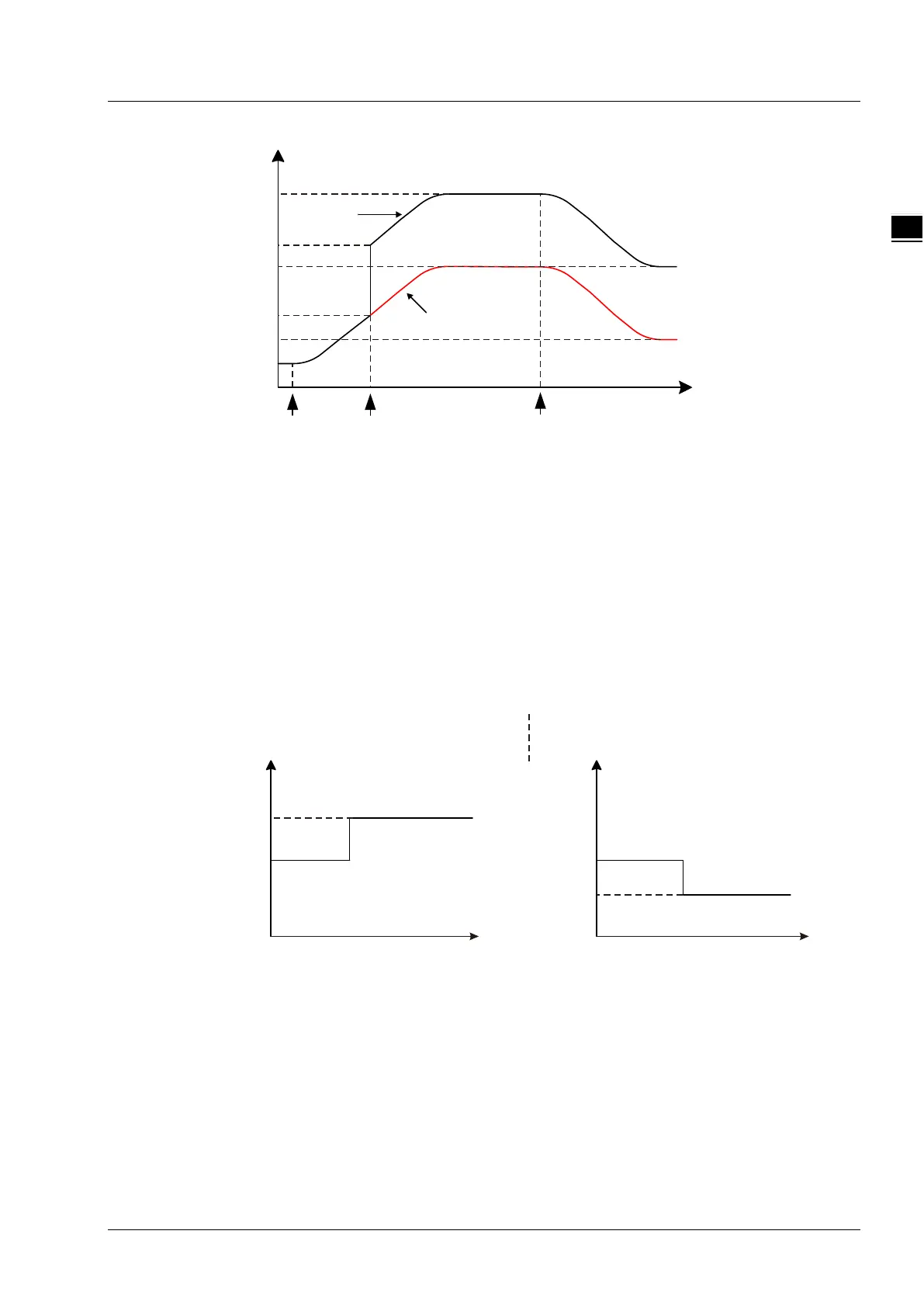
Relationship between Position and Relative
Position, Relative and reference position which stands for the axis position at the moment when the
instruction starts being executed jointly determine the position setting value.
Relative is used to define the relationship between Position and reference position. When Relative
is set to TRUE, it is a relative relationship between Position and reference position and the position
setting value= reference position+ Position. When Relative is FALSE, it is an absolute relationship
between Position and reference position and the position setting value equals Position.
As shown in the following figures, the reference position is set to10000 and the value of Position is
6000 for the instruction execution. The corresponding execution results are respectively illustrated
for different Relative values as below.
ReferenceType
ReferenceType is used to select the command position or actual position as the reference position.
When ReferenceType is 0, the reference position is the command position of the axis. When
ReferenceType is 1, the reference position is the actual position of the axis.
When the command position is taken as the reference position, the instruction calculates the target
command position based on the current command position and the value of Position and it revises the
command position value into the target position value. Meantime, the actual position of the axis will
change accordingly. The law of the change is that the variation amount of the actual position is the
same as that of the command position. That is to say that the deviation between the command position
Position
8000
1000
0
Command Position
Actual Motion Curve
3000
5000
6000
Execute
Perform Absolute
Positioni ng o f
Perform Absolute
Positioning of
2000
5000
SetPosition
5000
Time
Position
16000
10000
Relative=TRUE
Before e xe cuti on
After e xecuti on
Time
0
Position
6000
10000
Before execution
Afte r executi on
Time
0
Relative=FALSE

 Loading...
Loading...