2 • DC Description
Doc. 065031-04 1/08 61
2.16.4 Integrated and Pulsed Amperometric Detection
Integrated and pulsed amperometric detection are similar to DC
amperometry (see Section 2.16.3
) in that molecules are oxidized or
reduced at the surface of an electrode. However, with these detection
modes, a series of potential changes is repeated over time. By repeatedly
pulsing between high positive and negative potentials, the electrode
surface is continually regenerated. Current is measured by integration
during a portion of the repeating potential vs. time waveform. See
Section 2.16.6
for more information about waveforms.
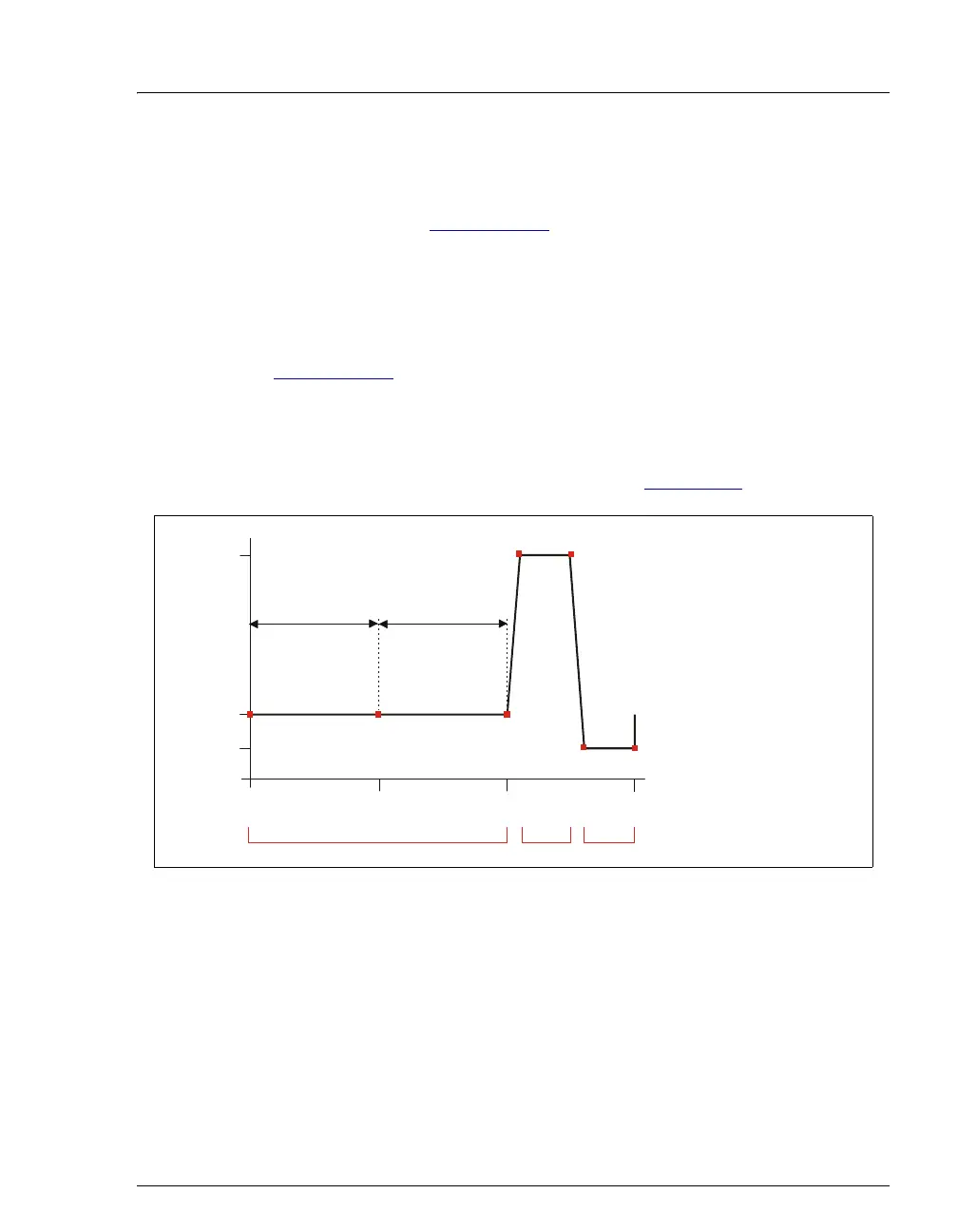
Pulsed Amperometric Detection
In pulsed amperometric detection (also known as PAD), current is
integrated at a single constant potential (see Figure 2-24
).
The potentials, labeled E1, E2, and E3, are applied for durations t1, t2,
and t3, respectively. At t1, the E1 potential is applied. After a delay, the
signal is measured by integrating the current for a fixed time. Current
integrated for a fixed time is charge and the units are coulombs. At t2 and
t3, positive and negative cleaning pulses are added to the waveform. This
waveform period repeats until the end of data acquisition or until another
waveform is specified.
Figure 2-24. Example Pulsed Amperometry Waveform
Integration
Potential
(Volts)
Time (Seconds)
0.2 0.40.0
0.6
+0.1
+0.7
t1
t2
t3
Delay
-0.1
E1
E2 E3
E3
. Reconditioning Potentia
E2
. Cleaning Potential
E1
. Analytical Potential
 Loading...
Loading...