3
deletion of the 16 unused bits). The extended precision data format has a 15-bit biased
integer exponent and a 64-bit mantissa.
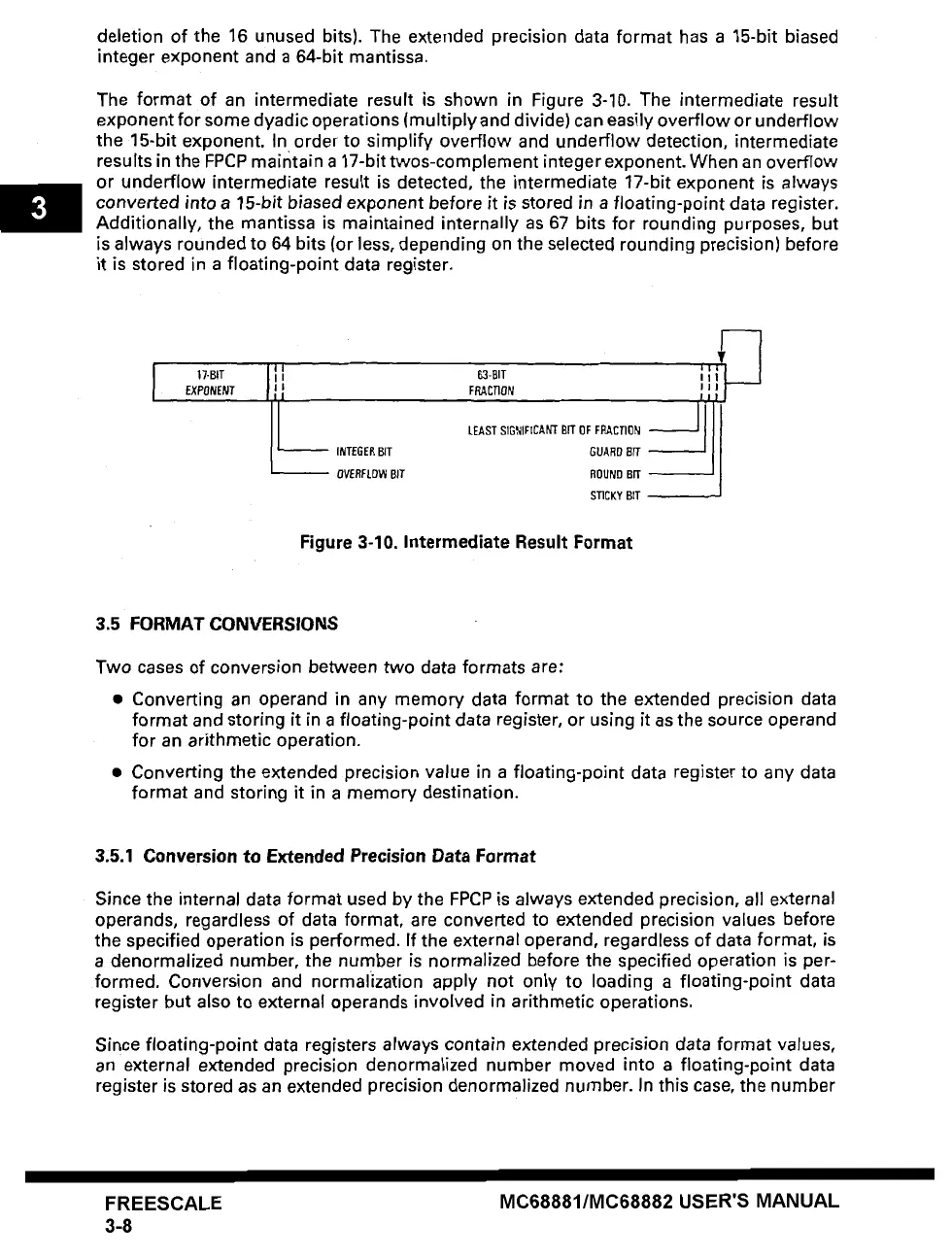
The format of an intermediate result is shown in Figure 3-10. The intermediate result
exponent for some dyadic operations (multiply and divide) can easily overflow or underflow
the 15-bit exponent. In order to simplify overflow and underflow detection, intermediate
results in the FPCP mairltain a 17-bit twos-complement integer exponent. When an overflow
or underflow intermediate result is detected, the intermediate 17-bit exponent is always
converted
into a 15-bit
biased exponent
before it is stored in a floating-point data register.
Additionally, the mantissa is maintained internally as 67 bits for rounding purposes, but
is always rounded to 64 bits (or less, depending on the selected rounding precision) before
it is stored in a floating-point data register.
JII
17-BIT I I 63-91T
EXPONENT
! ! FRACTION
1|
LEAST SIGNIFICANT BIT OF FRACTION
INTEGER BIT
GUARD 8Fr
OVERFLOW BIT ROUND BIT
STICKY BIT
Figure 3-10. Intermediate Result Format
3.5 FORMAT CONVERSIONS
Two cases of conversion between two
data
formats
are:
• Converting an operand in any memory data format to the extended precision data
format and storing it in a floating-point data register, or using it as the source operand
for an arithmetic operation.
• Converting the extended precision value in a floating-point data register to any data
format and storing it in a memory destination.
3,5.1 Conversion to Extended Precision Data Format
Since the internal data format used by the FPCP is always extended precision, all external
operands, regardless of data format, are converted to extended precision values before
the specified operation is performed. If the external operand, regardless of data format, is
a denormalized number, the number is normalized before the specified operation is per-
formed. Conversion and normalization apply not only to loading a floating-point data
register but also to external operands involved in arithmetic operations.
Since floating-point data registers arways contain extended precision
data
format values,
an external extended precision denormalized number moved into a floating-point data
register is stored as an extended precision denormalized number. In this case, the number
FREESCALE
3-8
MC68881/MC68882 USER'S MANUAL
 Loading...
Loading...