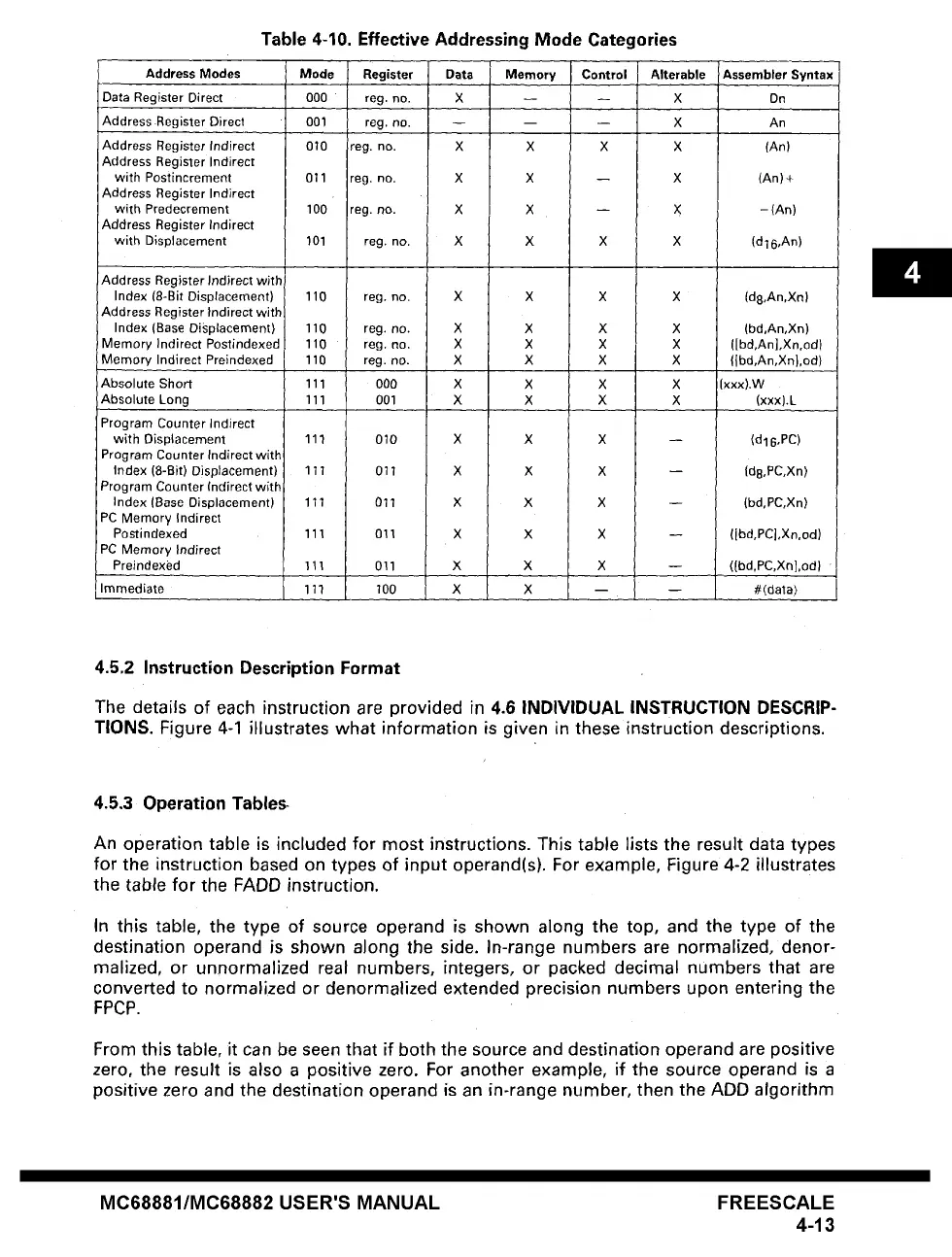
Table 4-10. Effective Addressing Mode Categories
Address Modes Mode Register Data Memory Control Alterable Assembler Syntax
Data Register Direct OOO reg. no.
X -- -- X
On
Address Register Direct
001 reg. no. --
-- --
X An
Address Register Indirect
010 reg. no. X X X X (An)
Address Register Indirect
with Postincrement
011 reg. no. X X -- X (An) +
Address Register Indirect
with Predecrement
100 reg. no. X X -- X -(An)
Address Register Indirect
with Displacement
101 reg. no. X X X X (d16,An)
Address Register
Indirect with
Index (8-Bit Displacement) 110 reg. no. X X
Address Register Indirect with
Index
(Base Displacement)
110 reg. no. X X
Memory Indirect Postindexed
110 reg, no. X X
i Memory Indirect
Preindexed 110 reg. no. X X
111 00O X X
111 001 X X
~ Absolute Short
Absolute Long
Program Counter
Indirect
with Displacement 111 010 X X
Program Counter Indirect withi
Index (8-Bit) Displacement) i 111 011 X X
Program Counter (ndirect
with
Index
(Base Displacement)
111 011 X X
PC Memory Indirect
Postindexed
111 011 X X
PC Memory Indirect
Preindexed 111 011 X X
Immediate
111 100 X X
X X (d8,An,Xn)
X X (bd,An,Xn)
X X ([bd,An],Xn,od)
X X {[bd,An,Xn],od)
X X llxxx).W
X X (xxx).L
X -- (d16,PC)
X -- [dB,PC,Xn)
X -- (bd,PC,Xn)
X -- ([bd,PC],Xn,od)
X
--
([bd,PC,Xn],od) I
-- --
#(data~
4.5.2 Instruction Description Format
The details of each instruction are provided in 4.6 INDIVIDUAL INSTRUCTION DESCRIP-
TIONS. Figure 4-1 illustrates what information is given in these instruction descriptions.
4.5.3 Operation Tables-
An operation table is included for most instructions. This table lists the result data types
for the instruction based on types of input operand(s). For example, Figure 4-2 illustrates
the table for the FADD instruction.
In this table, the type of source operand is shown along the top, and the type of the
destination operand is shown aJong the side. In-range numbers are normalized, denor-
realized, or unnormalized real numbers, integers, or packed decimal numbers that are
converted to normalized or denormalized extended precision numbers upon entering the
FPCP.
From this table, it can be seen that if both the source and destination operand are positive
zero, the result is also a positive zero. For another example, if the source operand is a
positive zero and the destination operand is an in-range number, then the ADD algorithm
MC68881/MC68882 USER'S MANUAL FREESCALE
4-13
 Loading...
Loading...