177
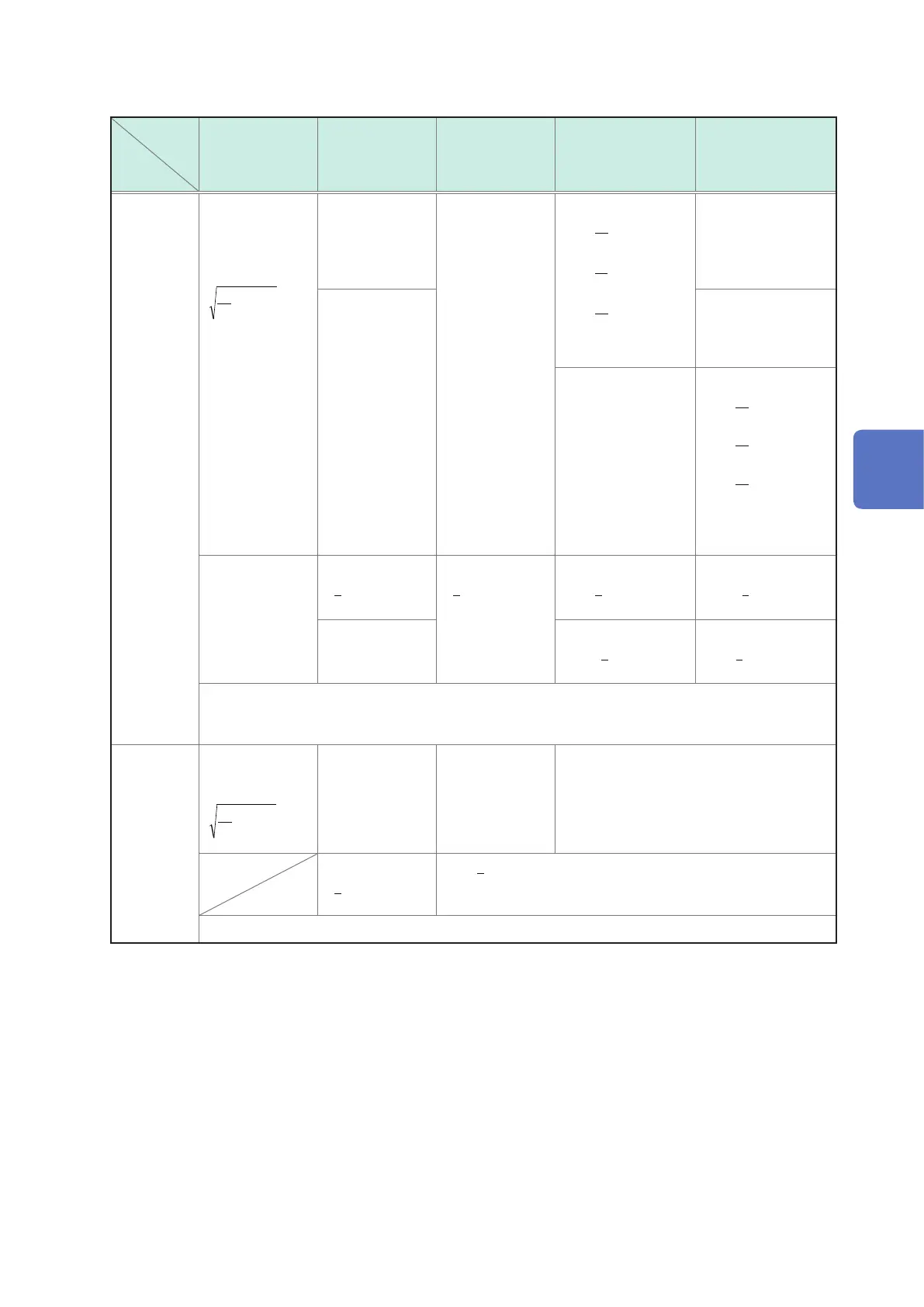
Calculation Formula
3. RMS voltage (Urms), RMS current (Irms)
Wiring
Item
Single phase
2-wire
1P2W
Single phase
3-wire
1P3W
3-phase 3-wire
3P3W2M
3-phase 3-wire
3P3W3M
3-phase 4-wire
3P4W
Urms
[Vrms]=
U
c
U
1
U
4
U
c
=
( )
∑
−
=
1
0
2
1
M
s
cs
U
M
U
1
U
2
U
4
U
1
U
2
U
3
(U
3S
=U
2S
−U
1S
)
U
4
Line voltage
U
12
=
( )
∑
−
=
−
1
0
2
21
1
M
s
ss
UU
M
U
23
=
( )
∑
−
=
−
1
0
2
32
1
M
s
ss
UU
M
U
31
=
( )
∑
−
=
−
1
0
2
13
1
M
s
ss
UU
M
Phase voltage
U
1
U
2
U
3
U
4
During 1P3W1U
Without
U
2
During 3P4W2.5E
U
3
(U
3S
=−U
1S
−U
2S
)
(
U
1S
+U
2S
+U
3S
= 0
is
the assumption)
Phase voltage
U
1
U
2
U
3
Line voltage
U
12
=
( )
∑
−
=
−
1
0
2
21
1
M
s
ss
UU
M
U
23
=
( )
∑
−
=
−
1
0
2
32
1
M
s
ss
UU
M
U
31
=
( )
∑
−
=
−
1
0
2
13
1
M
s
ss
UU
M
U
4
U
avg
=
( )
21
2
1
UU +
U
avg
=
( )
321
3
1
UUU ++
Line voltage
U
avg
=
( )
312312
3
1
UUU ++
Phase voltage
U
avg
=
( )
321
3
1
UUU ++
During 1P3W1U
Without
U
avg
Phase voltage
U
avg
=
( )
321
3
1
UUU ++
Line voltage
U
avg
=
( )
312312
3
1
UUU ++
• For 3P3W2M wiring, it is assumed that
U
1S
−U
2S
+U
3S
= 0
• For 3P3W3M wiring, phase voltage
U
is measured from the virtual neutral point, and line voltage is
determined by calculation.
Irms
[Arms]=
I
c
I
1
I
4
I
c
=
( )
∑
−
=
1
0
2
1
M
s
cs
I
M
I
1
I
2
I
4
I
1
I
2
I
3
(I
3S
=−I
1S
−I
2S
)
I
4
I
1
I
2
I
3
I
4
I
avg
=
( )
21
2
1
II +
I
avg
=
( )
321
3
1
III ++
• For 3P3W2M wiring, it is assumed that
I
1S
+I
2S
+I
3S
=0
.
c
: Measurement channel, M: Number of samples per period,
s
: Number of sample points
14
Specications

 Loading...
Loading...