Appx.29
Terminology
Timer event function Functionality for generating events at a set time interval and recording the measured value
and event waveform at that time.
This function allows you to capture instantaneous waveforms and other data regularly,
even if no abnormalities have occurred. Use this functionality when you wish to record a
waveform at a xed time interval.
Total harmonic
distortion factor
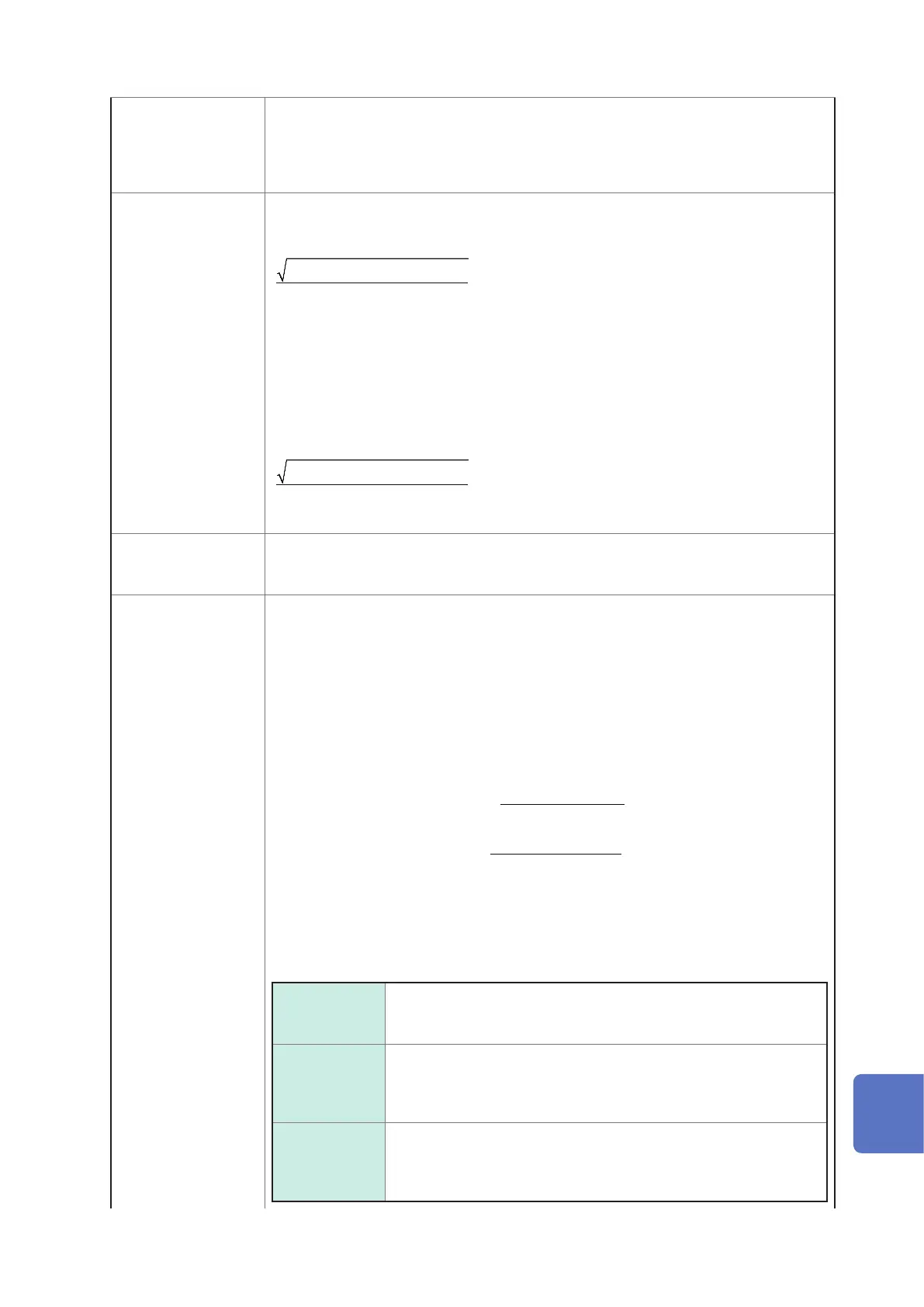
THD-F:
The ratio of the size of the total harmonic component to the size of the fundamental wave,
expressed as a percentage using the following equation:
(2nd order and above)
2
100[%]×
∑
Fundamental wave
(for the instrument, calculated to the 50th order)
This value can be monitored to assess waveform distortion for each item, providing a
yardstick that indicates the extent to which the total harmonic component is distorting the
fundamental waveform.
As a general rule, the total distortion factor for a high-voltage system should be 5% or
less; it may be higher at the terminal point of the system.
THD-R:
The ratio of the size of the total harmonic component to the size of the RMS, expressed
as a percentage using the following equation:
(2nd order and above)
2
100[%]×
∑
RMS
(for the instrument, calculated to the 50th order)
THD-F is typically used.
Transient
overvoltage
An event caused by lightning strikes, circuit-breaker and relay contact obstructions and
tripping, and other phenomena. Transient overvoltage are often characterized by steep
voltage changes and a high peak voltage.
Unbalance factor Unbalanced (symmetrical) 3-phase voltage (current):
3-phase AC voltage (current) with equal voltage and current magnitude for each phase
and 120° phase separation.
Unbalanced (asymmetrical) 3-phase voltage (current):
3-phase AC voltage (current) with unequal voltage magnitude for each phase or without
120° phase separation.
Degree of unbalance in 3-phase alternating voltage
Normally described as the voltage unbalance factor, which is the ratio of negative-phase
voltage or zero-phase voltage to positive-phase voltage
100[%]×
Negative-phase voltage
Voltage negative-phase unbalance factor
=
Positive-phase voltage
100[%]×
Zero-phase voltage
Voltage zero-phase unbalance factor
=
Positive-phase voltage
Zero-phase/positive-phase/negative-phase voltage:
The concept of a zero-phase-sequence/positive-phase-sequence/negative- phase-
sequence component in a three-phase alternating circuit applies the method of
symmetrical coordinates (a method in which a circuit is treated so as to be divided into
symmetrical components of a zero phase, positive phase, and negative phase).
Zero-phase-
sequence
component
Voltage that is equal in each phase. Described as [
V
0
] (Subscript 0:
Zero-phase-sequence component).
Positive-
phase-
sequence
component
Symmetrical three-phase voltage in which the value for each phase
is equal, and each of the phase is delayed by 120 degrees in the
following phase sequence: a, b, and c. Described as [
V
1
] (Subscript 1:
Positive-phase-sequence component).
Negative-
phase-
sequence
component
Symmetrical three-phase voltage in which the value for each phase
is equal, and each of the phases is delayed by 120 degrees in the
following phase sequence: a, b, and c. Described as [
V
2
] (Subscript 2:
Negative-phase-sequence component).
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
Appx. Ind.

 Loading...
Loading...