98
Changing the Waveform Display and Conguring Recording
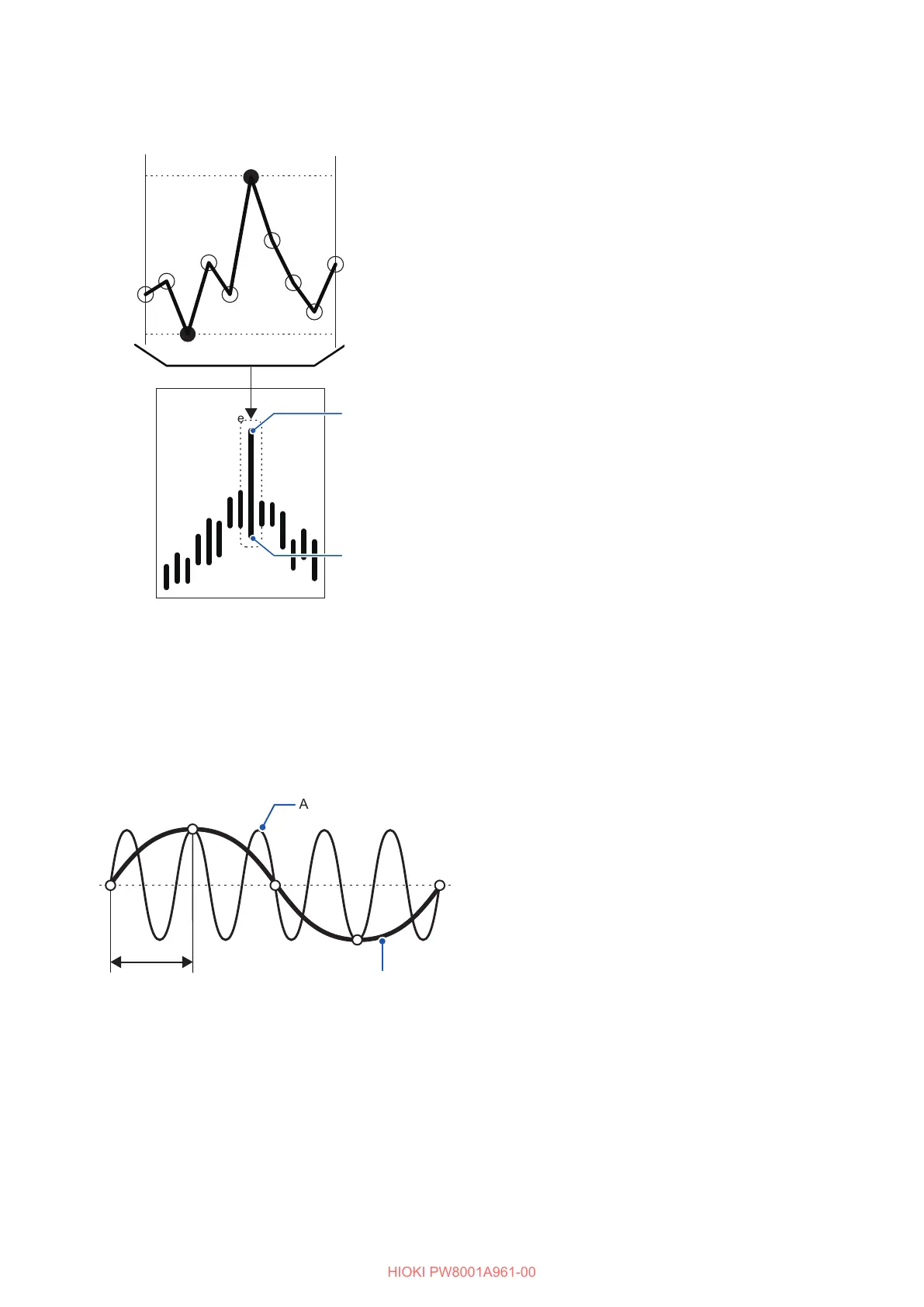
Peak-to-peak compression
Maximum value
Waveform
drawn at a rate
of 500 kS/s
Minimum value
Minimum value
Maximum value
Values sampled at rate of 15 MS/s
To compress a waveform sampled with a rate of 15 MS/s
to that composed of points with a rate of 500 kS/s by
using the peak-to-peak compression
Even if you change the sampling frequency setting,
the instrument samples signals internally with
a sampling rate of 15 MS/s. When reducing the
sampling frequency, decimate of sampling points
from a waveform sampled with the rate of 15 MS/s
at regular intervals may decimate the maximum
and minimum values in the interval. The peak-
to-peak compression is the way to select and
decimate other points leaving the maximum and
minimum values in the interval.
In this way, you can reduce the sampling frequency
maintaining accurate waveforms that preserve the
peaks of the uncompressed waveforms.
The waveform data to be saved consists of two
values per data point, the maximum and minimum
values as illustrated in the gure on the left.
Aliasing
Actual input signal
Sampling interval
Observed waveform
Aliasing has occurred
because the sampling
frequency is low relative
to synchronization of the
incoming signal.
When the change of a signal under measurement
becomes faster with respect to the sampling
frequency, a slow signal changes that do not exist
at a certain frequency are recorded.
This phenomena is called aliasing.

 Loading...
Loading...