19
If you specify an interface type but do not specify an interface number, this command displays
information about dropped packets on all interfaces of the specified type.
Examples
# Display information about dropped packets on GigabitEthernet 1/0/1.
<Sysname> display packet-drop interface gigabitethernet 1/0/1
GigabitEthernet1/0/1:
Packets dropped due to full GBP or insufficient bandwidth: 301
Packets dropped due to Fast Filter Processor (FFP): 261
Packets dropped due to STP non-forwarding state: 321
Packets dropped due to insufficient data buffer. Input dropped: 0 Output dropped:0
# Display the summary of dropped packets on all interfaces.
<Sysname> display packet-drop summary
All interfaces:
Packets dropped due to full GBP or insufficient bandwidth: 301
Packets dropped due to Fast Filter Processor (FFP): 261
Packets dropped due to STP non-forwarding state: 321
Packets dropped due to insufficient data buffer. Input dropped: 0 Output dropped:0
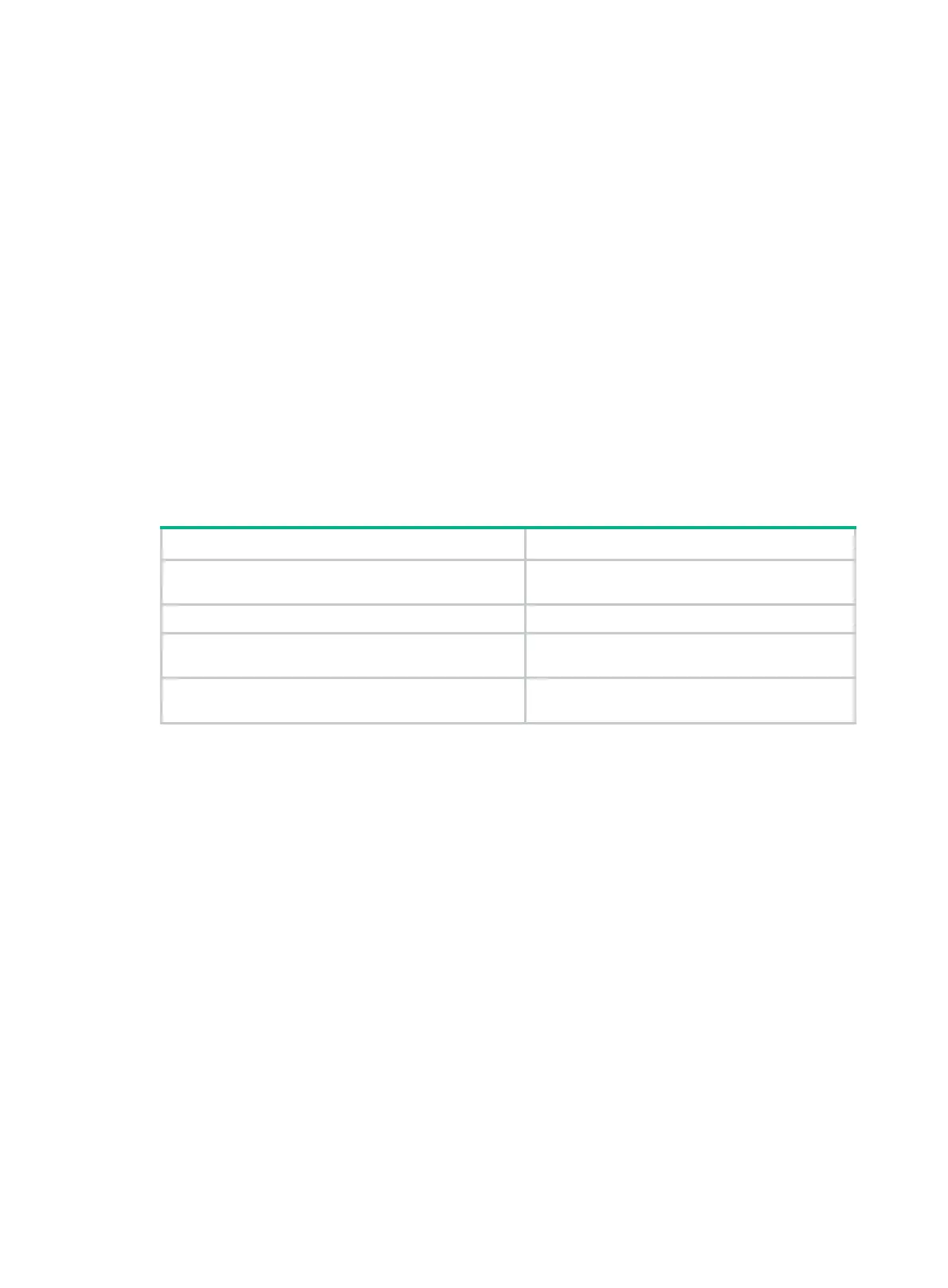
Table 6 Command output
Field Description
Packets dropped due to full GBP or insufficient
bandwidth
Packets that are dropped because the buffer is
used up or the bandwidth is insufficient.
Packets dropped due to Fast Filter Processor (FFP) Packets that are filtered out.
Packets dropped due to STP non-forwarding state
Packets that are dropped because STP is in the
non-forwarding state.
Packets dropped due to insufficient data buffer. Input
dropped: 0 Output dropped:0
Inbound and outbound packets that are dropped
due to insufficient data buffer.
duplex
Use duplex to set the duplex mode for an Ethernet interface.
Use
undo duplex to restore the default.
Syntax
duplex { auto | full | half }
undo duplex
Default
An Ethernet interface operates in autonegotiation mode.
Views
Ethernet interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
Parameters
auto: Configures the interface to autonegotiate the duplex mode with the peer.

 Loading...
Loading...














