Detailed description
2.7 Structure and functions of the basic program
Basic logic functions: PLC Basic program powerline (P3 pl)
Function Manual, 11/2006, 6FC5397-0BP10-2BA0
49
)&
'!Q P S
'!Q P R S
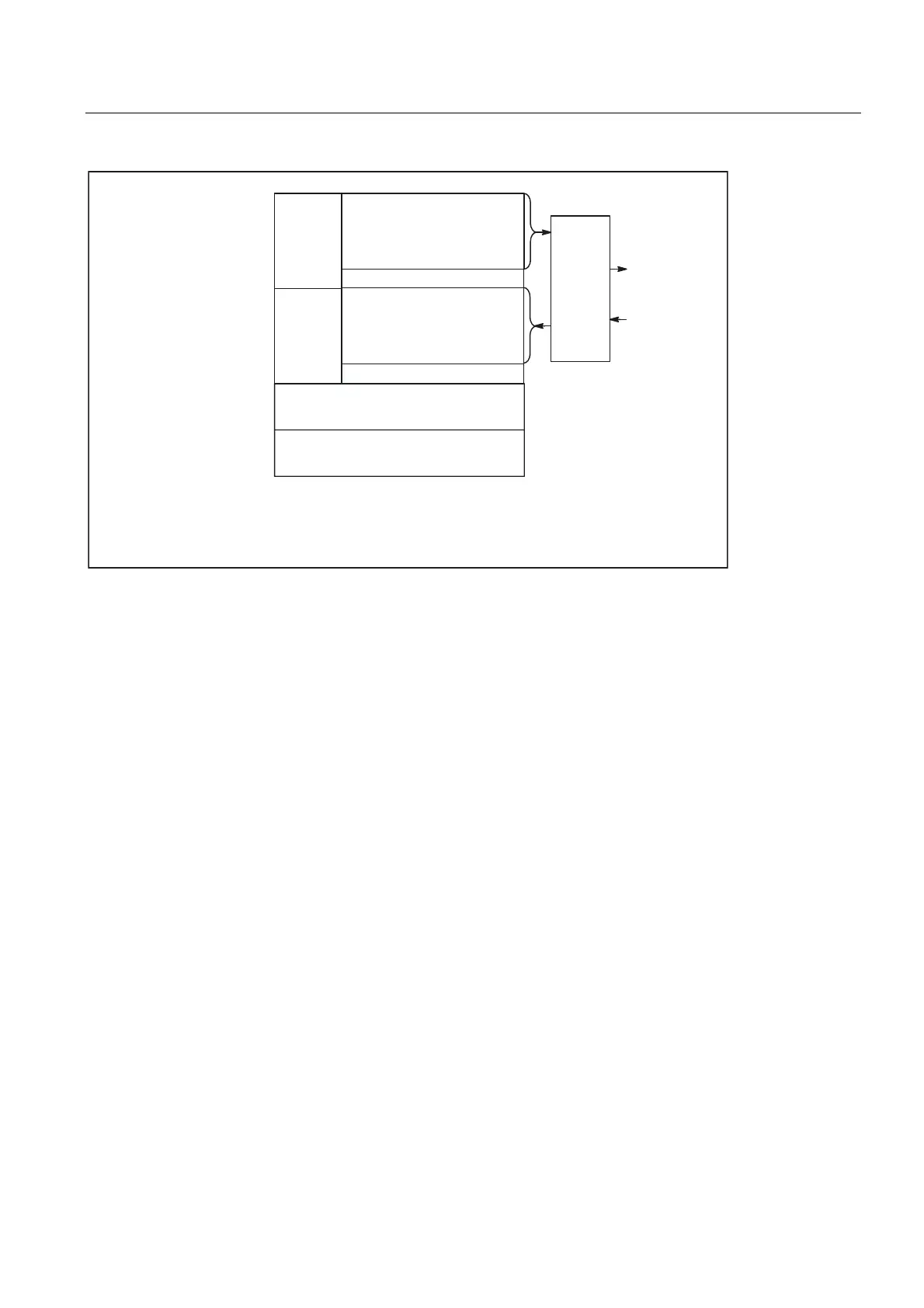
5HFHLYHGDWD
PRQLWRULQJ
0RQLWRULQJRIWUDQVPLW
GDWD
'HIDXOWVHWWLQJ
6WDWXVRIFXVWRPL]HGNH\V
$FWLYHGLUHFWLRQNH\
)HHGUDWHVSLQGOH1&VWDWXV
&XUUHQW,1&PRGH
&XUUHQWPRGH
8VHUNH\V
.H\VZLWFK
'LUHFWLRQNH\V
)HHGUDWHVSLQGOHRYHUULGH
,1&PRGH
0RGHJURXSV
/LJKW
HPLWWLQJ
GLRGHV
/('V
.H\
VLJQDOV
$'S
$'R
0RGH
JURXS
1&.D[LV
VSLQGOH
LQWHUIDFH
4%P
,%Q
Figure 2-11 Interface to and from machine control panel
2.7 Structure and functions of the basic program
2.7.1 General
General
The program is modular in design, i.e., it is structured according to NCK functions.
In the operating system, a distinction is made between the following levels of execution:
• Startup and synchronization (OB 100)
• Cyclic mode (OB 1)
• Process interrupt handling (OB 40)
Each section of the basic program - as illustrated in the figure below - must be called by the
user in OBs 1, 40 and 100.

 Loading...
Loading...























