Functions
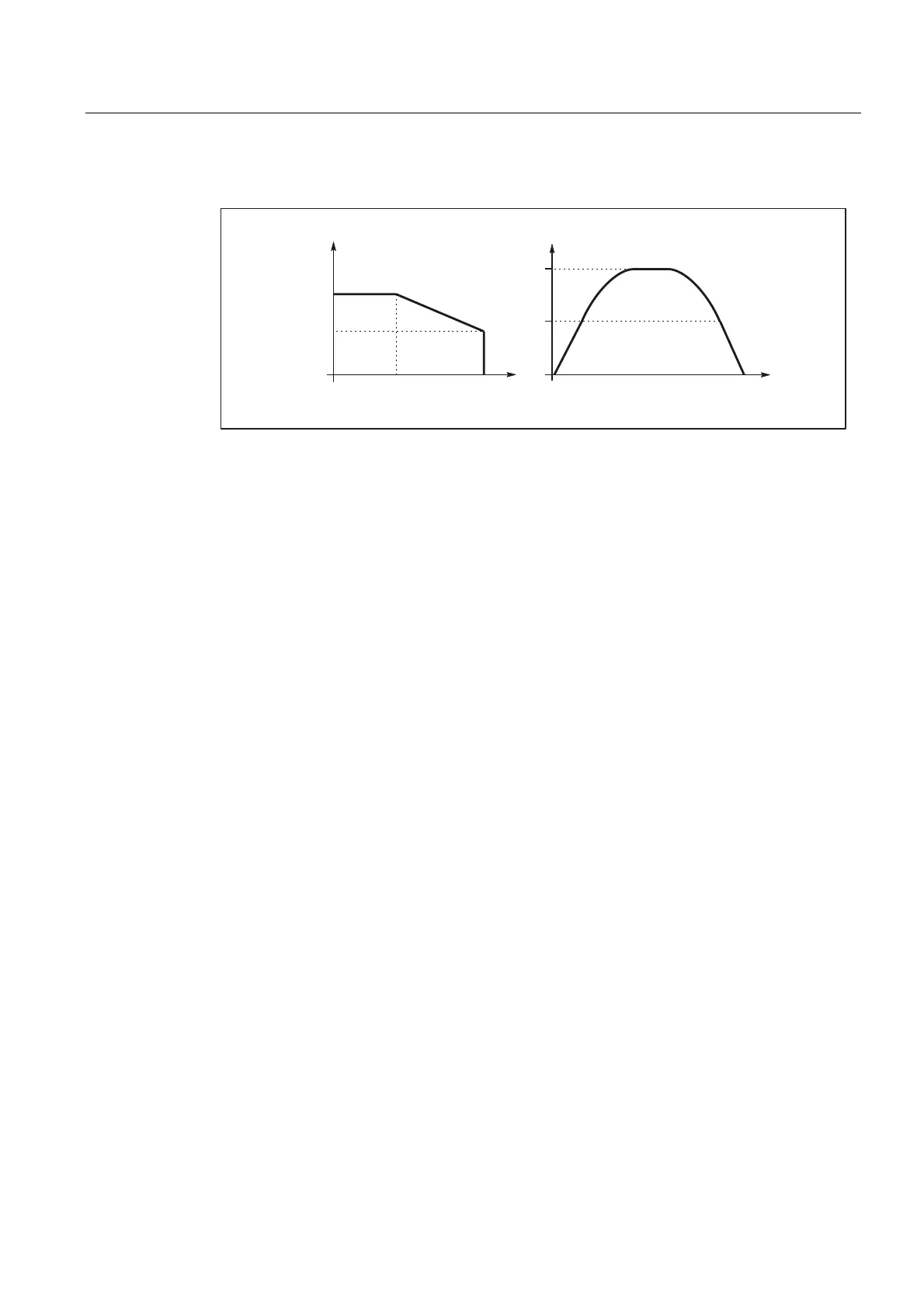
2.18 Kneeshaped acceleration characteristic curve
Basic logic functions: Acceleration (B2)
Function Manual, 11/2006, 6FC5397-0BP10-2BA0
45
Linear characteristic
Y
PD[
Y
UHG
D
UHG
D
PD[
Y
UHG
Y
PD[
YD
Y
W
Figure 2-8 Acceleration and velocity characteristic with acceleration reduction: 2 = linear
The key data for the characteristic curves equate to:
v
max
= $MA_MAX_AX_VELO
v
red
= $MA_ACCEL_REDUCTION_SPEED_POINT * $MA_MAX_AX_VELO
a
max
= $MA_MAX_AX_ACCEL
a
red
= (1 - $MA_ACCEL_REDUCTION_FACTOR) * $MA_MAX_AX_ACCEL
2.18.1.2 Effects on path acceleration
Function
The path acceleration characteristic curve is generated on the basis of the types of
characteristic for the axes that are of relevance for the path. If axes with different types of
characteristic curve are interpolated together, the acceleration profile for the path
acceleration will be determined on the basis of the reduction type that is most restrictive.
The following order of priorities applies, whereby 1 = top priority:
1. Acceleration reduction: 0 = constant characteristic
2. Acceleration reduction: 1 = hyperbolic characteristic
3. Acceleration reduction: 2 = linear characteristic
4. No acceleration reduction effective
A situation, whereby no acceleration reduction is active, arises for example when:
MD35220 $MA_ACCEL_REDUCTION_SPEED_POINT = 1
and/or
MD35230 $MA_ACCEL_REDUCTION_FACTOR = 0

 Loading...
Loading...























