Detailed description
2.6 Interface structure
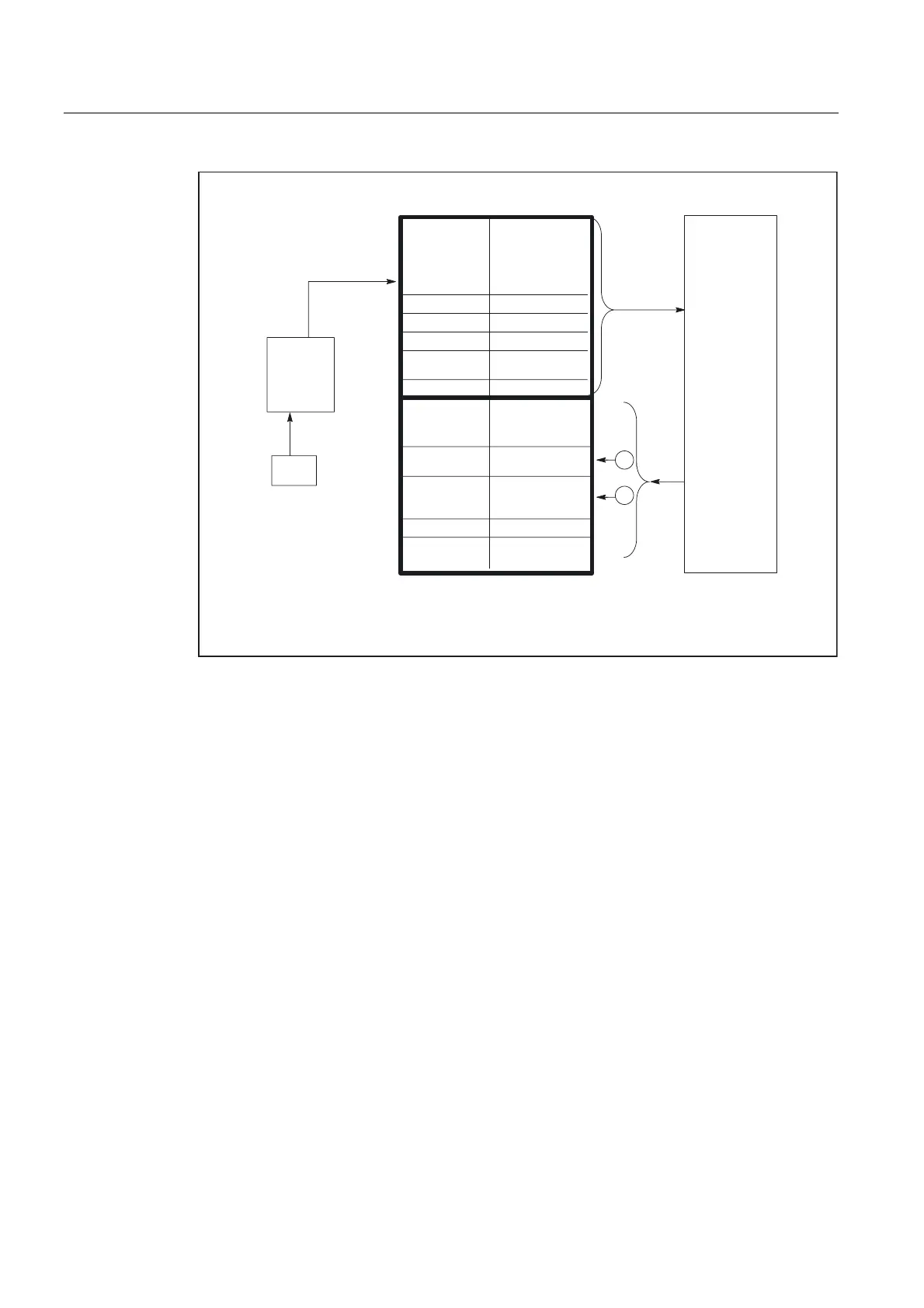
Basic logic functions: PLC Basic program powerline (P3 pl)
42 Function Manual, 11/2006, 6FC5397-0BP10-2BA0
%\WH
'%
1&.
6WDWXVVLJQDOV
*ULQGLQJ
7HFKQRORJ\
&RQWUROVLJQDOV
5HVHUYH
,1&PRGH
VHOHFWLRQ
WKURXJK
B)&
B)&
YDOXHVRI06DQG)GLVWULEXWRUVRIEDVLFSURJUDP
$[LV
VSLQGOH
GULYH
6WDWXVVLJQDOV
06YDOXH
6WDWXVVLJQDOV
6HWJHDUVWDJH
$[LDO)YDOXH
6WDWXVVLJQDOV
$FWLYH,1&PRGH
6WDWXVVLJQDOV
'ULYHVLJQDOV
6SLQGOH
VLJQDOV
$[LVVLJQDOV
6KDUHG
D[LVVSLQGOH
VLJQDOV
*ULQGLQJ
7HFKQRORJ\
&RQWUROVLJQDOV
'ULYHVLJQDOV
$[LVVLJQDOV
/LPLWVZLWFK
&RQWUROVLJQDOV6SLQGOHVLJQDOV
6KDUHG
D[LVVSLQGOH
VLJQDOV
,1&PRGH
7UDYHUVHVLJQDOV
&RQWUROVLJQDOV
)HHGUDWHVSLQGOH
RYHUULGH
%3
0&3
Figure 2-7 Interface between PLC and axes/spindles/drives
2.6.3 Interface PLC/HMI
General
The following groups of functions are required for the PLC/HMI interface:
• Control signals
• Machine operation
• PLC messages
• PLC status display
Control signals
Some control signals are signal inputs from the machine control panel, for example, which
have to be taken into account by the HMI software. This group of signals includes, for
example, display actual values in MCS or WCS, key disable, etc. These are exchanged via a
separate HMI interface data block (DB19).

 Loading...
Loading...























