Functions
2.18 Kneeshaped acceleration characteristic curve
Basic logic functions: Acceleration (B2)
46 Function Manual, 11/2006, 6FC5397-0BP10-2BA0
Note
Machine axes featuring stepper motor and DC drive can be interpolated together.
2.18.1.3 Substitute characteristic curve
Function
If the programmed path cannot be traversed using the parameterized acceleration
characteristic curve (e.g., active kinematic transformation), a substitute characteristic curve
is generated by reducing the dynamic limit values. The dynamic limit values are calculated to
ensure that the substitute characteristic curve provides the best possible compromise
between maximum velocity and constant acceleration.
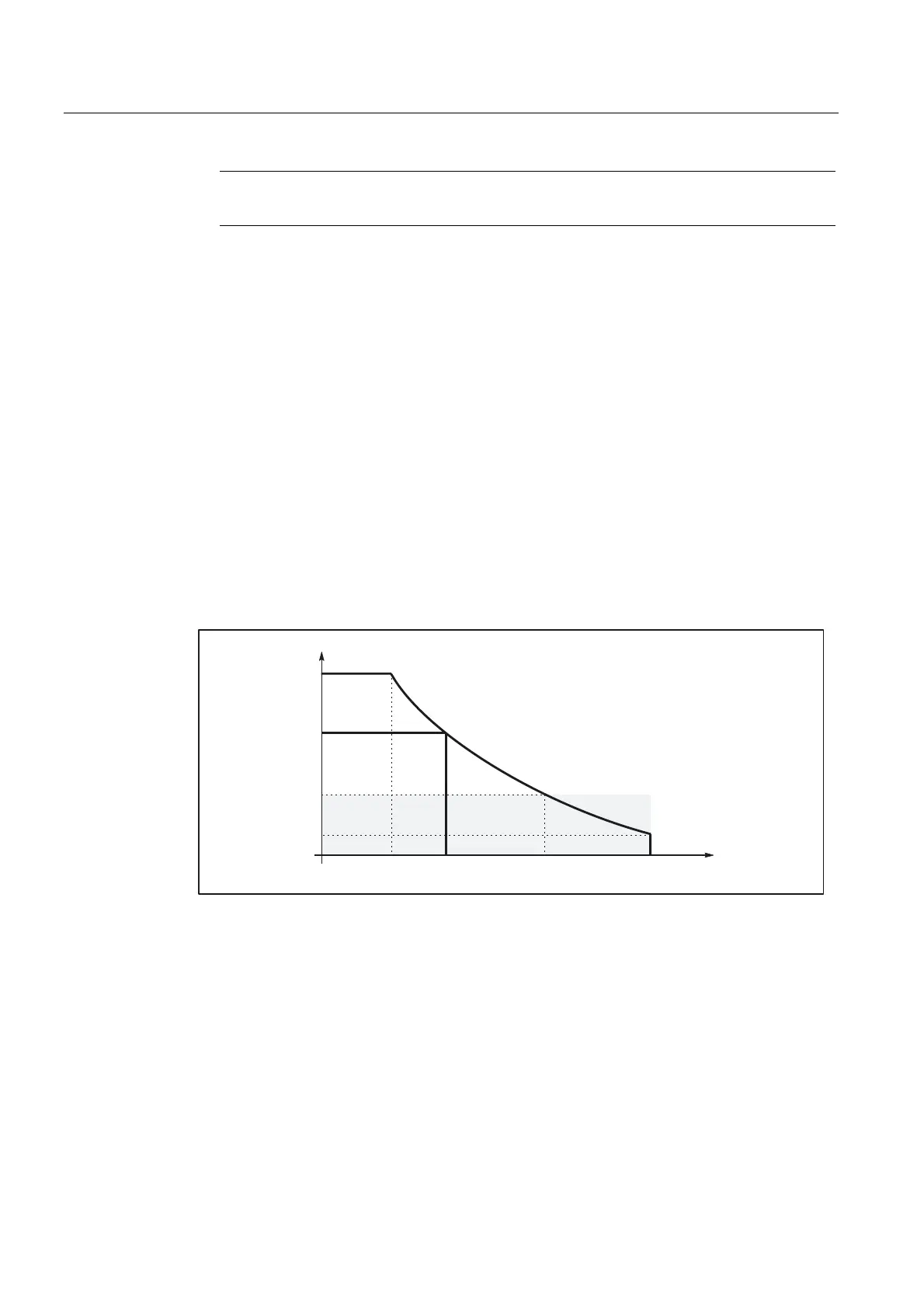
Substitute characteristic curve with linear path sections
Limitation to this value is applied if the programmed path velocity is greater than that at
which 15% of the maximum acceleration capacity is still available (v
15%a
). Consequently,
15% of the maximum acceleration capacity/motor torque always remains available, whatever
the machining situation.
/RFNHG]RQH
Y
D
Y
SURJ
D
D
HUV
D
UHG
D
PD[
Y
UHG
Y
PD[
D
Y
Figure 2-9 Substitute path characteristic curve: Linear path
a
ers
: Substitute characteristic curve constant acceleration
a
15%
: Minimal constant acceleration
a
15%
= 0.15 @ (a
max
- a
red
) + a
red
v
ers
: Substitute characteristic curve velocity
v
prog
: Programmed velocity
v
15%a
: Velocity at a
15%

 Loading...
Loading...























