Detailed description
2.3 Coordinate systems
Basic logic functions: Axes, coordinate systems, frames (K2)
Function Manual, 11/2006, 6FC5397-0BP10-2BA0
47
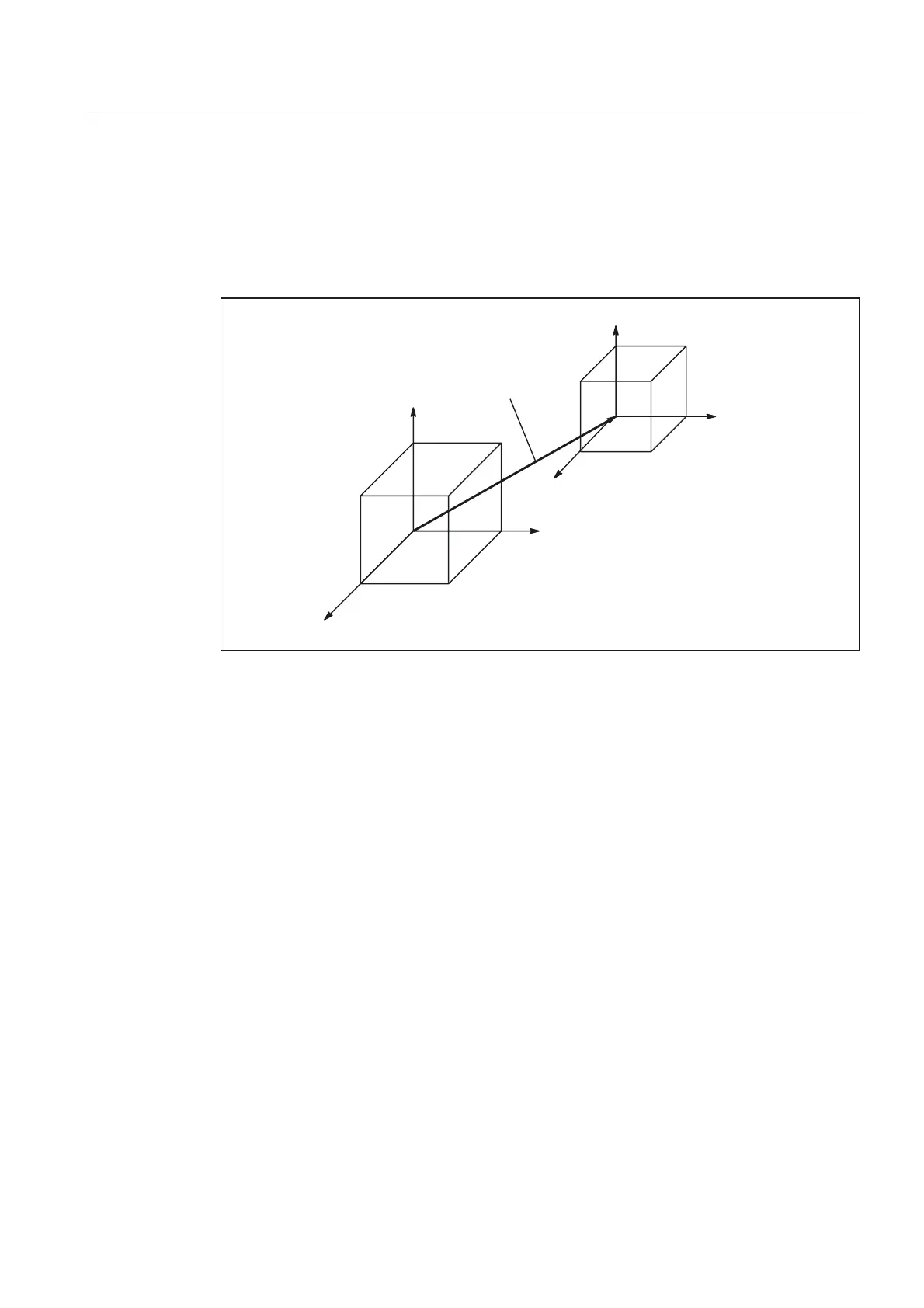
2.3.5 Basic zero system (BZS)
Basic zero system (BZS)
The basic zero system (BZS) is the basic coordinate system with a basic offset.
;
=
<
;
<
=
%DVLFFRRUGLQDWHV\VWHP%&6
%DVLF]HURV\VWHP%=6
%DVLFRIIVHW
Figure 2-18 Basic offset between BCS and BZS
Basic offset
The basic offset describes the coordinate transformation between BCS and BZS. It can be
used, for example, to define the palette window zero.
The basic offset comprises:
• Zero offset external
• DRF offset
• Superimposed motion
• Chained system frames
• Chained basic frames

 Loading...
Loading...























