Detailed description
2.7 Structure and functions of the basic program
Basic logic functions: PLC basic program solution line (P3 sl)
74 Function Manual, 11/2006, 6FC5397-0BP10-2BA0
03,'3
'3
++8
1&.
(WKHUQHW
0&3
0&3
'
3
5
3URILEXVFRQIIRU
0&3++8
&3
'VO
LQW3/&
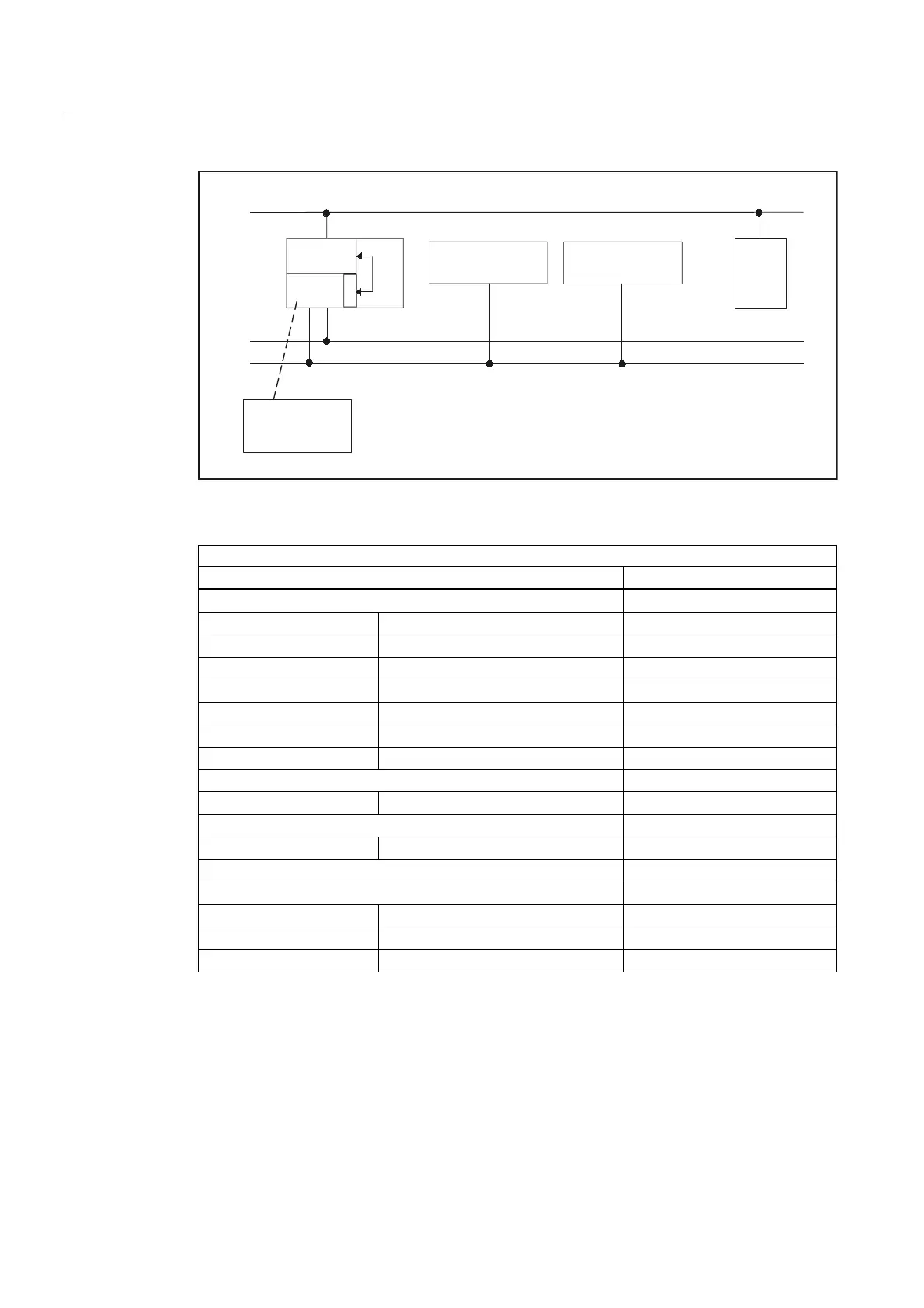
Figure 2-17 840D sl Profibus connection
Relevant parameters (FB 1)
MCP HHU
MCPNum = 1 or 2 (number of MCPs) HHU = 5 (via CP 840D sl)
MCP1In MCP2In BHGIn
MCP1Out MCP2Out BHGOut
MCP1StatSend (n.r.) MCP2StatSend (n.r.) BHGStatSend
MCP1StatRec MCP2StatRec BHGStatRec
MCP1BusAdr MCP2BusAdr BHGInLen
MCP1Timeout MCP2Timeout BHGOutLen
MCP1Cycl (n.r.) MCP2Cycl BHGTimeout (n.r.)
MCPMPI = FALSE BHGCycl (n.r.)
MCP1Stop MCP2Stop BHGRecGDNo
MCPBusType = b#16#33 BHGRecGBZNo (n.r.)
BHGRecObjNo (n.r.)
MCPSDB210= FALSE BHGSendGDNo (n.r.)
MCPCopyDB77 = FALSE BHGSendGBZNo (n.r.)
BHGSendObjNo (n.r.)
BHGMPI = FALSE
BHGStop
MCP failure normally switches the PLC to the STOP state. If this is undesirable, OB 82, OB
86 can be used to avoid a stop. The basic program has by default the OB 82 and OB 86 call.
FC5 is called in these OBs. This FC5 checks whether the failed slave is an MCP. If this is the
case, no PLC stop is triggered. Setting "MCPxStop" := TRUE causes the basic program to
deactivate the MCP as a slave via SFC 12. If the PLC does not switch to the stop state
following the failure of or a fault on the MCP, an interrupt message will be generated via the
basic program. The interrupt is deleted when the station recovers.

 Loading...
Loading...























