Advanced cardiac measurements and analysis
Vivid S70 / S60 – User Manual 8-49
BC092760-1EN 01
Pediatric Z-score measurements
Several publications exist on the relation between the size / age
/ sex of a patient, and measured values for different pediatric
heart measurements. The most typical approach is to normalize
measured values against body surface area, BSA.
NOTE: When entering the patient’s height and weight in the Patient info
and exam screen (Figure 4-3 on page 4-5), BSA will
automatically be calculated.
When BSA for a patient is known, these relations make it
possible to calculate the expected value, Z0, for a given
measurement. And after performing a measurement, a Z-score
can be calculated, describing the relationship between Z0 and
the observed value:
• The sign of the Z-score shows whether the observed value
is higher or lower than expected. Values above Z0 give
positive Z-scores, values below Z0 give negative Z-scores.
• The magnitude of the Z-score quantifies how many standard
deviations the observed value is away from Z0, and thus
quantifies normality/abnormality.
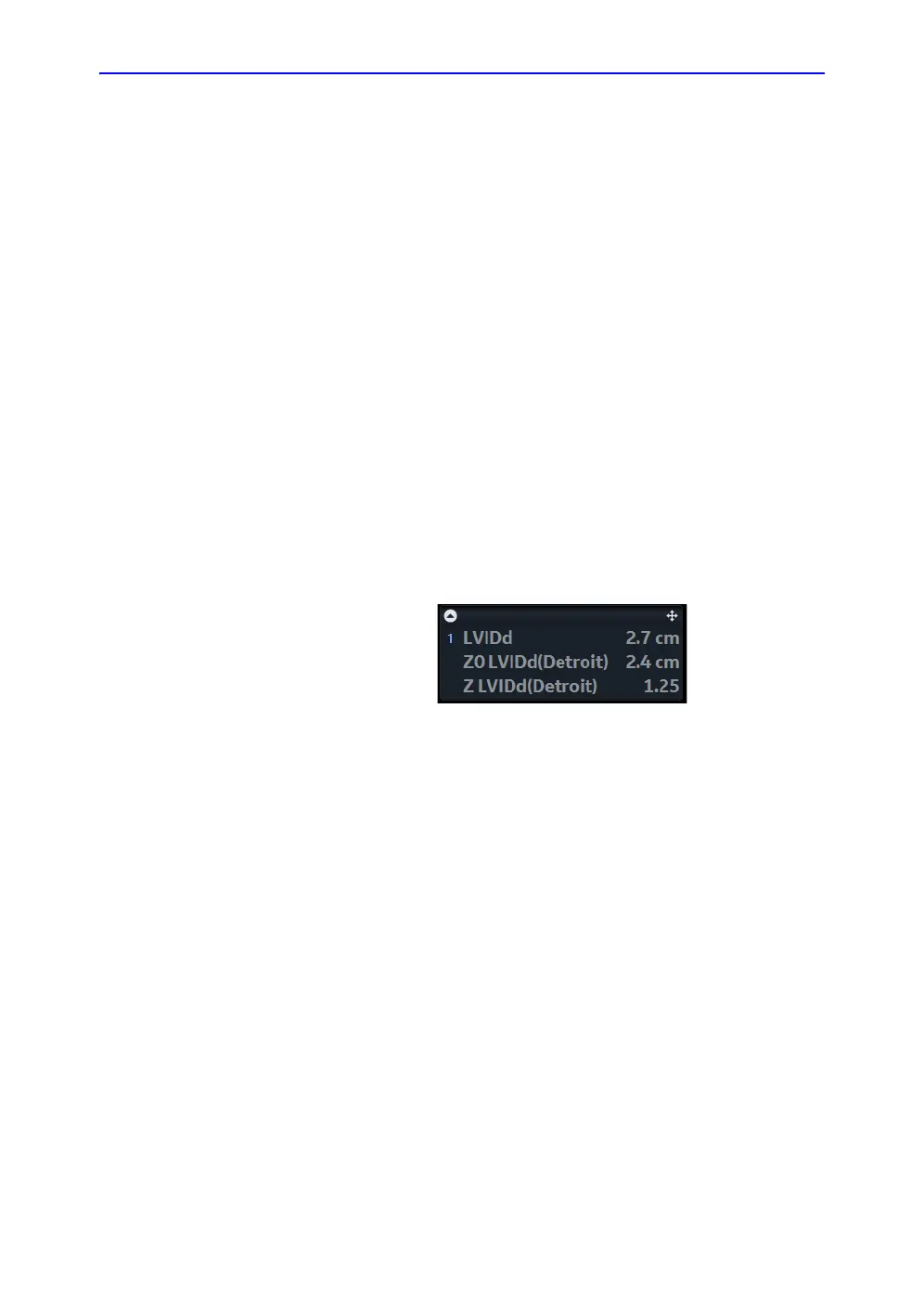
Figure 8-24. Example: Result window after measuring LVIDd.
In tn the example shown in Figure 8-24, the measured value is
higher than the Z0 value predicted by the Detroit publication,
leading to a positive Z-score.
A list of supported publications and related measurements for
Z-score calculations can be found in the reference manual. To
select which of these should be used, enter Config -> Meas/
Text -> Measurement menu. Under Pediatric Heart, press the
Z-score button to display a dialog where it is possible to select
what publication to use. It is also possible to select/deselect
individual Z-score parameters by enabling/disabling them as
described under ‘Configuration of the Measurement menu’ on
page 12-21.
 Loading...
Loading...