v IPINTERFACE_DOES_NOT_EXIST
IP Interface name does not exist
v TARGET_PORT_BAD_ADDRESS
Remote port address is illegal or does not belong to the remote target
v BAD_LOCAL_IP_PORT
An ID of a local IP port must be specified
Deactivating Connectivity to a Remote Target
Deactivates connectivity between a port on the local storage system and a port on
a remote target.
target_connectivity_deactivate target=TargetName
< ipaddress=IPaddress local_ipinterface=IPInterface > |
< fcaddress=wwpn local_port=PortID > [ force_on_olvm_peer=<yes|no> ]
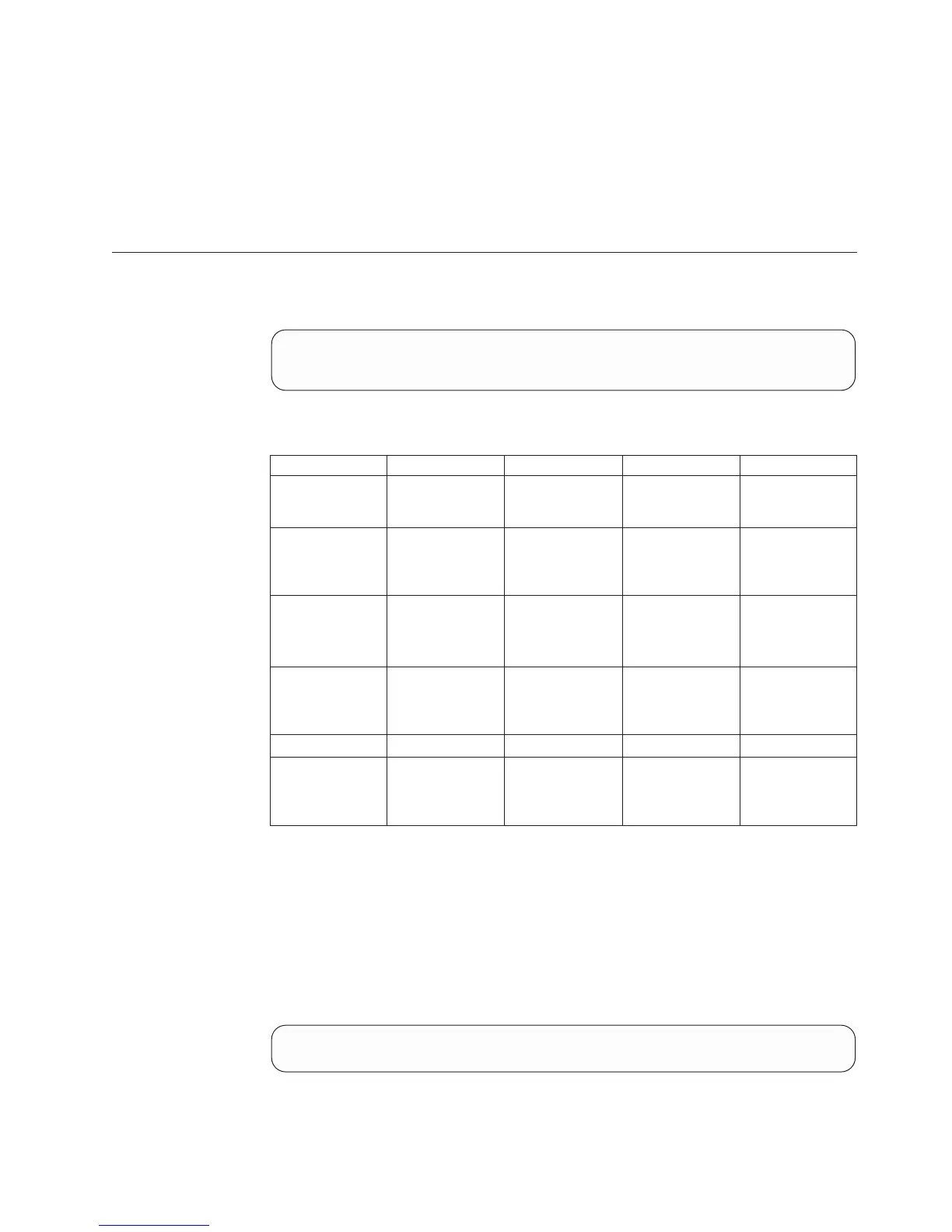
Parameters:
Name Type Description Mandatory Default
target Object name Remote target of
the connectivity
definition.
Y N/A
ipaddress N/A IP address of the
port on the remote
target (iSCSI
targets only).
N N/A
local_
ipinterfac
e
Object name Local IP interface
that is connected
to the remote port
(iSCSI only).
N N/A
fcaddress N/A FC address of the
port on the remote
target (FC targets
only).
N N/A
local_port N/A Port identifier. N N/A
force_on_
olvm_peer
Boolean Informs the system
if the command
should be applied
on an olvm peer.
NNo
This command deactivates connectivity.
Each connectivity definition can be either active or inactive. The system does not
use an inactive connectivity definition. Target Connectivity is active by default.
Connectivity can be reactivated using Activating Connectivity to a Remote Target.
This command has no effect if the connectivity is already deactivated.
Example:
target_connectivity_deactivate
target=Nextra2 local_module=101
Output:
Chapter 10. Remote Target Connectivity 179

 Loading...
Loading...











