BIOS Initialization Intel® Server System S7000FC4UR
Revision 1.0
130
FBDIMM. A degrading DRAM typically generates errors faster over time, which is detected by
the leaky bucket algorithm.
The BIOS initializes the LBC for memory ECC correctable errors to a value of 10. These
counters are on a per-rank basis. See the Glossary section for a definition of the term rank.
14.2.14.4.2 Error Period
The error period, or decay rate, defines the rate at which the leaky bucket counter values are
decremented. The decay period is the time period for the leaky bucket count to decay to 0.
The expected Memory ECC Correctable Error frequency is directly related to the FBDIMM size.
Therefore, BIOS should only report a DIMM Sparing failover if the FBDIMMs on a branch
exceed the sparing threshold of 10 errors within the time period indicated below:
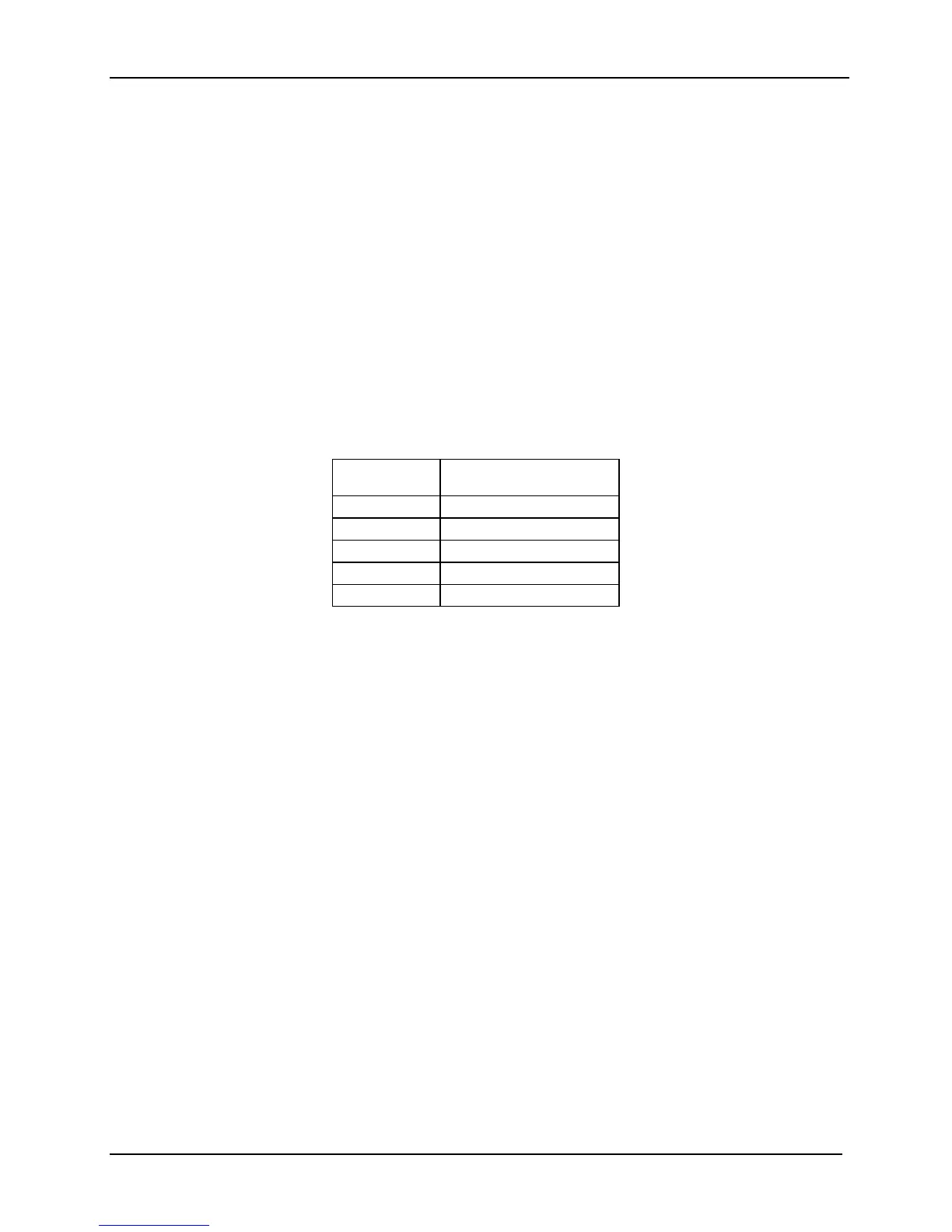
Table 30. Leaky Bucket Counter Error Decay Periods
FBDIMM Size Decay Period
(Approximate Duration)
512 MB 672 hours
1 GB 336 hours
2 GB 168 hours
4 GB 84 hours
8 GB 42 hours
14.2.14.4.3 Recoverable Error Handling in Non-Redundant Mode
In the event of any recoverable memory sub-system error (e.g. Multi-Bit ECC) the chipset issues
an AMB fast reset to all FBDIMMs on the branch. It then retries the memory transaction. If either
the fast reset or the retry transaction fails BIOS logs a SEL entry for Uncorrectable ECC
Memory Error and halts the system with an NMI.
If the fast reset and transaction retry are both successful no SEL entry is logged and the system
continues operation.
See the chipset technical documentation for a detailed description regarding the FBDIMM Error
Recovery Scheme. This documentation includes detailed information for both memory read and
memory write transactions in non-redundant mode.
 Loading...
Loading...