Intel® Server System S7000FC4UR TPS BMC Functional Specifications
Revision 1.0
255
22.2 Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
The BMC works with the ACPI BIOS and with the server board hardware.
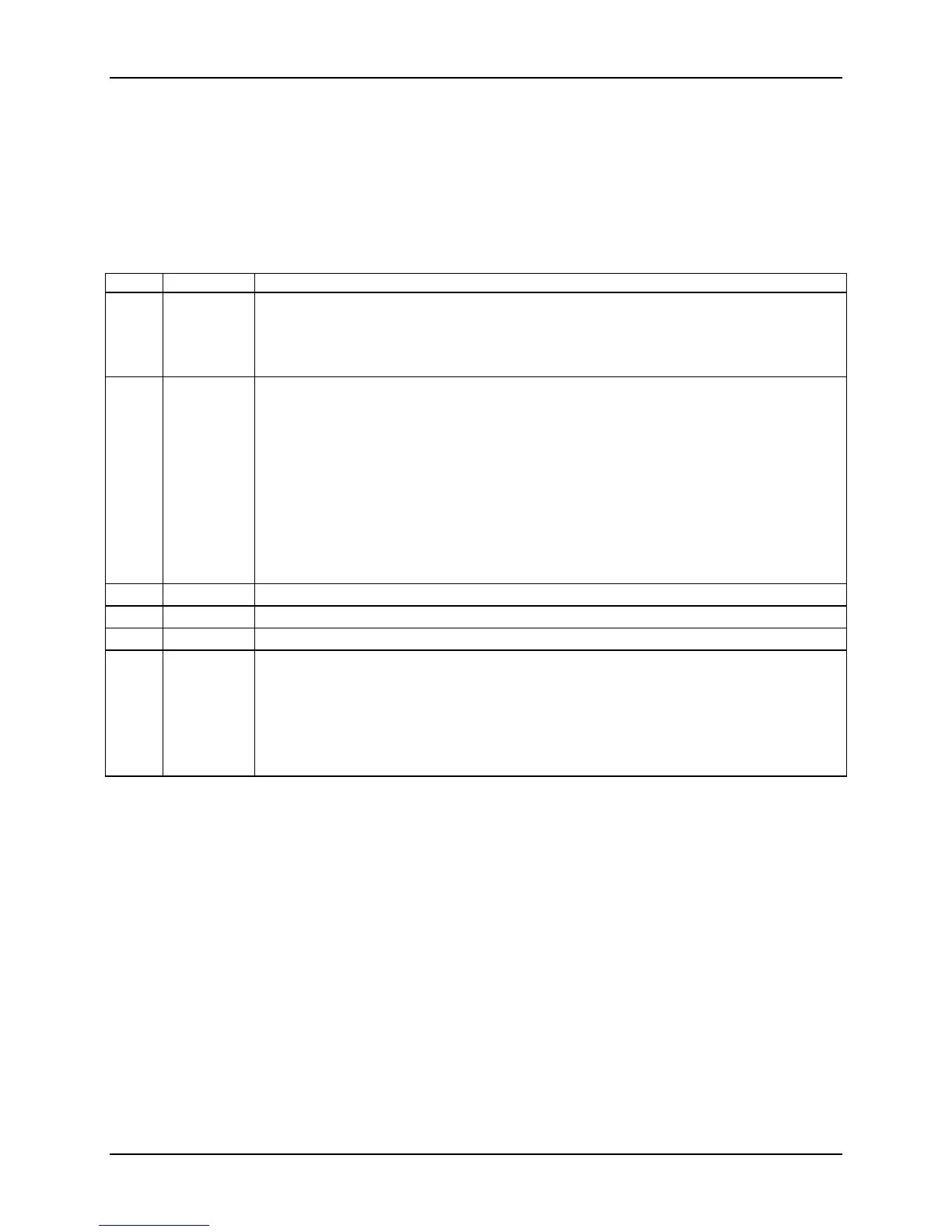
Table 95. ACPI Power States
State Supported Description
S0 Yes Working
The front panel power LED is on (not controlled by the BMC).
The fans spin at the normal speed, as determined by sensor inputs.
Front panel buttons work normally.
S1 Yes Sleeping. Hardware context maintained; equates to processor and chipset clocks stopped.
The front panel power LED blinks at a rate of 1 Hz with a 50% duty cycle (not controlled
by the BMC).
If enabled via the Set ACPI Configuration Mode command, the server board fans are
set to sleep speed as specified in the associated OEM TControl SDR for each fan
domain. Otherwise, fan control is the same as for ACPI S0 state. The DIMM
temperature sensors do not contribute to the fan speed control algorithm.
The watchdog timer is stopped.
The power, reset, front panel NMI, and ID buttons are unprotected.
The BMC detects that the system has exited the ACPI S1 sleep state when it is notified by
the BIOS SMI handler.
S2 No Not supported
S3 No Not supported
S4 No Not supported
S5 Yes Soft off.
The front panel buttons are not locked.
The front panel power LED is off
The fans are stopped.
The power up process goes through the normal boot process.
The power, reset, front panel NMI, and ID buttons are unlocked.
22.2.1 ACPI Power Control
The chipset implements ACPI-compatible power control. Power control requests are routed to
the power push-button input of the chipset, allowing the ACPI-compatible power push-button
logic in the chipset to be used. To support secure mode, the BMC can block the power button
signal.
22.2.2 ACPI State Synchronization
The BIOS keeps the BMC synchronized with the system ACPI state. The BIOS provides the
ACPI state when the server transitions between the power and the sleep states. It uses the
SMM interface to provide the ACPI state.

 Loading...
Loading...