Intel® Server System S7000FC4UR HSC Functional Specifications
Revision 1.0
303
29. HSC Functional Specifications
29.1 Platform Determination
The HSC provides a unique platform identifier through several management interfaces. The
table below shows the identifiers returned by the interfaces on the backplane. The I
2
C
identification is returned as part of the IPMI Get Device ID response. The SAFTE and SES
responses are part of the inquiry data. The firmware BootInfo identifier is embedded in the
firmware image header.
Table 106. Platform Identification
Interface Identifier
I2C/IPMB 0A0Dh
I2C/SAF-TE SCA HSBP M12….
I2C/SES SCA HSBP M12….
Firmware BootInfo SCA HSBP M12
29.1.1 Auto Detection of Platform Type
The HSC firmware is shared by both server systems, but the HSC communication through the
SGPIO differs. The HSC firmware configures to the appropriate bus adapter type by detecting a
unique data pattern on the SLoad line provided by BIOS during the first 20 seconds of POST.
The table shows the unique SGPIO data pattern for the ESB2 configuration. If the pattern is not
seen during the first 20 seconds of POST, the HSC will assume default the SGPIO mode.
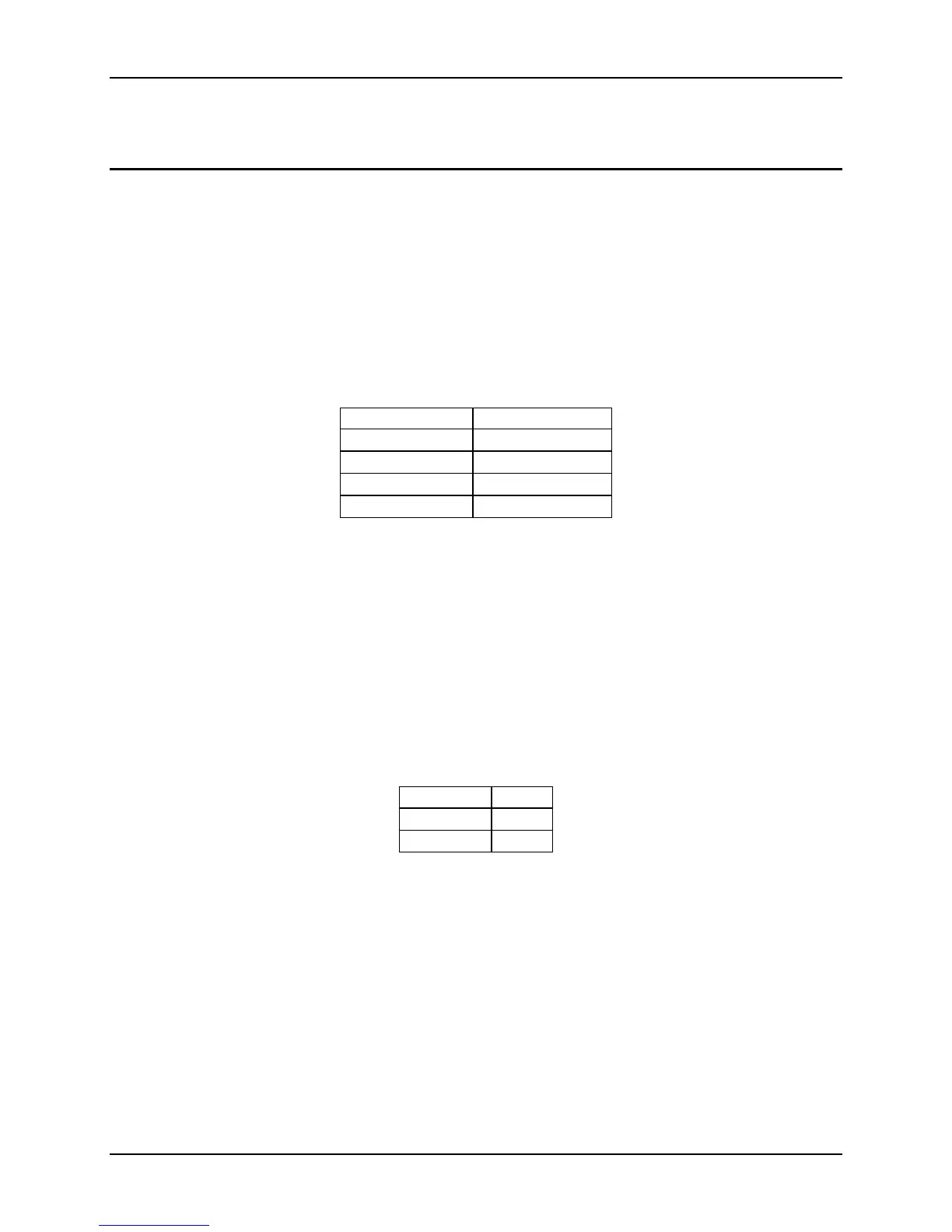
Table 107. Bus Adapter Identification
Signal Value
SLOAD 0x0C
SDATA0_in 0xB6D
29.2 System Initialization
29.2.1 Non-Volatile Setting Initialization
Upon initialization, the HSC reads non-volatile settings from its I
2
C EEPROM. These settings
include initial sensor configuration values and FRU/sensor record integrity headers. If an I
2
C
EEPROM cannot be found, then default values are used.

 Loading...
Loading...