7: Networking
EMG™ Edge Management Gateway User Guide 98
802.1X is an enterprise class access protocol for protecting networks via authentication. There are
three components to 802.1X authentication:
A supplicant, or client, which requires authentication (the EMG).
An authenticator, or access point, which acts as a proxy for the client, and restricts the client's
communication with the authentication server.
An authentication server (usually RADIUS), which decides whether to accept the client's
request for network access.
Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) is used to pass the authentication information between
the supplicant (the EMG) and the authentication server. The EAP type handles and defines the
authentication. The access point acting as authenticator is only a proxy to allow the supplicant and
the authentication server to communicate. The EMG supports the following EAP protocols:
LEAP: Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol (LEAP) uses dynamic WEP keys and
mutual authentication with a modified version of MS-CHAP between the EMG and a RADIUS
server.
EAP-TLS: uses TLS and Public key Infrastructure (PKI) to set up authentication with a
RADIUS server. This method requires the use of a client-side certificate for communicating
with the server.
EAP-TTLS: uses TTLS (Tunneled Transport Layer Security) and server-side certificates to set
up authentication between the EMG and a RADIUS server. The actual authentication is,
however, performed using passwords.
PEAP: Protected EAP uses server-side public key certificates to authenticate the EMG with a
RADIUS server. PEAP authentication creates an encrypted TLS tunnel between the EMG and
the server. The exchange of information is encrypted and stored in the tunnel ensuring the
user credentials are kept secure.
FAST: Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling uses Protected Access Credential (PAC)
for verifying clients on the network. Instead of using a certificate to achieve mutual
authentication, FAST authenticates by means of a PAC (Protected Access Credential) stored
on the EMG, which can be managed dynamically by the authentication server. The PAC can
be provisioned (distributed one time) to the client either manually or automatically. Manual
provisioning is delivery to the client via disk or a secured network distribution method.
Automatic provisioning (used on the EMG) is an in-band distribution.
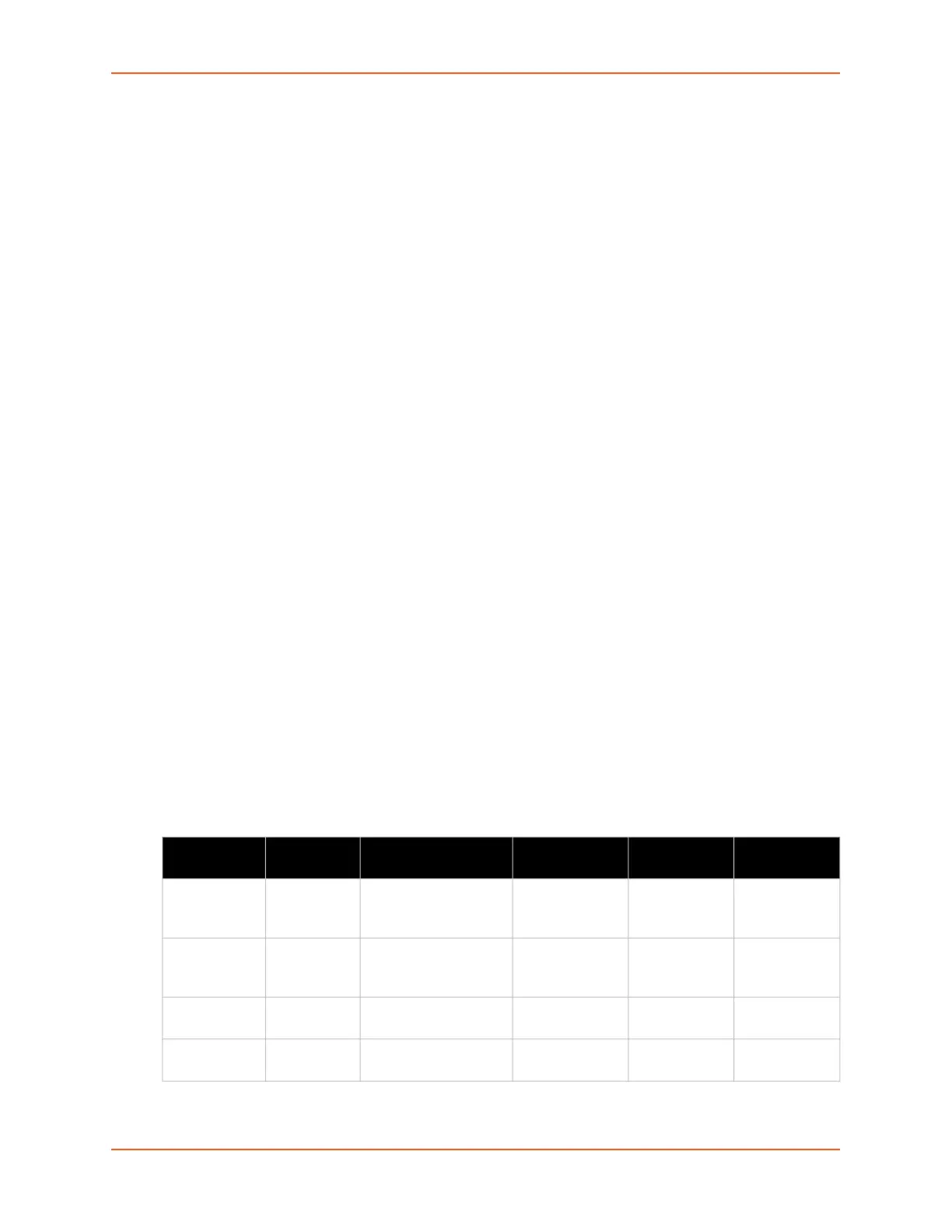
This table summarizes the features of each EAP protocol:
EAP Protocol
Feature
TLS TTLS PEAP FAST LEAP
Client-side
certificate
required
yes no no no (PAC) no
Server-side
certificate
required
yes yes yes no (PAC) no
WEP key
management
yes yes yes yes yes
Rogue AP
detection
no no no yes yes

 Loading...
Loading...