S0605050K
Page 5
Air Conditioner
Return to Master Table of Contents
• Refrigerant (R134a) is compressed to approximately 15 kg/cm
2
(213 psi) within the compressor.
• The compressed refrigerant flows into the condenser at high temperature (approximately 80°C
(176˚F)).
• The refrigerant in the condenser is cooled to approximately 60° by the condenser fan. At this
time the refrigerant changes from the gas to the liquid state, even though the temperature has
only been reduced 20°C (68˚F). (From 80° - 60°C (176˚ - 140˚F)).
• The refrigerant in its liquid form is injected into the evaporator through the expansion valve. At
this time the pressure is reduced by approximately 2 kg/cm
2
(28 psi) and the temperature is also
reduced. As a result, the refrigerant absorbs the heat from the air surrounding the evaporator
creating a cooling effect and changes from the gas to the liquid state.
• The refrigerant once again flows into the compressor in the gaseous state and the process is
repeated.
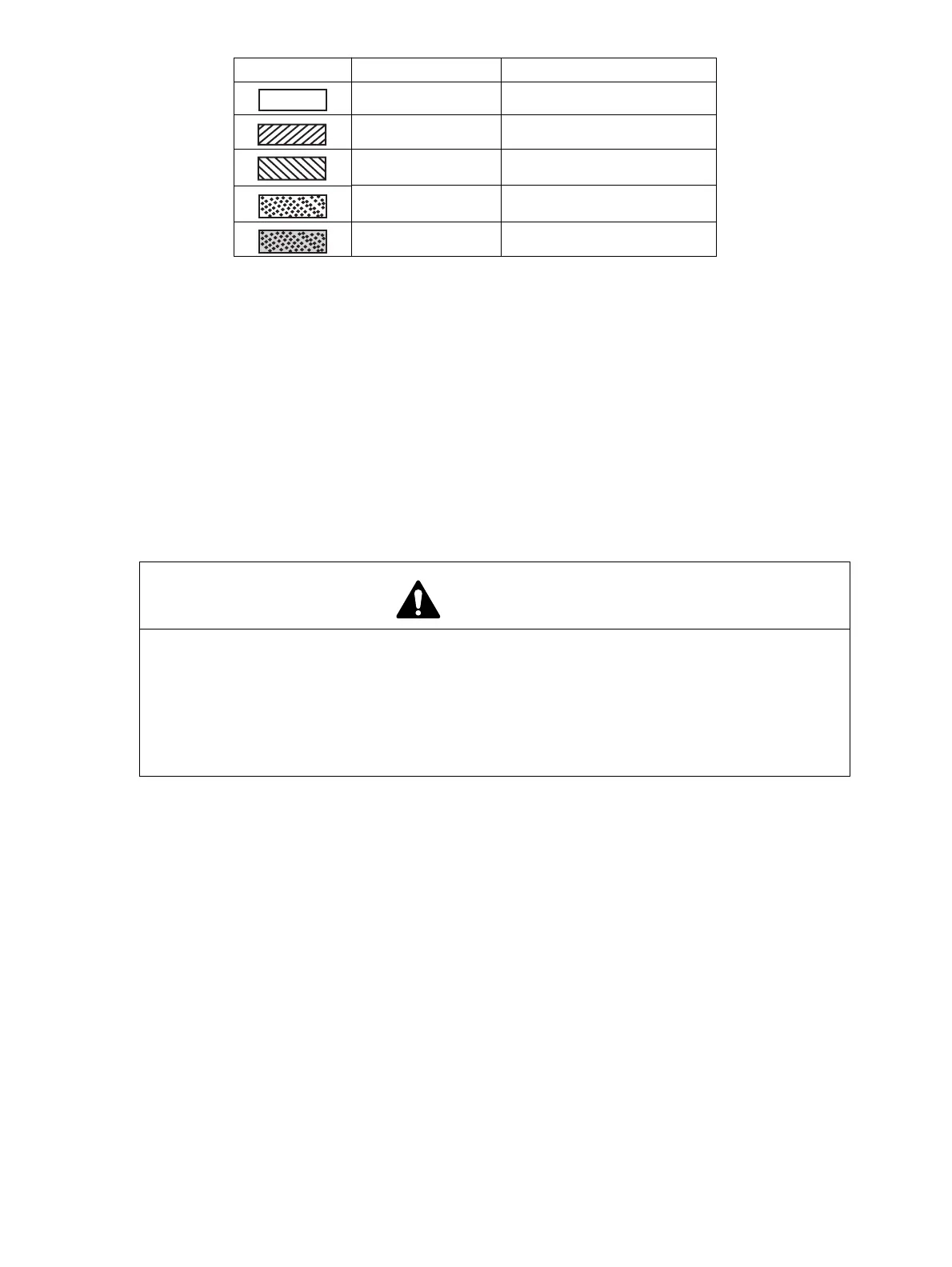
Shading Temperature Refrigerant State
High High Pressure Gas
High High Pressure Liquid
Low Low Pressure Liquid
High High Pressure Gas/Liquid
Low Low Pressure Gas
WARNING!
Refrigerant gas is pressurized and sealed in the air-conditioning system. Special
precautions are required for the proper recharging or release of refrigerant. Release of
refrigerant into the atmosphere is strictly regulated by law. Make sure that you are in
compliance with all mandated federal, state and municipality requirements, before starting
any service or repair of the air conditioner. Refrigerant gas used in the system must meet
or exceed specifications for R134a refrigerant, or any subsequently issued
environmentally-mandated standard.
 Loading...
Loading...