S0705010
Page 4
Cylinders
Return to Master Table of Contents
THEORY OF OPERATION
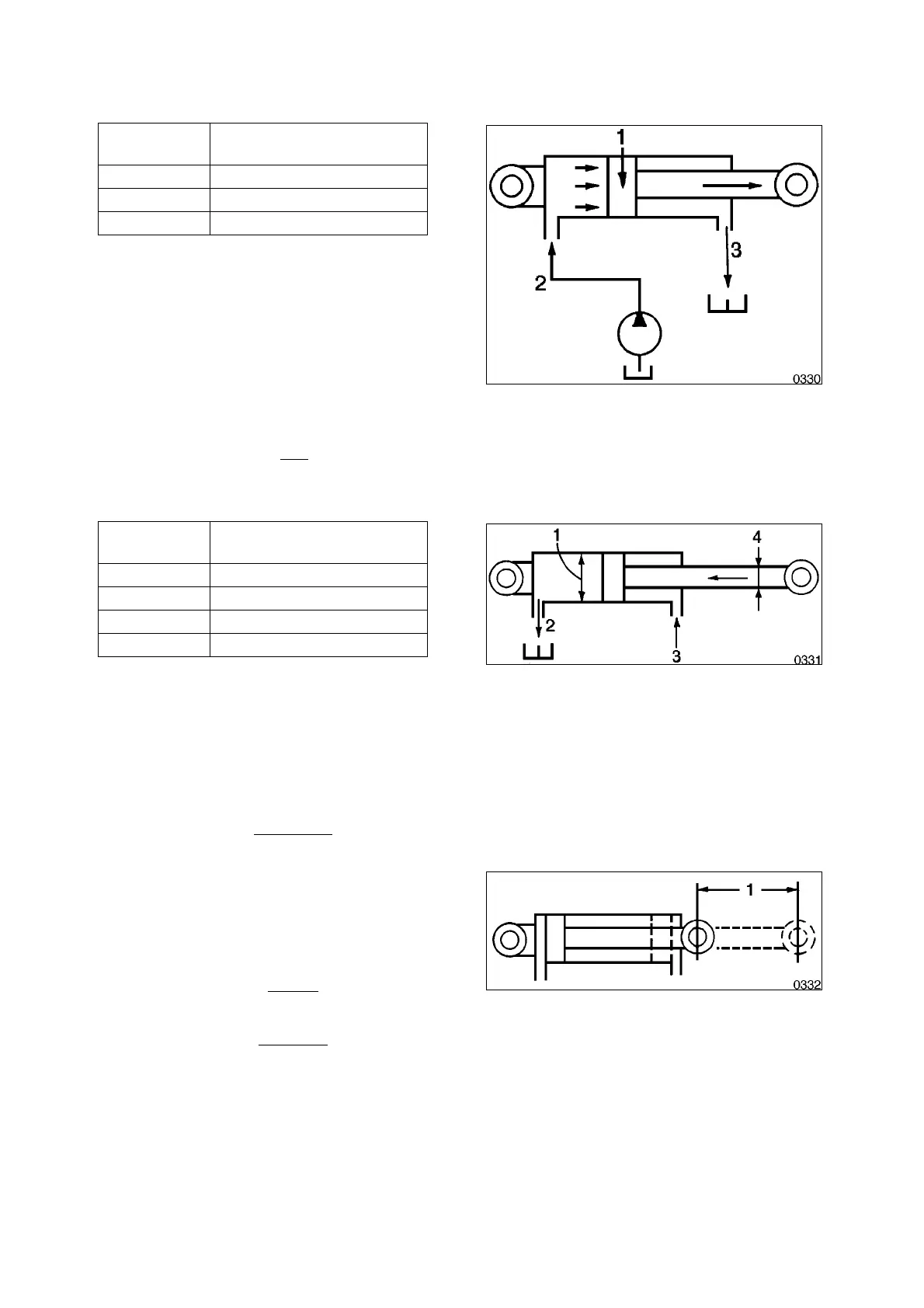
Cylinder piston rods are extended or retracted
by oil flow to back side of cylinder (shown as "oil
path A") or to front of cylinder ("oil path B").
The cylinder rod is extended as oil flow is
pumped through the circuit to the back side of
the piston. The force (F1) of the piston stroke
can be expressed by the formula below, where
P = circuit oil pressure and the inside diameter
of the cylinder is expressed by B (Figure 2).
(P: Pressure,
π
= 3.14, B: Cylinder Inside Diameter)
When the cylinder rod is retracted, oil flow
through the circuit from the pump to the front
side of the cylinder generates a force (F2) that
can be expressed by the formula in which the
diameter of the piston rod is expressed by R,
and the other two terms are the same as in the
preceding expression.
Because the volume of oil needed to lengthen
the cylinder rod (Q1) is greater than the volume
of oil required to retract the cylinder rod, it takes
more time to decrease cylinder stroke length
than it does to lengthen it.
Q
1
> Q
2
Reference
Number
Description
1 Piston
2 Oil Path A
3 Oil Path B
F
1
= P x
π
B
2
4
Reference
Number
Description
1 Cylinder Inside Diameter - B
2 Oil Path A
3 Oil Path B
4 Rod Diameter
F
2
= P x
π
(B
2
-R
2
)
4
Q
1
= S x
π
(B
2
)
4
Q
2
= S x
π
(B
2
-R
2
)
4
Figure 2
Figure 3
Figure 4
 Loading...
Loading...