13.2 SECOND HARMONIC BLOCKING LOGIC (POC INPUT)
V00626
I>Lift 2HI>Lift 2H
Low current (hard-coded)Low current (hard-coded)
IA 2
nd
harm / IA fund
&
&
2ndHarm Thresh2ndHarm Thresh
IA2H StartIA2H Start
IB2H StartIB2H Start
1
& I2H Any StartI2H Any Start
IC2H StartIC2H Start
&
I>Lift 2HI>Lift 2H
&
2ndHarm Thresh2ndHarm Thresh
&
I>Lift 2HI>Lift 2H
&
2ndHarm Thresh2ndHarm Thresh
&
Low current (hard-coded)Low current (hard-coded)
Low current (hard-coded)Low current (hard-coded)
IB 2
nd
harm / IB fund
IC 2
nd
harm / IC fund
IA fundamentalIA fundamental
IA 2ndHarmIA 2ndHarm
IA fundamentalIA fundamental
IB 2ndHarm IB 2ndHarm
IC 2ndHarmIC 2ndHarm
IC 2ndHarmIC 2ndHarm
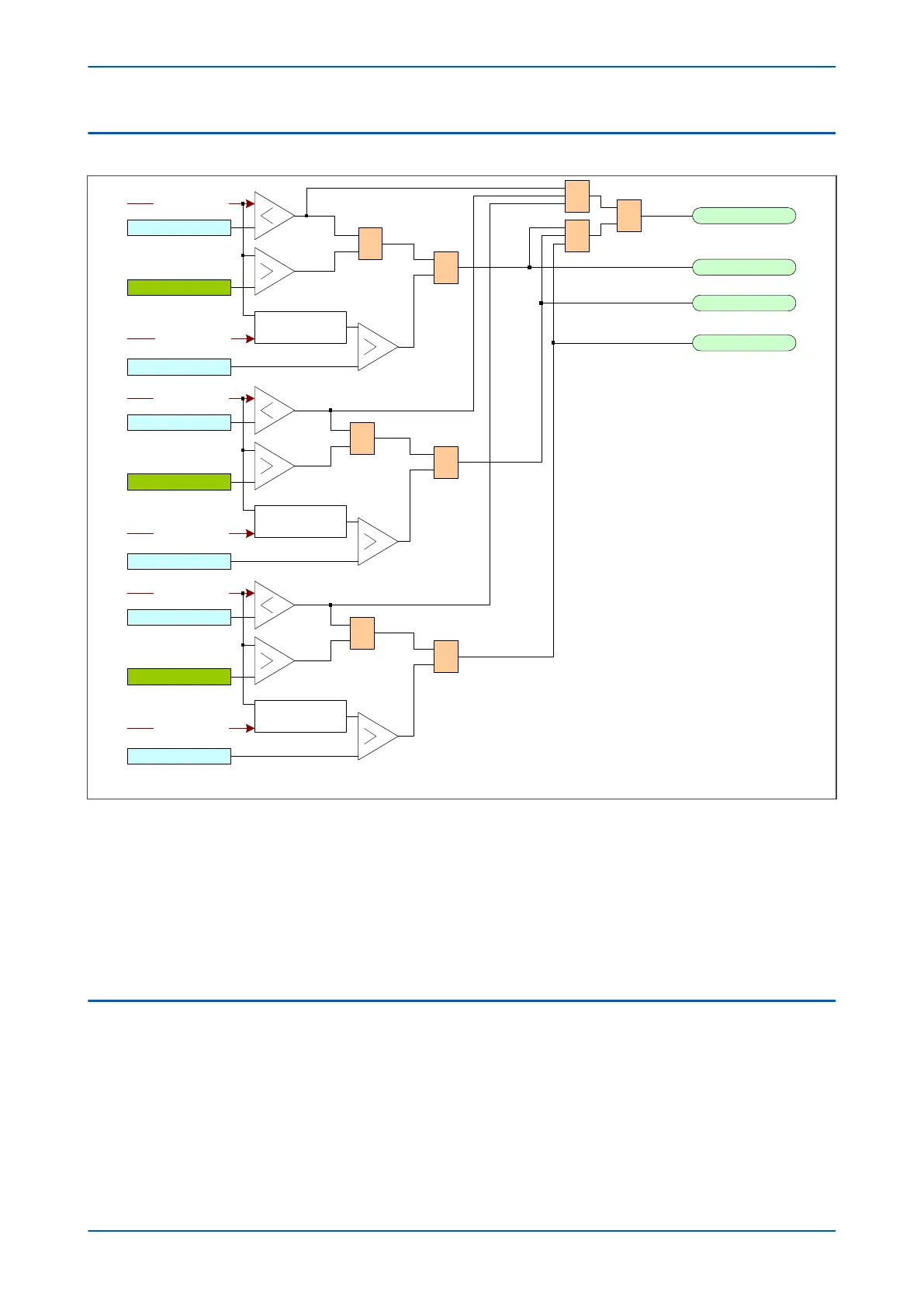
Figure 71: 2nd Harmonic Blocking Logic (POC Input)
The f
unction works by identifying and measuring the inrush currents present in the phase currents at switch on. It
does this by comparing the value of the second harmonic current components to the value of the fundamental
component. If this ratio exceeds the set thresholds, then the blocking signal is generated. The threshold is defined
by the 2ndHarm Thresh setting.
We only want the function to block the protection if the fundamental current component is within the normal
range. If this exceeds the normal range, then this is indicative of a fault, which must be protected. For this reason
there is another settable trigger I>lift 2H, which when exceeded, stops the 2nd harmonic blocking function.
13.3 APPLICATION NOTES
13.3.1 SETTING GUIDELINES
During the energization period, the second harmonic component of the inrush current may vary. The second
harmonic lev
el may be different for each phase, which is why phase segregated blocking is available.
If the setting is too low, the 2nd harmonic blocking may prevent tripping during some internal faults. If the setting
is too high, the blocking may not operate for low levels of inrush current which could result in undesired tripping of
the overcurrent element during the energization period.
P24xM Chapter 6 - Current Protection Functions
P24xM-TM-EN-2.1 147

 Loading...
Loading...











