Lower slope
Operate region
Bias current
Differential current
V00677
Restraint region
Higher
slope
Minimum operating current
First knee point Second knee point
Figure 85: Three-slope REF bias characteristic
The flat ar
ea of the characteristic is the minimum differential current required to cause a trip (operate current) at
low bias currents. From the first kneepoint onwards, the operate current increases linearly with bias current, as
shown by the lower slope on the characteristic. This lower slope provides sensitivity for internal faults. From the
second knee point onwards, the operate current further increases linearly with bias current, but at a higher rate.
The second slope provides stability under through fault conditions.
Note:
In Restricted Earth Fault applications, Bias Current Compensation is also known as Low Impedance REF.
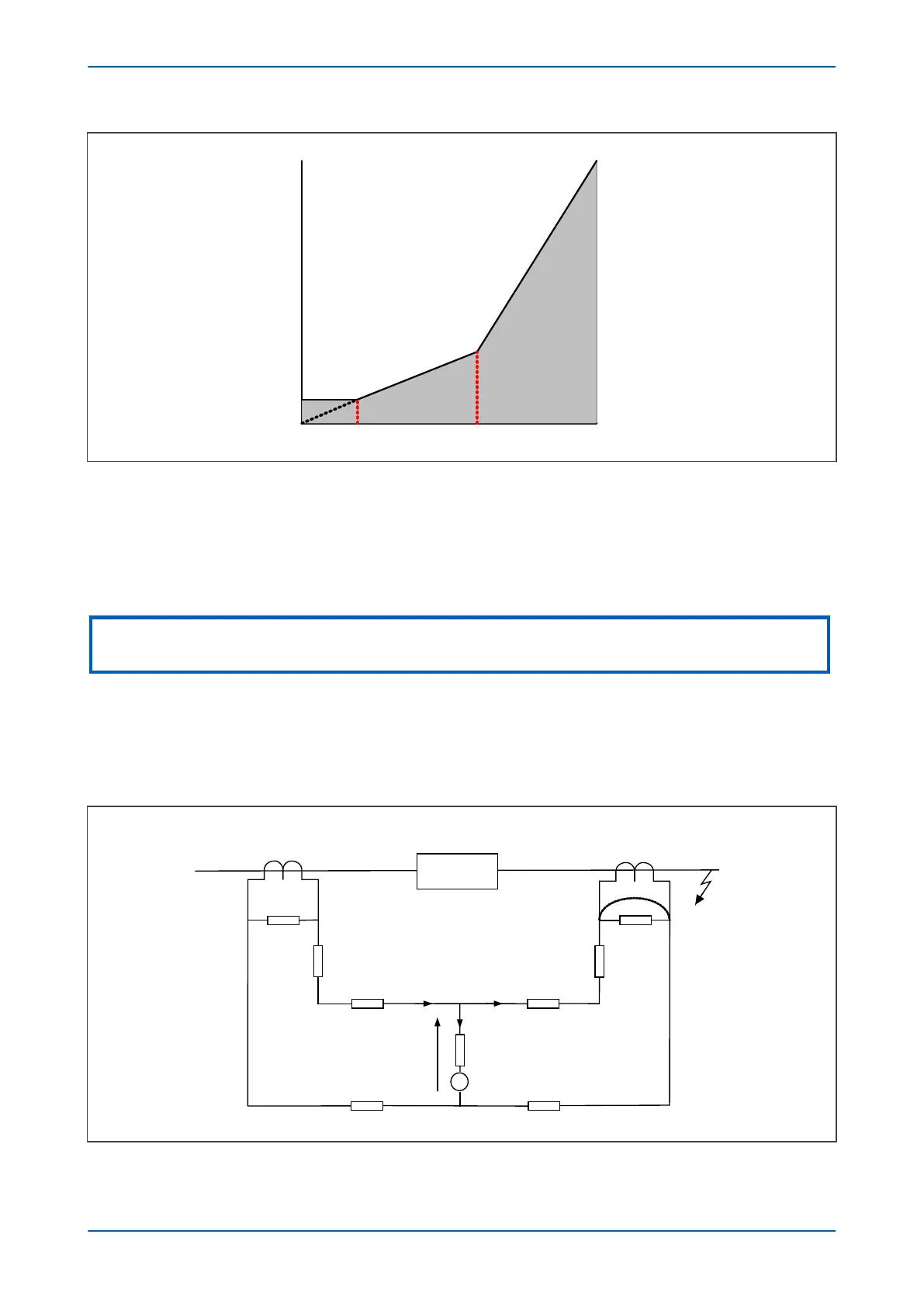
2.1.2 HIGH IMPEDANCE REF PRINCIPLE
This scheme is very sensitive and can protect against low levels of fault current, typical of winding faults.
High Impedance REF pr
otection is based on the differential principle. It works on the circulating current principle as
shown in the following diagram:
V00671
R
Z
m1
R
CT1
R
L1
Z
m2
V
s
R
CT2
R
L3
I
F
I
S
R
L4
R
L2
Healthy CT
Saturated CT
A-G
Protected
circuit
I
R
ST
I = I
s
+ I
F
Figure 86: High Impedance REF principle
Chapter 7 - Restricted Earth Fault Protection P24xM
170 P24xM-TM-EN-2.1

 Loading...
Loading...











