JVL Industri Elektronik A/S - User Manual - Integrated Stepper Motors MIS23x, 34x, 43x 255
10.7 More details of CANopen Theory
Reset Node:
This is an instruction for transition from the Operational, Pre-Operational or Stopped
states to Initialization. After the Reset Node instruction, all objects (1000h-9FFFh) are re
-
set to the Voltage On stage.
Reset Communication:
This is an instruction for transition from Operational or Stopped to Initialization. After
the Reset Communication instruction, all communication objects (1000h-1FFFh) are re
-
set to the initial state.
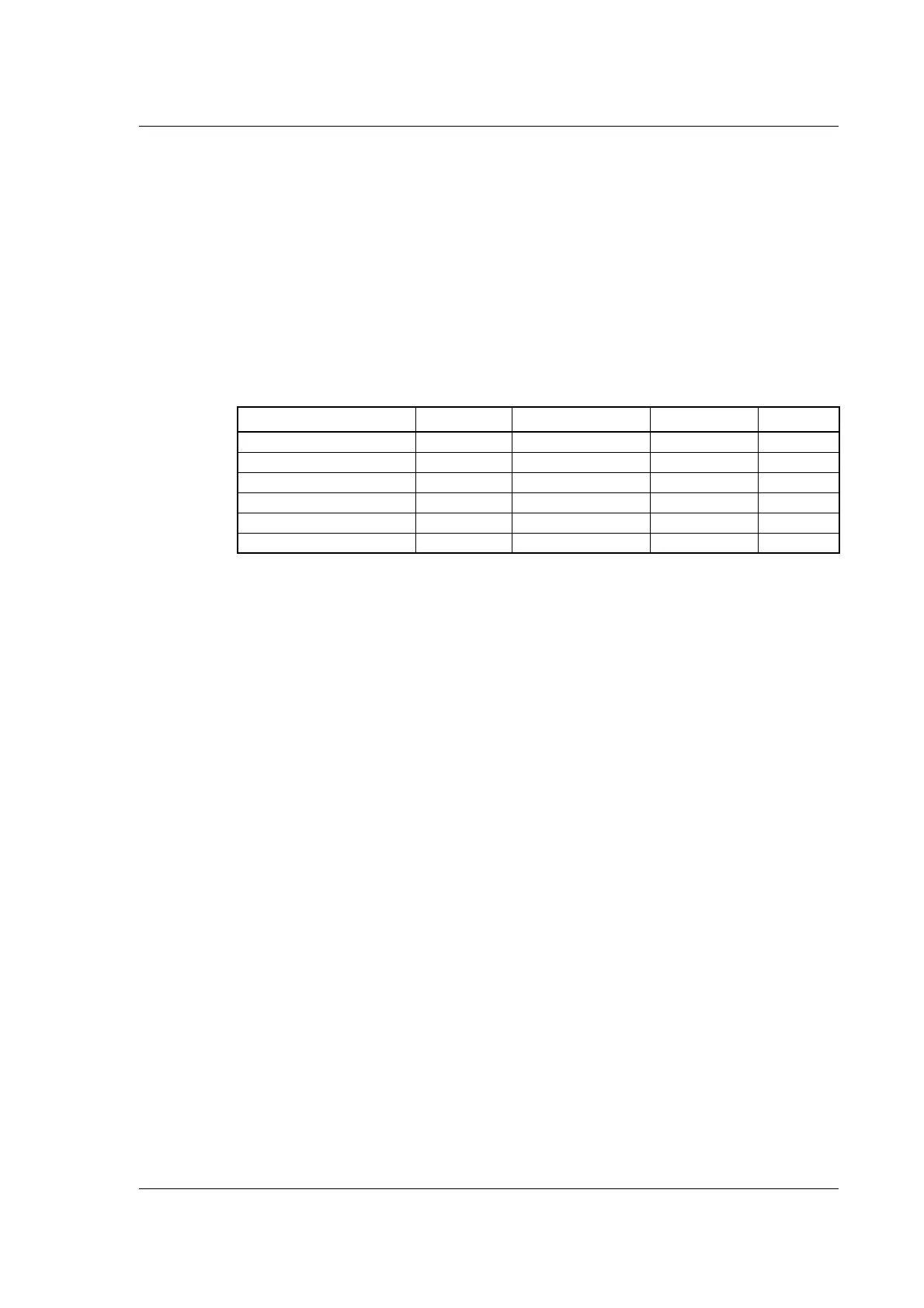
In the various communication states, nodes can only be accessed via CANopen using spe-
cific communication services. Further, the nodes in the various states only send specific
telegrams. This is clearly shown in the following table:
10.7.7 Error Control Services
Two possibilities exist for performing Error Control:
- Node Guarding/Life Guarding
- Heartbeat
Node Guarding/Life Guarding
With Node Guarding, the CANopen master sends each slave an RTR telegram (Remote
Transmit request) with the COB-ID 1792 (700h) + node-ID.
Using the same COB-ID, the slave responds with its communications state, i.e. either
Pre-Operational, Operational or stopped.
The CANopen slave also monitors the incoming RTR telegram from the master.
The cycle of the incoming RTR telegrams is set using the Guard Time Object.
The number of RTR telegrams which can fail (at a maximum) before the slave initiates a
Life Guarding event is defined using the Life time factor object.
The Node Life Time is calculated from the product of the Guard Time and Life Time Fac-
tor. This is the maximum time that the slave waits for an RTR telegram.
The figure below shows a Node Guarding/Life Guarding protocol.
Initializing Pre-Operational Operational Stopped
PDO X
SDO X X
Synchronization Object X X
Emergency Object X X
Boot-Up Object X
Network Management object X X X

 Loading...
Loading...