MAX32660 User Guide
Maxim Integrated Page 142 of 195
Note that this arbitration scheme works with any number of bus masters: if more than two masters begin transmitting
simultaneously, the arbitration continues as each master cedes the bus until only one master remains transmitting. Data is
not corrupted because as soon as each master realizes it has lost arbitration it stops transmitting, leaving the data on SDA
intact.
Once a master has lost arbitration it stops generating SCL, sets I2Cn_INTFL0.areri, and clears I2Cn_MSTR_MODE.start,
I2Cn_MSTR_MODE.restart, and I2Cn_MSTR_MODE.stop to 0.
The I
2
C master peripheral is compliant with the bus arbitration requirements of the I
2
C specification. I
2
C bus arbitration is
handled by the peripheral hardware and requires no additional configuration.
12.12 SCL Clock Generation for Standard, Fast and Fast-Plus Modes
The master generates the I
2
C clock on the SCL line. Application code must configure the I2Cn_CLKHI and I2Cn_CLKLO
registers for the desired I
2
C operating frequency.
The I
2
C peripheral clock is supplied directly by the system peripheral clock,
.
The SCL high time is configured in the I
2
C Clock High Time register field I2Cn_CLKHI.scl_hi. The SCL low time is configured in
the I
2
C Clock Low Time register field I2Cn_CLKLO.scl_lo. Each of these fields is 8-bits.
Equation 12-5: I
2
C Clock High Time Calculation
Equation 12-6: I
2
C Clock Low Time Calculation
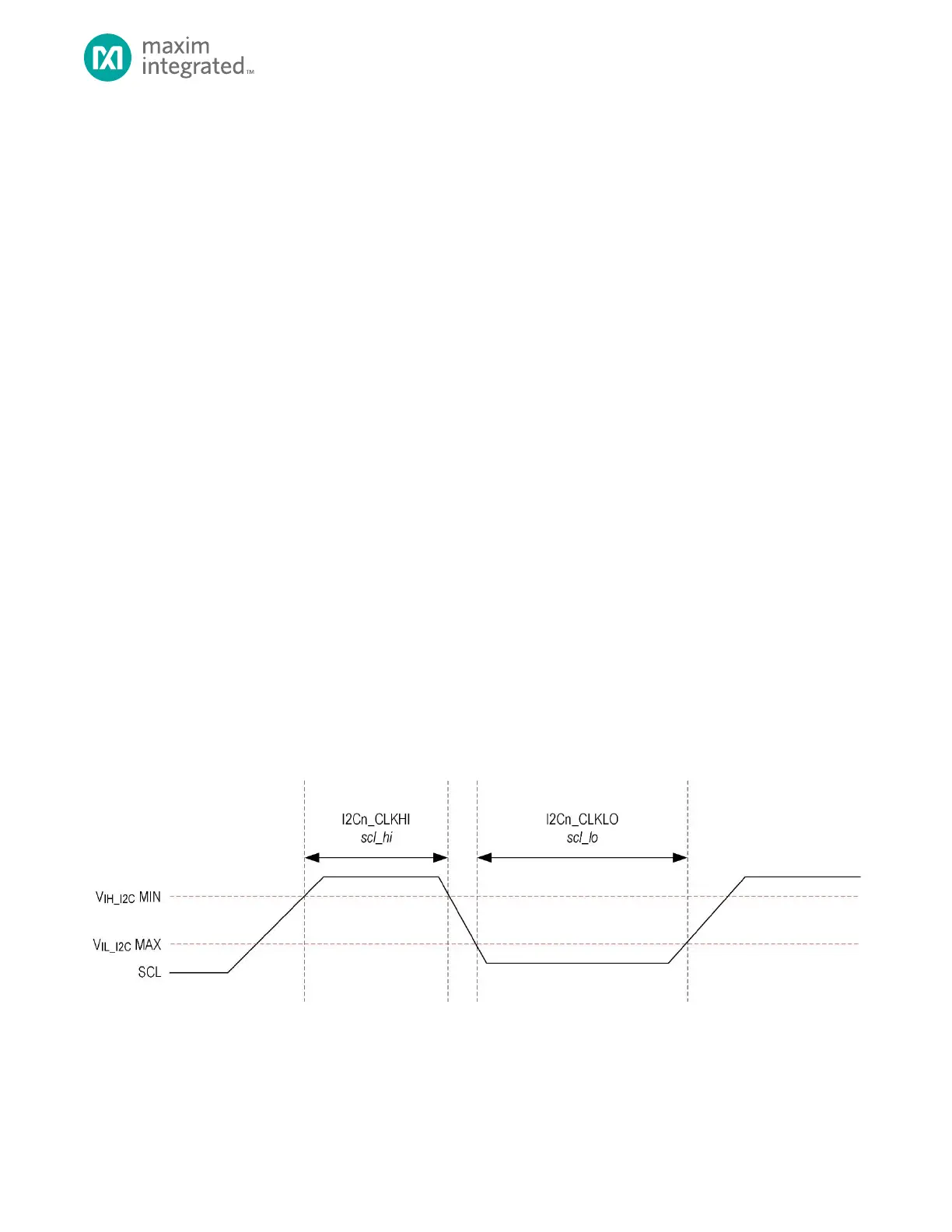
Figure 12-4 shows the association between the SCL clock low and high times for Standard, Fast and Fast-Plus I
2
C
frequencies.
Figure 12-4: I
2
C Clock Period
During synchronization, external masters or external slaves may be driving SCL simultaneously. This affects the SCL duty
cycle. By monitoring SCL, the controller can determine whether an external master or slave is holding SCL low. In either
case, the controller waits until SCL is high before starting to count the number of SCL high cycles. Similarly, if an external
master pulls SCL low before the controller has finished counting SCL high cycles, then the controller starts counting SCL low
cycles and releases SCL once the time period, I2Cn_CLKLO.scl_lo, has expired.
 Loading...
Loading...