MAX32660 User Guide
Maxim Integrated Page 73 of 195
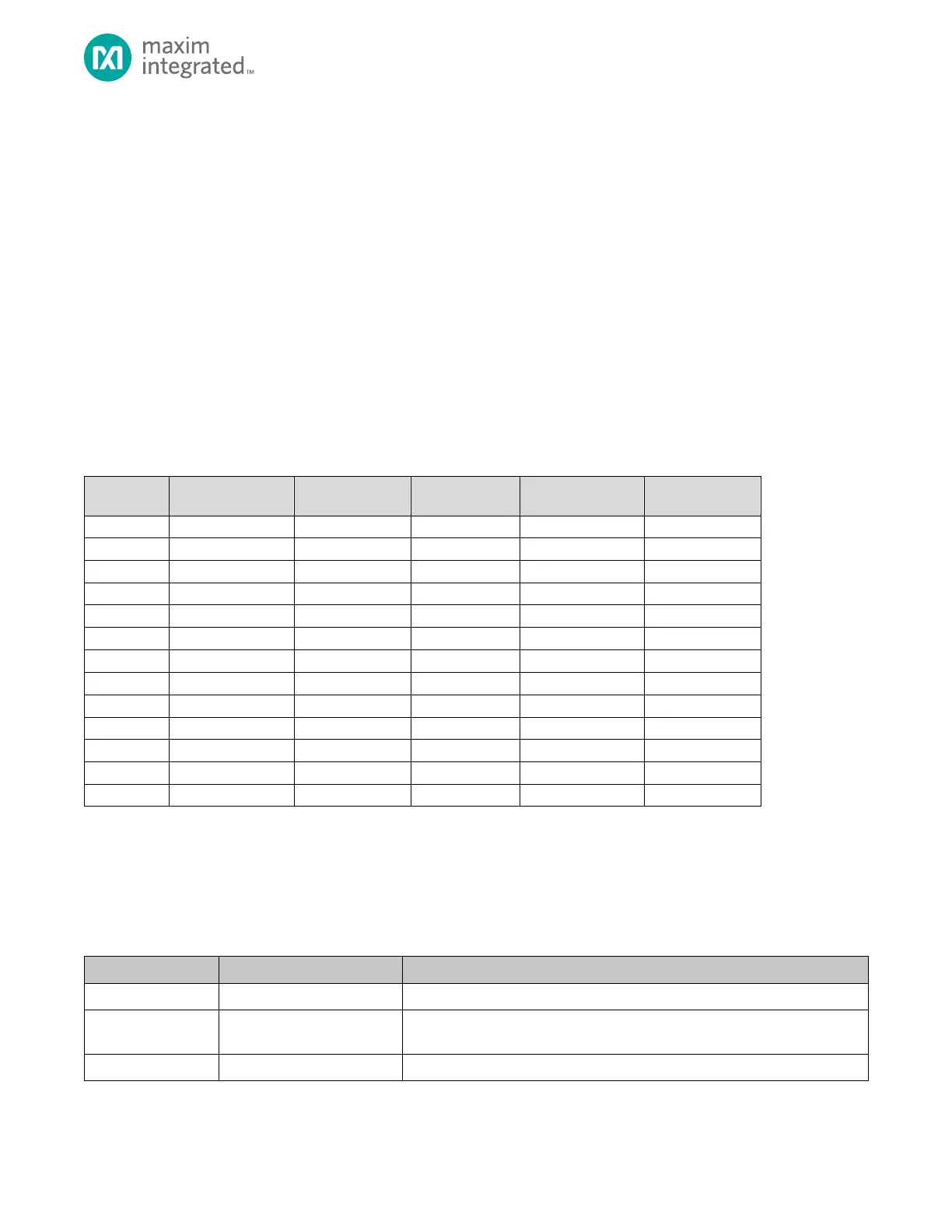
7.3 DMA Source and Destination Addressing
For memory addresses, the DMAn_SRC and DMAn_DST registers are used to program the addresses of the source and
destination. For peripherals, however, the address is fixed based on the DMAn_CFG.reqsel value set.
Table 7-3 shows how the source address, destination address and the address increment controls are constructed based on
the DMAn_CFG.reqsel bitTable 7-3 shows the values for the DMAn_CFG.reqsel bit.
DMAn_CFG.srcinc and the DMAn_CFG.dstinc bits, respectively. If there is a 0 in the column, then the bit is forced to 0. For
peripherals, a value of 0 for the DMAn_CFG.srcinc or DMAn_CFG.dstinc generally indicates the source or destination
DMAn_CFG.reqsel = 0x2, then the transfer is an
SPI1 RX (receive). In this case, the DMAn_CFG.srcinc is fixed to 0 because the source for the SPI1 RX is the SPI1 receive FIFO
address. However, the destination address is programmable, allowing the data from the SPI1 receive FIFO to be written to a
programmable address in memory. The destination starting address is set using the DMAn_DST register and is incremented
automatically if DMAn_CFG.dstinc is set to 1.
Table 7-3: Source and Destination Address Definition
7.4 Data Movement from Source to DMA FIFO
Table 7-4 shows the register and bit fields used to control the movement of data into DMA FIFO. The source is a peripheral
or memory.
Table 7-4: Data movement from source to DMA FIFO

 Loading...
Loading...