50
Setting Measurement Conditions (basic settings)
For setting range and accuracy
Open circuit voltage (V) mode and Constant voltage (CV) mode setting
Normal operation
When low-Z high-precision mode
(p. 55) is on
Open circuit voltage setting range 0.010 V to 5.000 V 0.010 V to 1.000 V
Open circuit voltage accuracy
1 MHz or less: ±10% rdg. ±10 mV,
1.0001 MHz or more: ±20% rdg. ±10 mV
Output impedance 100
Ω
±10
Ω
10
Ω
±2
Ω
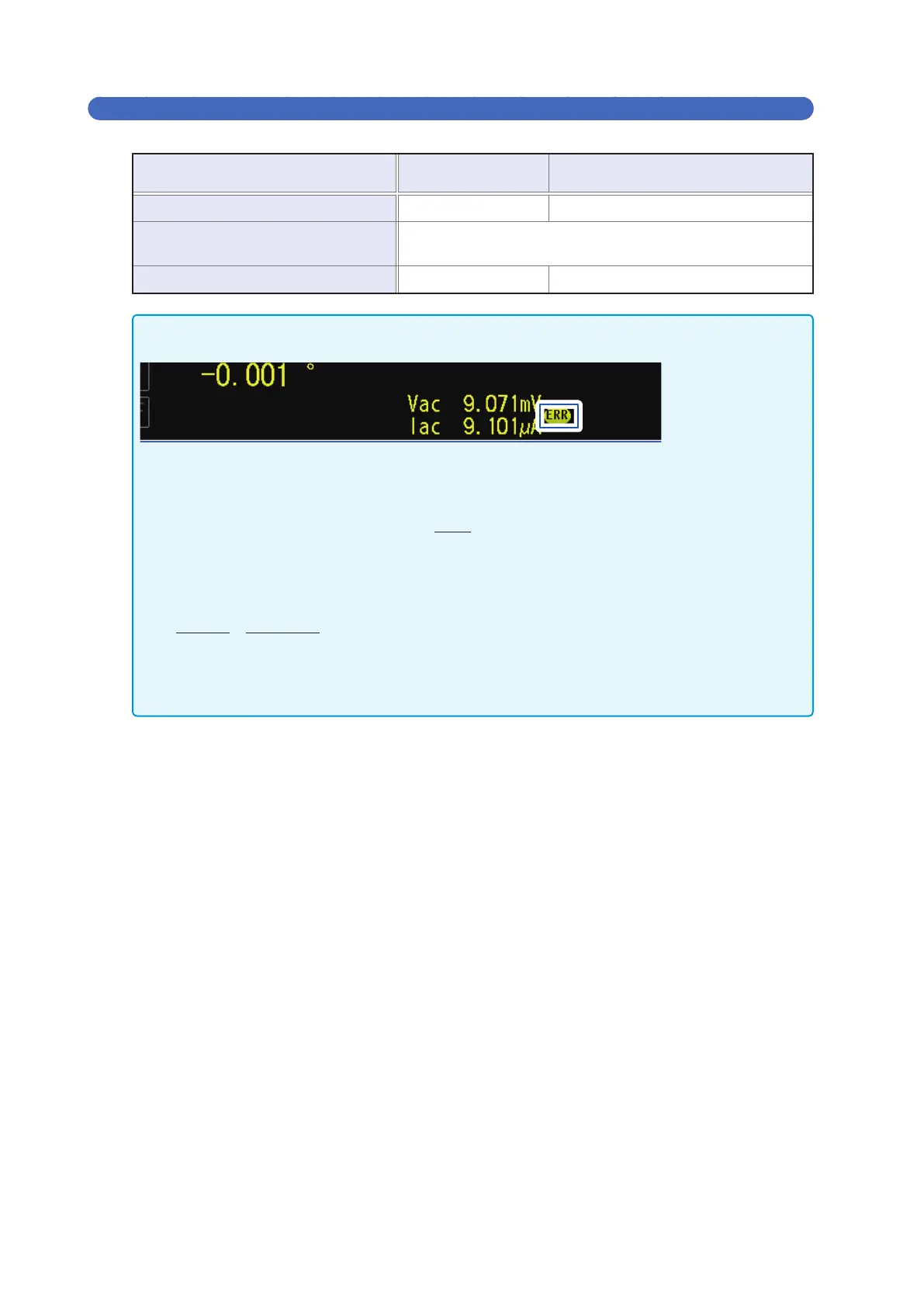
For some samples, you may not be able to perform constant-voltage measurement (measurement in con-
stant-voltage mode) In this situation, the following error will be displayed:
Constant voltage measurement will not be performed. Change the constant-voltage value to a value that is
less than or equal to the value displayed for Vac.
(Example: Constant-voltage measurable range when measuring a C value of 1 µF at 10 kHz)
The sample impedance
Zm
is as follows:
Zm
=
Rm
+
jXm
=
0
[
Ω
] -
j15.9
[
Ω
]
Xm =
-1
(2πfC
)
The impedance
Zm’
as seen from the instrument’s voltage generator is as follows:
Zm’
=
Ro
+
Zm
=
100
[
Ω
] -
j15.9
[
Ω
] Ro:
Output resistance (100 [
Ω
])
Accordingly, the voltage
Vm
across both leads of the sample is as follows:
Vm =
|
Zm
|
×Vo
|
Zm’
|
=
15.9
[
Ω
]×
Vo
101.3
[
Ω
]
V
o
:
generator output
Since the instrument’s voltage generator output range is 10 [mV] to 5 [V] as per the above table, the con-
stant-voltage measurable range is
Vm
= 1.6 [mV] to 0.78 [V] based on the above formula.
When low-Z high-precision mode is enabled, the output resistance
Ro
will be 10 [
Ω
].
 Loading...
Loading...