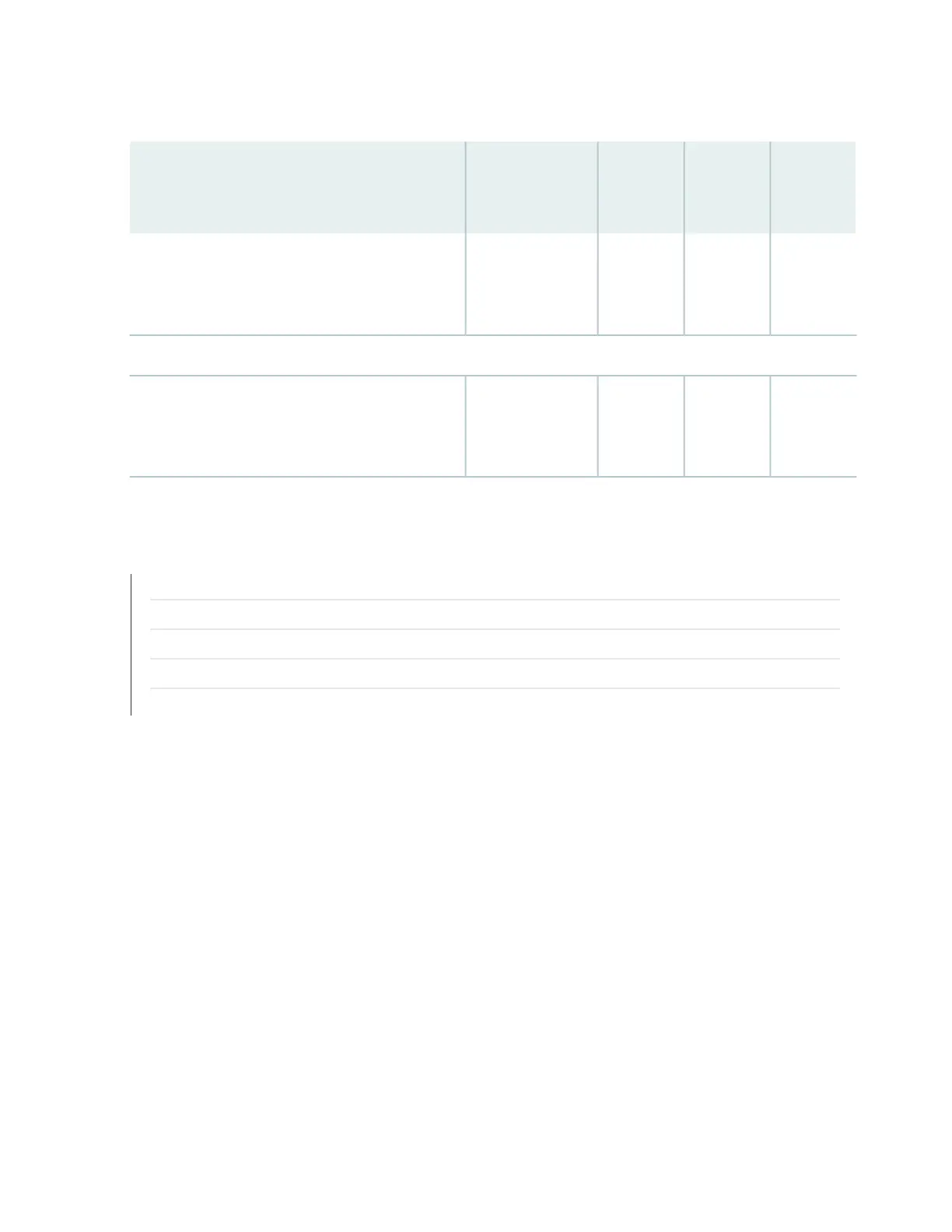
Table 44: DPCs Supported in MX240, MX480, and MX960 Routers (continued)
First
Junos OS
Release
Maximum
Throughput
per DPCPorts
DPC Model
NumberDPC Name
9.140 Gbps40DPCE-X-40GE-TX
EOL (see
PSN-2011-07-315.)
Tri-Rate Enhanced Ethernet Services DPC
Services
9.3–2 (Not
supported)
MS-DPC
EOL (see
PSN-TSB16812)
Multiservices DPC
SEE ALSO
Protocols and Applications Supported by DPCs and Enhanced DPCs (DPC and DPCE-R)
Protocols and Applications Supported by Enhanced Ethernet Services DPCs (DPCE-X)
Protocols and Applications Supported by Enhanced Queuing IP Services DPCs (DPCE-R-Q)
Protocols and Applications Supported by Enhanced Queuing Ethernet Services DPCs (DPCE-X-Q)
Protocols and Applications Supported by the Multiservices DPC (MS-DPC)
MX960 DPC Port and Interface Numbering
Each port on a DPC corresponds to a unique interface name in the CLI.
In the syntax of an interface name, a hyphen (-) separates the media type from the DPC number (represented
as an FPC in the CLI). The DPC slot number corresponds to the first number in the interface. The second
number in the interface corresponds to the logical PIC number. The last number in the interface matches
the port number on the DPC. Slashes (/) separate the DPC number from the logical PIC number and port
number.
type-fpc/pic/port
•
type—Media type, which identifies the network device. For example:
•
ge—Gigabit Ethernet interface
•
so—SONET/SDH interface
•
xe—10-Gigabit Ethernet interface
69
 Loading...
Loading...