R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT System Overview
Measured Quantities
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 46
Z-Parameters
The Z-parameters describe the impedances of a DUT with open output ports (I = 0). The analyzer
provides the full set of Z-parameters including the transfer impedances (i.e. the complete nxn Z-matrix for
an n port DUT).
This means that Z-parameters can be used as an alternative to S-parameters (or Y-parameters) in order
to completely characterize a linear n-port network.
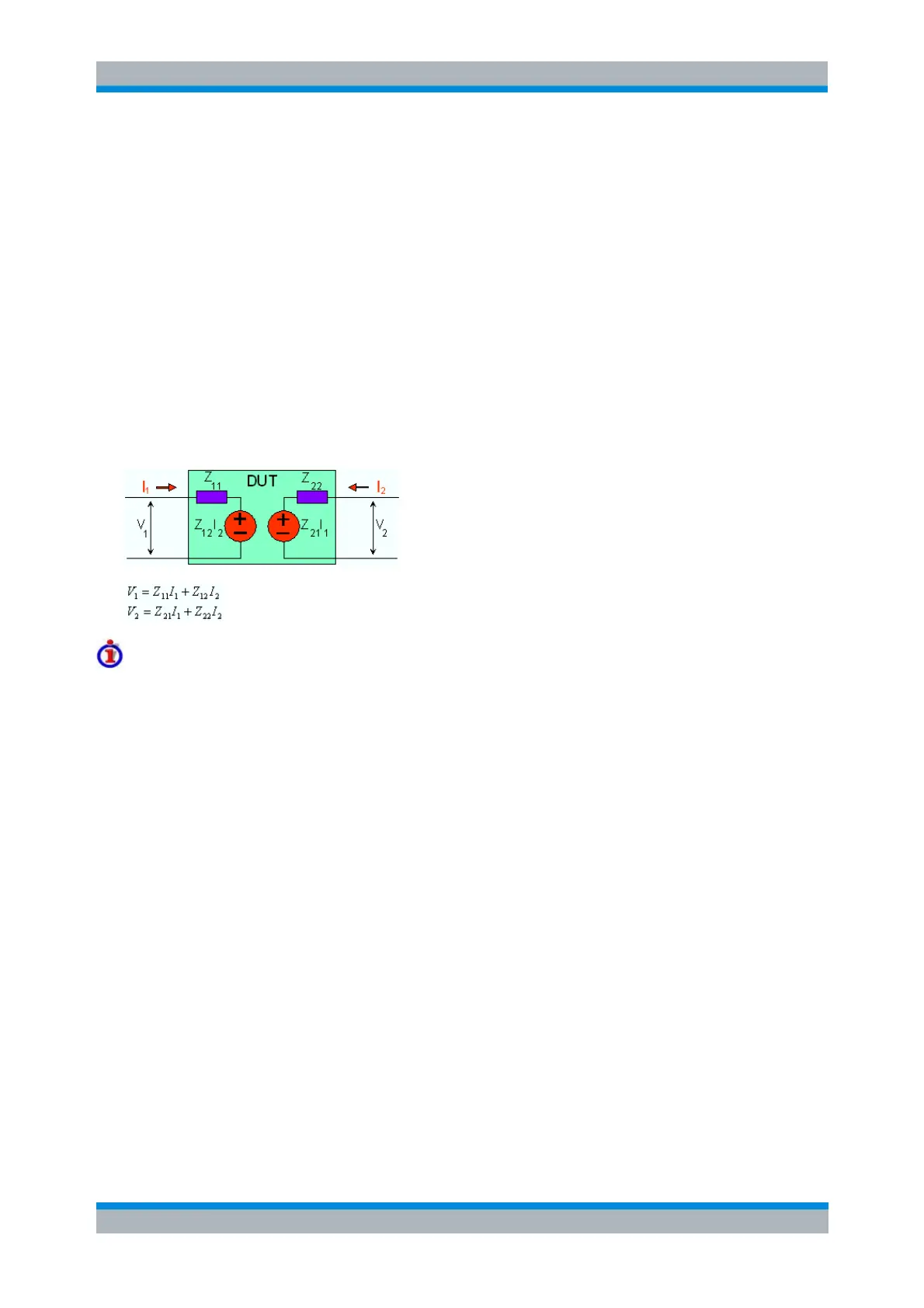
2-Port Z-Parameters
In analogy to S-parameters, Z-parameters are expressed as Z
ij
, where where i denotes the measured and
j the stimulated port.
The Z-parameters for a two-port are based on a circuit model that can be expressed with two linear
equations:
Meaning of Z-parameters
The four 2-port open-circuit Z-parameters can be interpreted as follows:
Z
11
is the input impedance, defined as the ratio of the voltage V
1
to the current I
1
, measured at
port 1 (forward measurement with open output, I
2
= 0).
Z
21
is the forward transfer impedance, defined as the ratio of the voltage V
2
to the current I
1
(forward measurement with open output, I
2
= 0).
Z
12
is the reverse transfer impedance, defined as the ratio of the voltage V
1
to the current I
2
(reverse measurement with open input, I
1
= 0).
Z
22
is the output impedance, defined as the ratio of the voltage V
2
to the current I
2
, measured at
port 2 (reverse measurement with open input, I
1
= 0).
Z-parameters can be easily extended to describe circuits with more than two ports or several modes of
propagation.
Admittance Parameters
An admittance is the complex ratio between a current and a voltage. The analyzer provides two
independent sets of admittance parameters:
Converted admittances (each admittance parameter is obtained from a single S-parameter)
Y-parameters (complete description of the n-port DUT)
 Loading...
Loading...