R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT System Overview
Measured Quantities
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 45
Impedance Parameters
An impedance is the complex ratio between a voltage and a current. The analyzer provides two
independent sets of impedance parameters:
Converted impedances (each impedance parameter is obtained from a single S-parameter)
Z-parameters (complete description of the n-port DUT)
Converted Impedances
The converted impedance parameters describe the input impedances of a DUT with fully matched
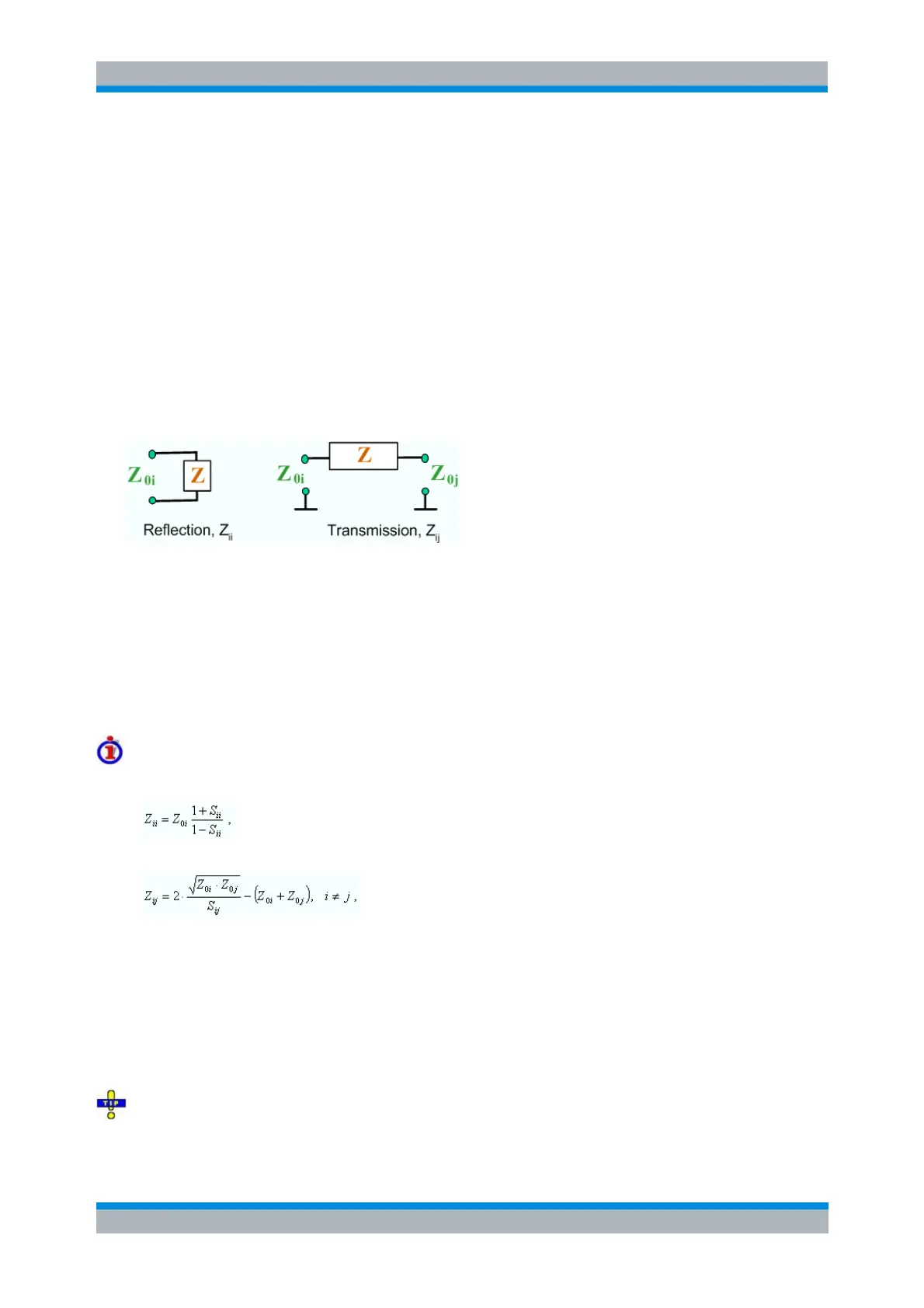
outputs. In the figures below the indices i and j number the analyzer/DUT ports, Z
0i
is the reference
impedance at the DUT port i.
The analyzer converts a single measured S-parameter to determine the corresponding converted
impedance. As a result, converted Z-parameters cannot completely describe general n-port DUTs:
A reflection parameter Z
ii
completely describes a one-port DUT. For n-port DUTs (n>1) the
reflection parameters Z
ii
describe the input impedances at ports i (i = 1 to n) under the condition
that each of the other ports is terminated with its reference impedance (matched-circuit
parameters).
A two-port transmission parameter Z
ij
(i ≠ j) can describe a pure serial impedance between the two
ports.
Relation with S-parameters
The converted impedances Z
ii
are calculated from the reflection S-parameters S
ii
according to:
The transmission parameters are calculated according to:
The converted admittances are defined as the inverse of the impedances.
Examples:
Z
11
is the input impedance of a 2-port DUT that is terminated at its output with the reference
impedance Z
0
(matched-circuit impedance measured in a forward reflection measurement).
The extension of the impedances to more ports and mixed mode measurements is analogous to
S-parameters. Z
dd44
is the differential mode input impedance at port 4 of a DUT that is terminated
at its other ports with the reference impedance Z
0
. See More Impedances for detailed information.
You can also read the converted impedances in a reflection coefficient measurement from the Smith
chart.
 Loading...
Loading...