R&S
®
ZVA / R&S
®
ZVB / R&S
®
ZVT System Overview
Measured Quantities
Operating Manual 1145.1084.12 – 30 50
and admittances) for balanced measurements. The analyzer can measure mixed mode parameters as
soon as a balanced port configuration is selected.
Mixed mode parameters are used to distinguish the following three port modes:
s: Single-ended (for unbalanced ports)
d: Differential mode (for balanced ports)
c: Common mode (for balanced ports)
The notation of a general S-parameter is S
<mout><min><out><in>
, where <mout> and <min> denote the output
and input port modes, <out> and <in> denote the output and input port numbers.
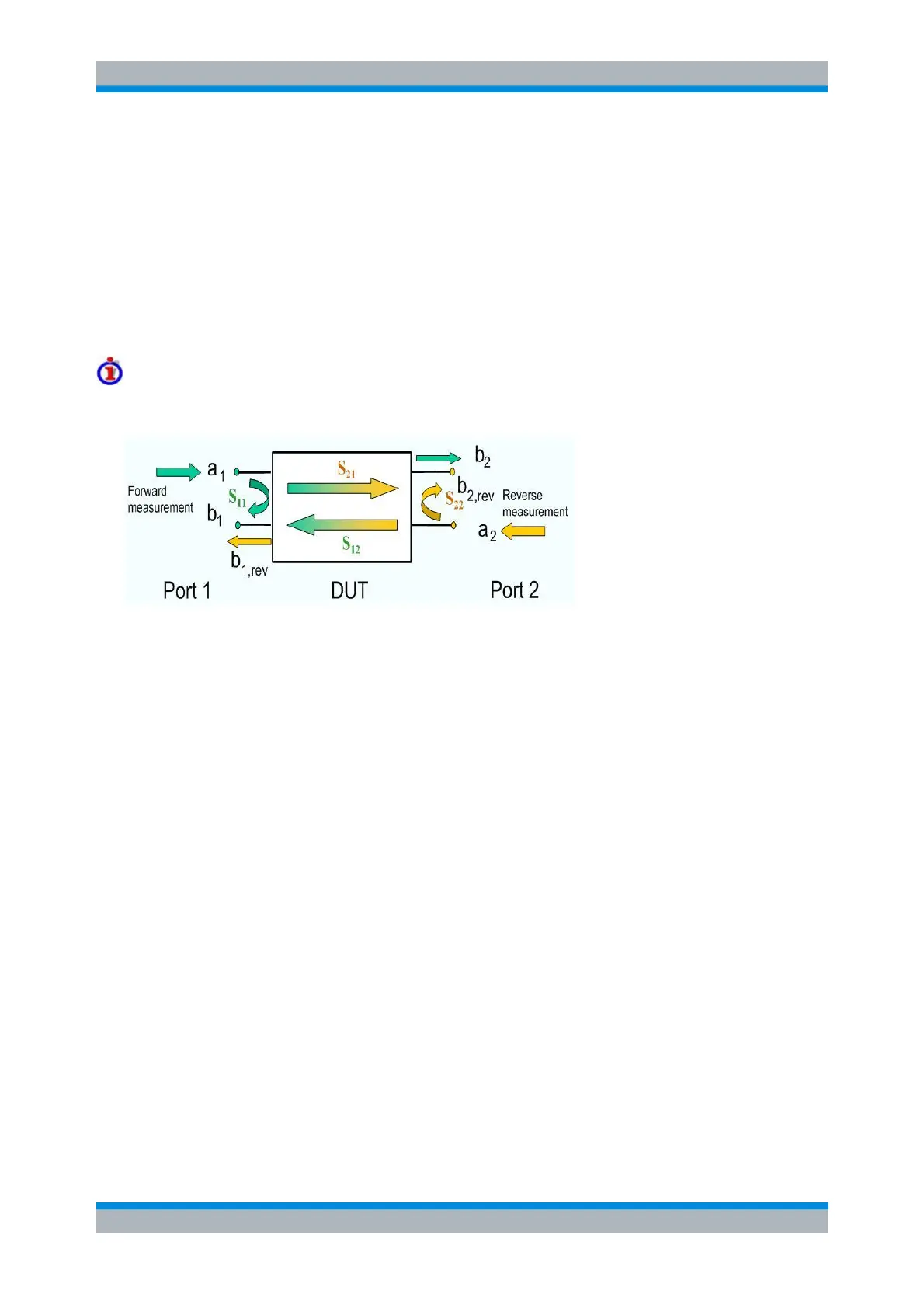
Meaning of 2-port mixed mode S-parameters
The mixed mode 2-port S-parameters can be interpreted as follows:
S
<mout><min>11
is the mixed mode input reflection coefficient, defined as the ratio of the wave
quantities b1 (mode mout) to a1 (mode min), measured at PORT 1 (forward measurement with
matched output and a2 = 0).
S
<mout><min>21
is the mixed mode forward transmission coefficient, defined as the ratio of the wave
quantities b2 (mode mout) to a1 (mode min) (forward measurement with matched output and a2 =
0).
S
<mout><min>12
is the mixed mode reverse transmission coefficient, defined as the ratio of the wave
quantities b1 (mode mout) (reverse measurement with matched input, b1' in the figure above and
a1 = 0) to a2 (mode min).
S
<mout><min>22
is the mixed mode output reflection coefficient, defined as the ratio of the wave
quantities b2 (mode mout) (reverse measurement with matched input, b2' in the figure above and
a1 = 0) to a2 (mode min), measured at PORT 2.
If <mout> is different from <min>, the S-parameters are called mode conversion factors.
Mixed Mode Parameters for Different Test Setups
Which types of mixed mode parameter are available depends on the measured device and the port
configuration of the analyzer. The following examples of mixed more parameters can all be obtained with
a 4-port analyzer.
1. DUT with only single-ended ports: No balanced port definition necessary, the analyzer provides
single-ended multiport parameters.
2. DUT with one balanced port: Only reflection and mode conversion measurements with differential
and common mode parameters.
 Loading...
Loading...