10
10-144
MULTIJUNCTION TIMERS
10.7 TID (Input-Related 16-Bit Timer)
32180 Group User’s Manual (Rev.1.0)
10.7.4 TID Counters (TID0CT, TID1CT and TID2CT)
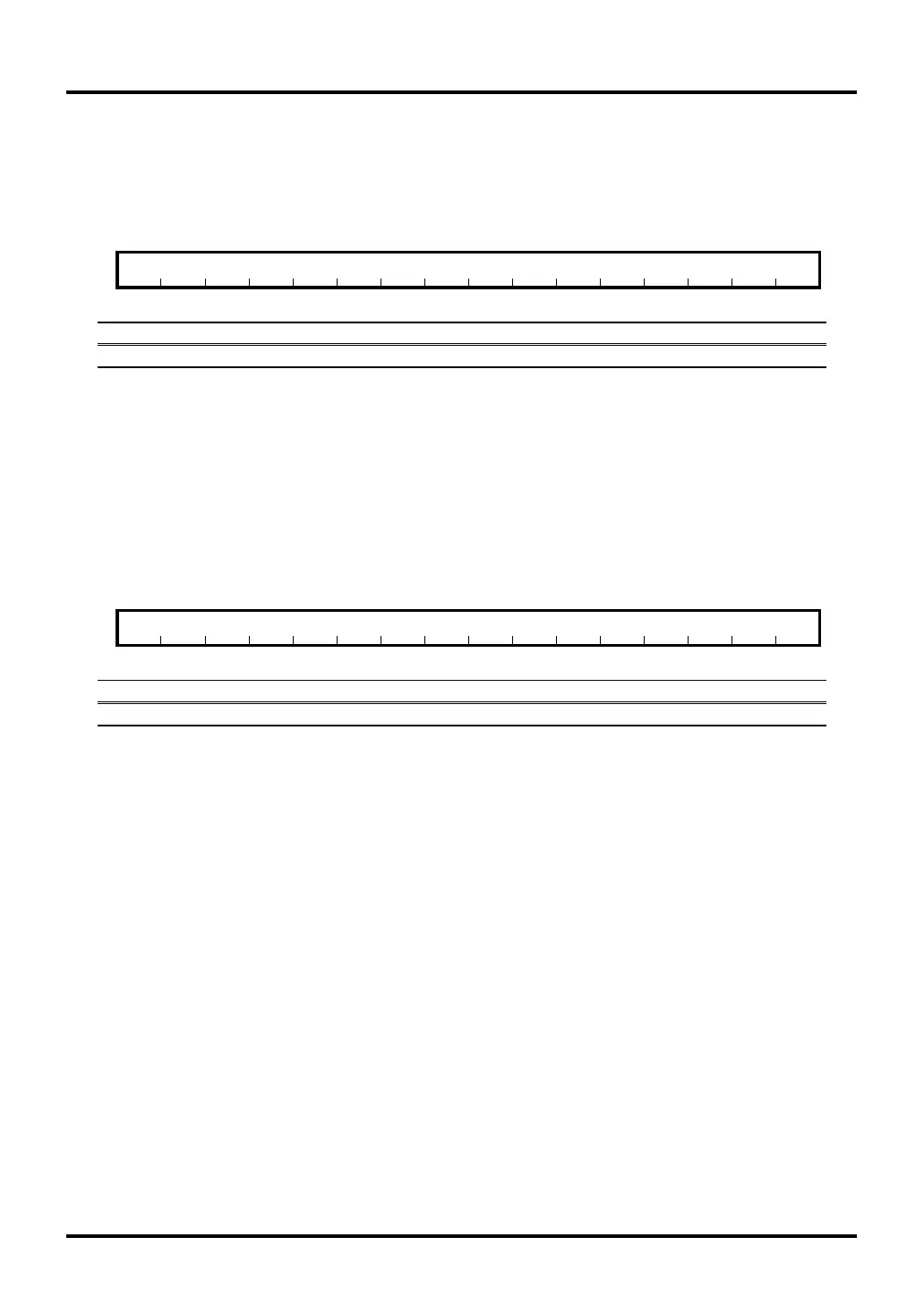
TID0 Counter (TID0CT) <Address: H’0080 078C>
TID1 Counter (TID1CT) <Address: H’0080 0B8C>
TID2 Counter (TID2CT) <Address: H’0080 0C8C>
b01234567891011121314b15
TID0CT, TID1CT, TID2CT
????????????????
<After reset: Undefined>
b Bit Name Function R W
0–15 TID0CT, TID1CT, TID2CT 16-bit counter value R W
Note: • This register must always be accessed in halfwords.
The TID counters are a 16-bit up/down-counter. After the timer is enabled (by writing to the enable bit in soft-
ware), the counter starts counting synchronously with the count clock.
10.7.5 TID Reload Registers (TID0RL, TID1RL and TID2RL)
TID0 Reload Register (TID0RL) <Address: H’0080 078E>
TID1 Reload Register (TID1RL) <Address: H’0080 0B8E>
TID2 Reload Register (TID2RL) <Address: H’0080 0C8E>
b01234567891011121314b15
TID0RL, TID1RL, TID2RL
????????????????
<After reset: Undefined>
b Bit Name Function R W
0–15 TID0RL,TID1RL,TID2RL 16-bit reload register value R W
Note: • This register must always be accessed in halfwords.
The TID reload registers are used to reload data into the TID counter registers (TID0CT, TID1CT and TID2CT).
The content of the reload register is loaded into the counter in the following cases:
• When the counter is enabled in fixed period count mode
• When the counter has underflowed in fixed period count mode
Simply because data is written to the reload register does not mean that the data is loaded into the counter. The
counter is loaded with data in only the above cases.

 Loading...
Loading...











