4.5 Test Run
YASKAWA TM.V1000.01 V1000 Drive Installation & Start-Up Manual (Preliminary 01-19-07) 169
Start-Up Programming &
Operation
4
■ Precision Settings for Auto-Tuning
Basic motor nameplate data can be used to auto-tune a motor. However, improved
performance can be achieved by using precise data for base voltage and base
frequency. If the base no-load voltage and frequency are known, enter this data
when executing auto-tuning to improve performance.
◆ No-Load Operation
This section explains how to operate the drive with the motor uncoupled from the
load during a test run. Performing the test run is necessary to confirm that the auto-
tuned parameters generate the desired motor performance.
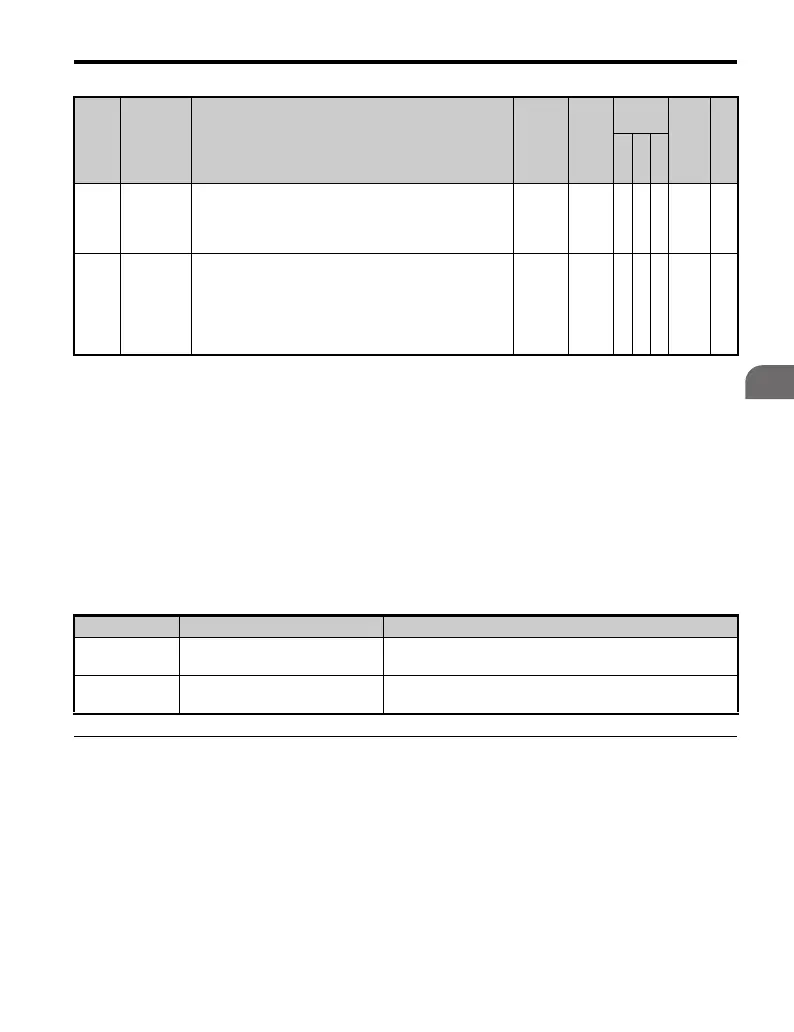
T1-07
Motor
Base
Speed
Sets the base speed of the motor in revolutions per
minute r/min (RPM).
Enter the motor base speed for extended speed range
motors.
0 to
24000
1750
r/min
AA− 707 407
T1-11
Motor
Iron Loss
Provides the iron loss for determining the Energy
Saving coefficient.
When power is cycled, the value set to E2-10 will
appear (the motor iron loss). If T1-02 is changed, an
initial value for the motor capacity will appear that is
close to the capacity that was changed.
0 to
65535
14W A −− 70B 408
<1> Select motor 2 to display this selection.
<2> Voltage and frequency settings for a vector motor or drive motor are often lower than for standard
motors. Be sure to enter Auto-Tuning data according the motor nameplate and Motor data sheets. If
the no-load voltage and frequency values are known, enter those values into T1-03 and T1-05
<3> The default setting for this parameter is determined by the drive capacity (set by parameter o2-04).
Parameter Normal Settings Precision Tuning
T1-03 Enter the motor rated voltage
Enter the no-load voltage when the motor is operating at its
rated revolutions per minute
T1-05 Enter the motor base frequency
Enter the no-load frequency when the motor is operating at its
rated revolutions per minute
No. Name Description Range Def.
Control
Mode
Addr.
Hex
Pg.
V
F
O
L
V
P
M

 Loading...
Loading...