62 •
••
• Allen-Bradley QUICKDESIGNER
Reading Bit Data in BTW Files
This section describes how to use Block Transfer Tag names to read bit data from BTW data files in
the target display.
To read bit information in a data file, you need to specify the name of the data file, the word within the
file and a bit specifier. The command format used to specify bit data is FILENAME[word]/bit.
Example: BTW0120[07]/04. In the following example, the name of the data file is BTW0120 and the
size of the file is 16 words. The example illustrates several Tag Names and their relationship to the data
file.
BTW0120
Tag Name Data File Location Bit Location
BTW0120[00]/00 Word 0 Bit 00
BTW0120[01]/02 Word 1 Bit 02
BTW0120[07]/04 Word 7 Bit 04
BTW0120[14]/12 Word 14 Bit 12
BTW0120[15]/15 Word 15 Bit 15
Writing Word Data to BTR Files
The PLC uses BTR functions to read data from remote modules. This section describes how to use
Block Transfer Tag names to write word data to BTR data files in the target display.
To write word information to a data file, you need to specify the name of the data file and the word
within the file. The command format used to specify the data is FILENAME[word]. Example:
BTR0120[02]. In the following example, the name of the data file is BTR0120 and the size of the file
is 16 words. The example illustrates several Tag Names and their relationship to the data file.
BTR0120
Tag Name Data File Location
BTR0120[00] Word 0
BTR0120[01] Word 1
BTR0120[02] Word 2
BTR0120[14] Word 14
BTR0120[15] Word 15
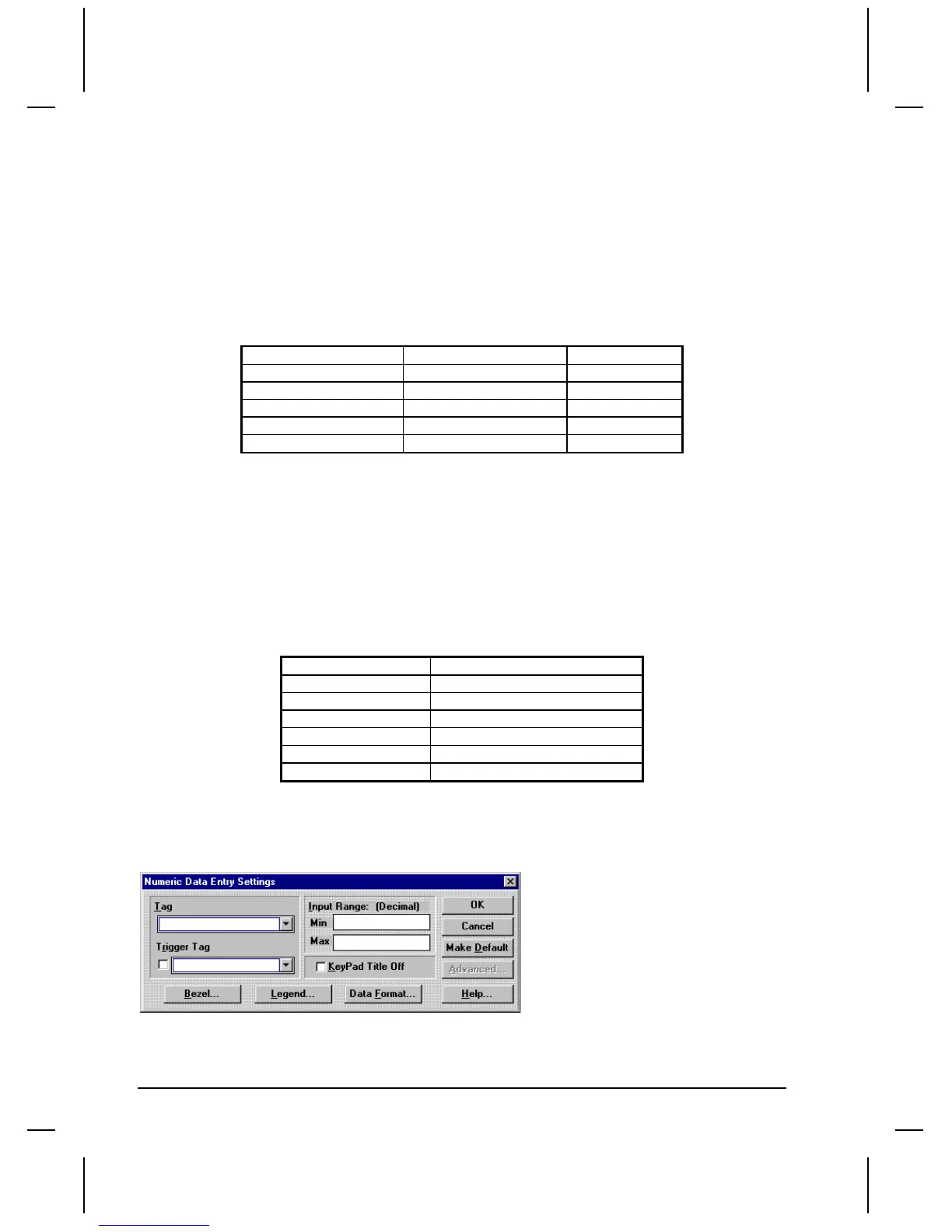
This command format allows you to write a word to the data file using an operator such as Numeric
Data Entry. For example, when creating a numeric data entry, you are presented with a setting menu
that requests a Tag name. If you entered BTR0120[2], the target display would write the data entered
from the data entry panel to word 2 in the data file labeled BTR0120.

 Loading...
Loading...