6-53
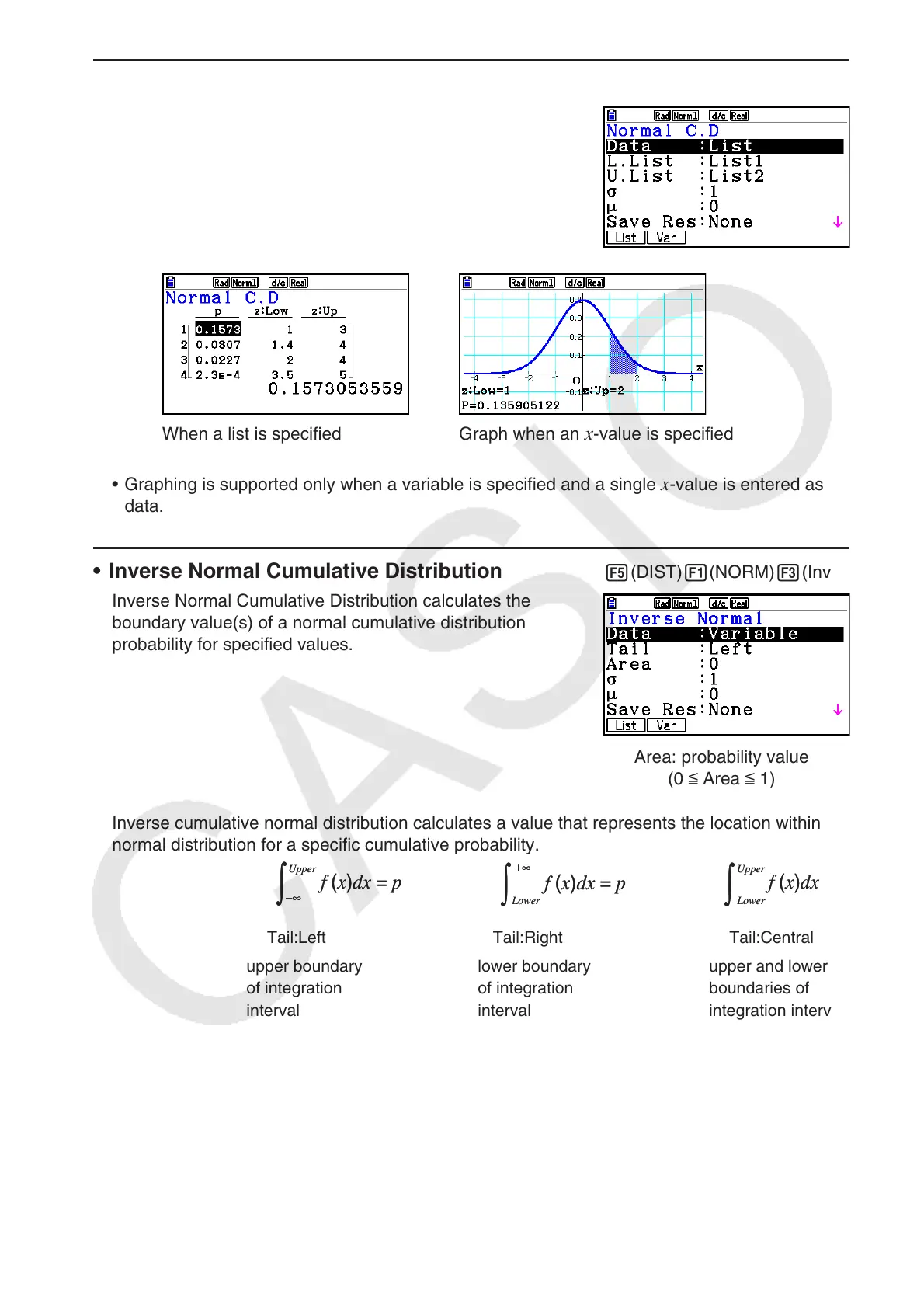
Tail:Left
upper boundary
of integration
interval
Tail:Right
lower boundary
of integration
interval
Tail:Central
upper and lower
boundaries of
integration interval
Specify the probability and use this formula to obtain the integration interval.
• This calculator performs the above calculation using the following: ∞ = 1E99, – ∞ = –1E99
• There is no graphing for Inverse Normal Cumulative Distribution.
• Normal Cumulative Distribution 5(DIST) 1(NORM) 2(Ncd)
Normal Cumulative Distribution calculates the normal
cumulative probability of a normal distribution between a
lower bound and an upper bound.
Calculation Result Output Examples
When a list is specified Graph when an
x -value is specified
• Graphing is supported only when a variable is specified and a single
x -value is entered as
data.
• Inverse Normal Cumulative Distribution 5(DIST) 1(NORM) 3(InvN)
Inverse Normal Cumulative Distribution calculates the
boundary value(s) of a normal cumulative distribution
probability for specified values.
Area: probability value
(0 < Area < 1)
Inverse cumulative normal distribution calculates a value that represents the location within a
normal distribution for a specific cumulative probability.
f (x)dx = p
−∞
∫
Upper
f (x)dx = p
+∞
∫
Lower
f (x)dx = p
∫
Upper
Lower
f (x)dx = p
−∞
∫
Upper
f (x)dx = p
+∞
∫
Lower
f (x)dx = p
∫
Upper
Lower

 Loading...
Loading...











