2-37
k Complex Number Format Using Polar Form
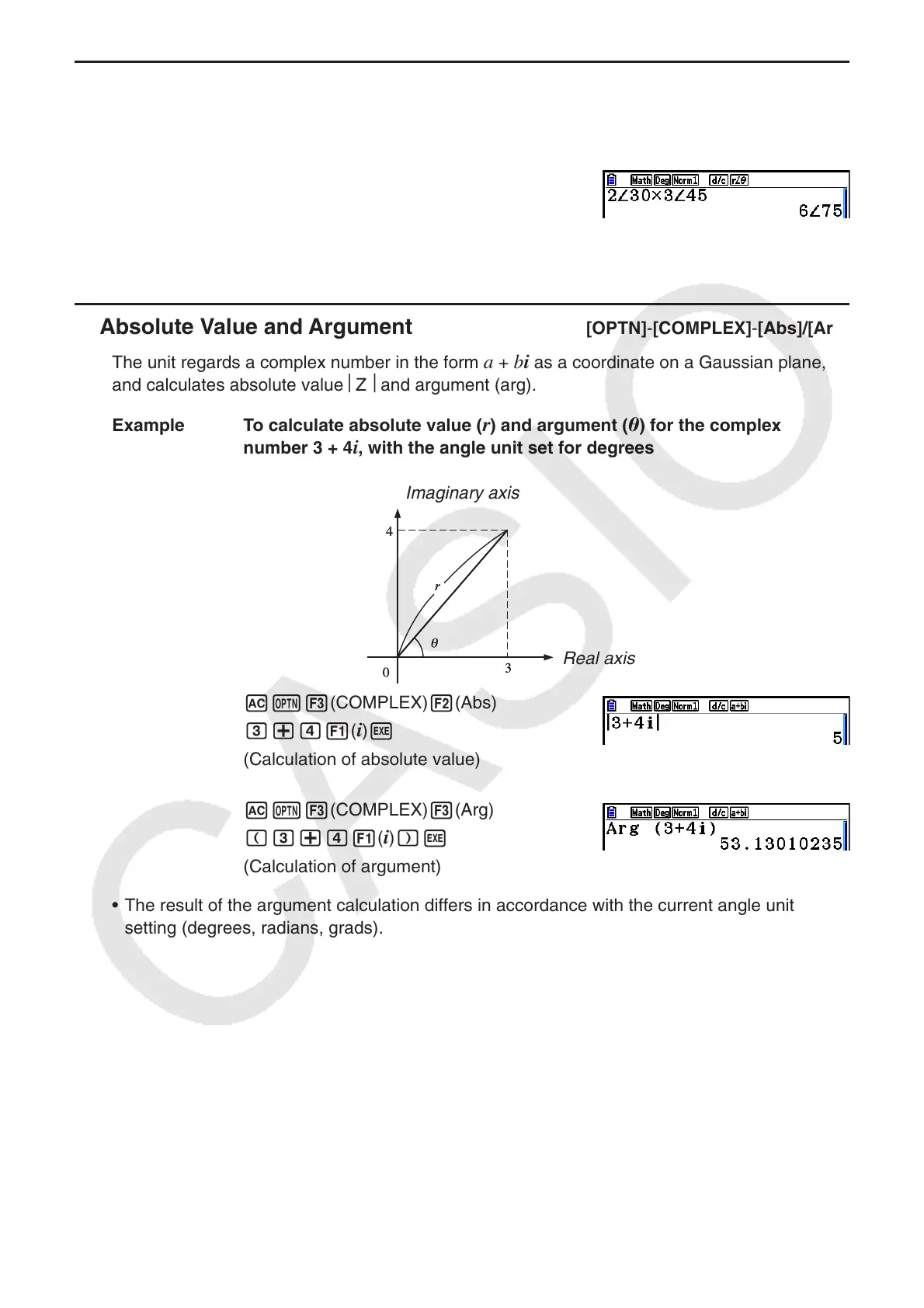
Example 2 ∠ 30 × 3 ∠ 45 = 6 ∠ 75
!m(SET UP) cccccc
1(Deg) c3(
r ∠ ) J
Ac!v( ∠ ) da*d
!v( ∠ ) efw
k Absolute Value and Argument [OPTN] - [COMPLEX] - [Abs]/[Arg]
The unit regards a complex number in the form
a + b i as a coordinate on a Gaussian plane,
and calculates absolute value ⎮ Z ⎮ and argument (arg).
Example To calculate absolute value (
r ) and argument ( ) for the complex
number 3 + 4 i , with the angle unit set for degrees
Imaginary axis
Real axis
AK3(COMPLEX) 2(Abs)
d+e1(
i ) w
(Calculation of absolute value)
AK3(COMPLEX) 3(Arg)
(d+e1(
i ) )w
(Calculation of argument)
• The result of the argument calculation differs in accordance with the current angle unit
setting (degrees, radians, grads).

 Loading...
Loading...











