System
Recording series of tests
268 A0534-30.0 HBM: public MGCplus
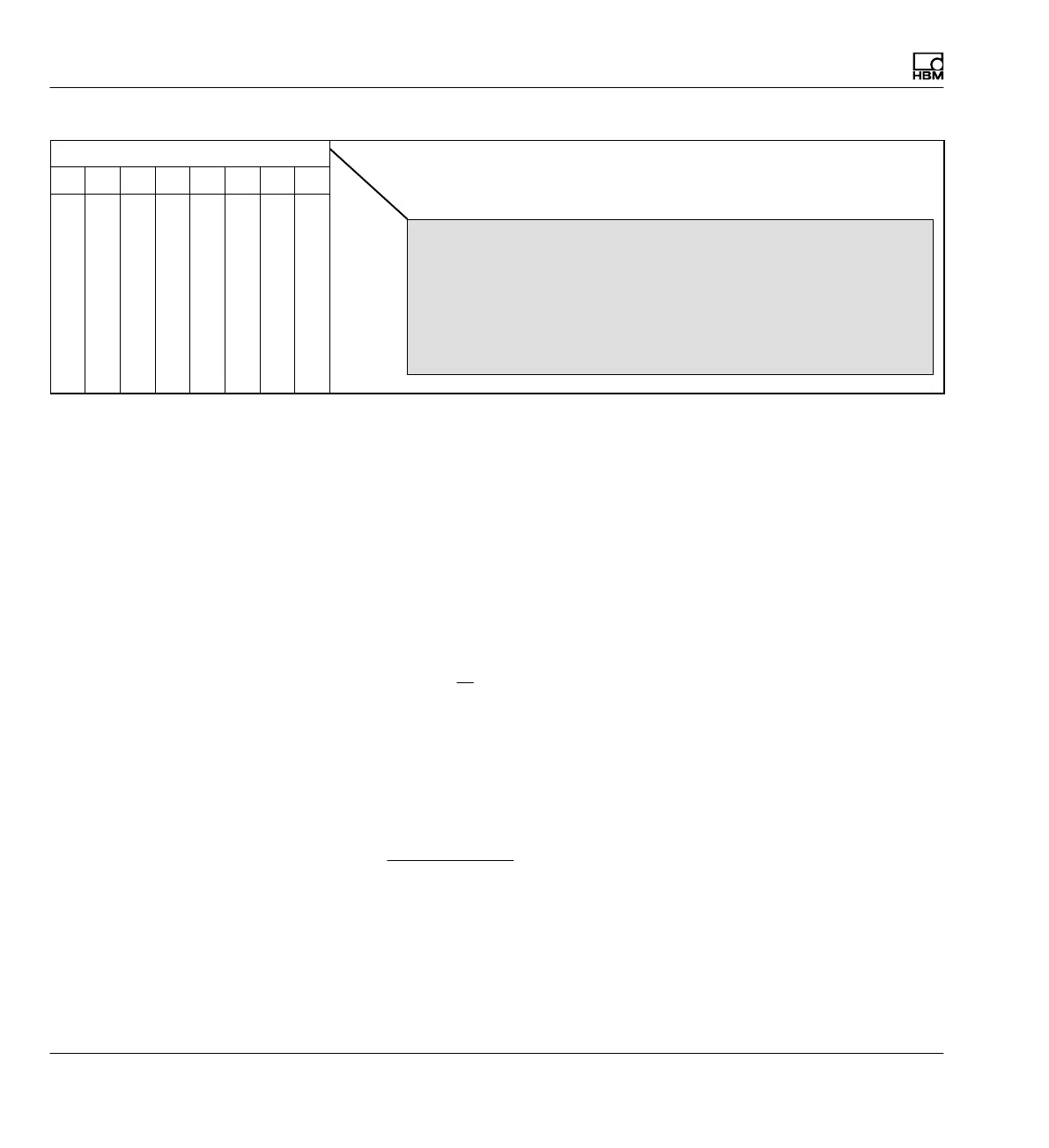
Bit no.
This status information is displayed as an integer in the range
sŮ{0 ... 255}.
When measured values are imported from an MEA file (4-byte
INT format) the status is checked to see whether it is s>15. If it
is, the corresponding measured value is replaced by a number
defined by the user.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
LV1 status
LV2 status
LV3 status
LV4 status
Gross value overflow
Net value overflow
Calibration error
Change flag
If measured values are stored in an MGCplus measurement file in a
different format than 4-byte INT, information about the measurement status
is irrevocably lost. So we recommend that the 4-byte format is always used
when saving.
An example of how 32-bit INT values in the status and the physically scaled
measured value can be converted, is given below. In this example, the
variable z is one such 32-bit value.
z Ů
NJ
–2.147.483.647,... , 2.147.483.648
Nj
The status s is obtained by carrying out the following mathematical
operations.
s + z–2
8
@
Ȳ
z
2
8
ȴ
1)
Obviously, it would be far more efficient to perform this operation in a
programming language such as C++ or Visual Basic, with the aid of
bitshifting operators (SHR, SHL).
The physically correctly scaled measured value can be calculated by
applying the following operation:
y +
z @ c
scale
(
2
8
@ 7.680.000
)
–c
offset
c
scale
and c
offset
represent the scaling information which is contained in the
relevant amplifier and also in the measurement files on the PC card hard
disk.
1)
The notation bxc here describes the floor function, which rounds the number down to the next smallest integer: b12.2c = 12; b-12.2c = -13
 Loading...
Loading...