Precautions for Correct Use
If 3: _mcCurrentDirection (Current direction) is specified for Direction, operation is in the same
command direction as the previous motion. Therefore, depending on the instructions that are
used together
, the direction may not be the same as the direction that was specified with the
input to the motion control instruction for the previous motion.
When you specify 3: _mcCurrentDirection (Current direction), check the current direction with
Dir.Posi (Positive Direction) and Dir.Nega (Negative Direction) in the Axis Variable.
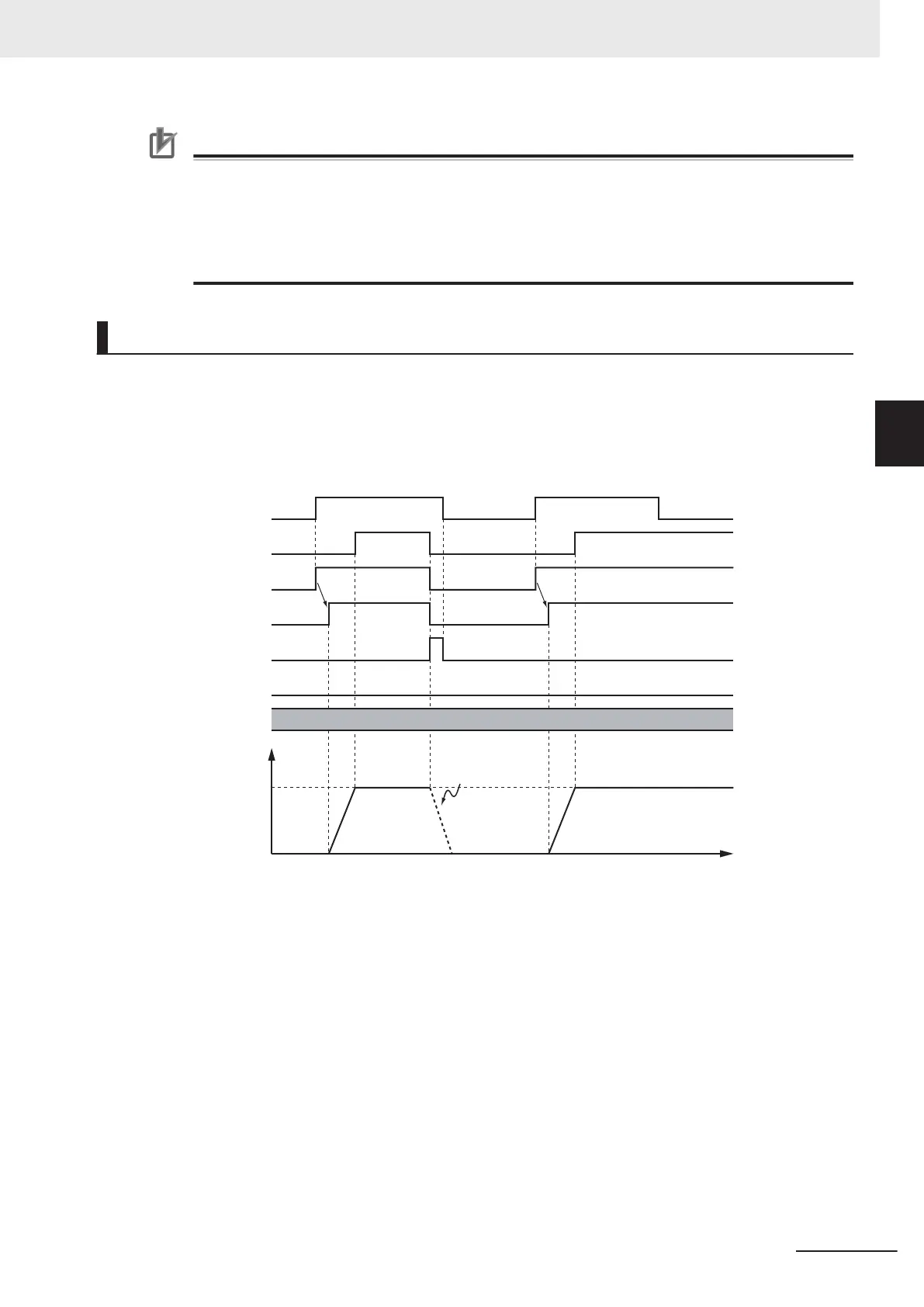
Timing Charts
• Busy (Executing) changes to TRUE at the same time as Execute changes to TRUE. Active (Control-
ling) changes to TRUE in the next period.
• InV
elocity (Target Velocity Reached) changes to TRUE when Velocity (Target Velocity) is reached.
• If another instruction aborts this instruction, CommandAborted changes to TRUE and Busy (Execut-
ing), Active (Controlling), and InVelocity (Target Velocity Reached) change to FALSE.
Time
Decelerates to a stop
when another instruction
causes an error.
Target velocity
Velocity
Busy
CommandAborted
InVelocity
Error
16#0000
Error
ID
Execute
Active
The InV
elocity (Target Velocity Reached) output variable indicates when the velocity has reached the
same velocity for this instruction and the re-executed motion control instruction. Therefore, after
InVelocity (Target Velocity Reached) changes to TRUE, even if the velocity is changed by the override
factor, InVelocity (Target Velocity Reached) will not change to FALSE.
If the override factor changes before InVelocity (Target Velocity Reached) changes to TRUE,
InVelocity (Target Velocity Reached) will change to TRUE when the new target velocity is reached.
You can specify Acceleration (Acceleration Rate), Deceleration (Deceleration Rate) and Jerk as input
variables.
When the Velocity (Target Velocity) is 0 and the instruction is executed, the axis will enter continuous
operation without motion.
The following chart shows an operation example of when Velocity (Target Velocity) is 0.
3 Axis Command Instructions
3-91
NY-series Motion Control Instructions Reference Manual (W561)
MC_MoveVelocity
3
Function
 Loading...
Loading...